2026-01-25 Sun
■ #6117. 伝説的入門書『古英語・中英語初歩』が新装復刊されます! [notice][kenkyusha][oe][me][review][timeline][link][kochushoho]

あの名著が復刊されます! 市河三喜・松浪有(著)『古英語・中英語初歩〈新装復刊〉』(研究社)が,1ヶ月後の2月25日に出版予定です(定価3300円).研究社公式HPの近刊案内より部分的に「試し読み」もできますので,ぜひチェックしてみてください.「英語史関連・周辺テーマの本」一覧にもアクセスできます.
本書の歴史をざっとたどってみます.
・ 1933--34年,市河三喜が雑誌『英語青年』(研究社)にて,後の『古代中世英語初歩』の母体となる連載記事を寄稿する
・ 1935年,市河三喜(著)『古代中世英語初歩』が出版される
・ 1955年,市河三喜(著)『古代中世英語初歩』改訂新版(研究社)市河 三喜・松浪 有(著)『古英語・中英語初歩』第2版(研究社)が出版される(←神山孝夫先生よりじきじきのご指摘により訂正いたしました.2026/01/27(Tue))
・ 1986年,市河三喜・松浪有(著)『古英語・中英語初歩』(研究社)が出版される(松浪による全面改訂)
・ 2023年,神山孝夫(著)『市河三喜伝』(研究社)が出版される
以下,hellog,heldio,その他で公開してきた『古英語・中英語初歩』に直接・間接に関係するコンテンツを時系列に一覧します.
・ 2025年4月28日,heldio で「#1429. 古英語・中英語を学びたくなりますよね? --- 市河三喜・松浪有(著)『古英語・中英語初歩』第2版(研究社,1986年)」を配信
・ 2025年5月1日,ari さんが note で「#268 【雑談】市河・松浪(1986)「古英語・中英語初歩」こと,ÞOMEB を買ってみた件!!」を公開する
・ 2025年5月3日,ぷりっつさんが note で「Gemini 君と古英語を読む」シリーズを開始する(5月9日まで6回完結のシリーズ)
・ 2025年5月5日,hellog で「#5852. 市河三喜・松浪有(著)『古英語・中英語初歩』第2版(研究社,1986年)」 ([2025-05-05-1]) が公開される
・ 2025年5月10日,helwa メンバーが本書を(計7冊以上)持ち寄って皐月収録会(於三田キャンパス)に臨む.参加者(対面あるいはオンライン)は,ari さん,camin さん,lacolaco さん,Lilimi さん,Galois さん,小河舜さん,taku さん,ykagata さん,しーさん,みーさん,寺澤志帆さん,川上さん,泉類尚貴さん,藤原郁弥さん.
・ 2025年5月12日,hellog で「#5859. 「AI古英語家庭教師」の衝撃 --- ぷりっつさんの古英語独学シリーズを読んで」 ([2025-05-12-1]) が公開される
・ 2025年5月15日,TakGottberg さんが,上記 heldio #1429 のコメント欄にて,(1986年版の)2011年第16刷の正誤表やその他の話題に言及(本記事の末尾を参照)
・ 2025年5月29日,heldio で「#1460. 『古英語・中英語初歩』をめぐる雑談対談 --- 皐月収録回@三田より」が配信される
・ 2025年10月5日,heldio にて「#1589. 声の書評 by khelf 藤原郁弥さん --- 神山孝夫(著)『市河三喜伝』(研究社,2023年)」が配信される
・ 2025年10月5日,hellog にて「#6005. khelf の新たなhel活「声の書評」が始まりました --- khelf 藤原郁弥さんが紹介する『市河三喜伝』」 ([2025-10-05-1]) が公開される
・ 2026年1月20日,研究社より新装復刊が公式にアナウンスされる
・ 2026年2月25日,出版予定
新装復刊を前に,本書とその周辺について,理解を深めていただければ.復刊の Amazon の予約注文はこちらよりどうぞ.
・ 市河 三喜,松浪 有 『古英語・中英語初歩〈新装復刊〉』 研究社,2026年.
・ 神山 孝夫 『市河三喜伝 --- 英語に生きた男の出自,経歴,業績,人生』 研究社,2023年.
2025-11-04 Tue
■ #6035. 英語史年表を作るのは難しい --- 「いのほたなぜ」の「超ざっくり英語史年表」制作裏話 [inohota][inohotanaze][inoueippei][timeline][historiography][notice][youtube][periodisation]
11月2日(日),井上逸兵さんと共著で上梓した『言語学でスッキリ解決!英語の「なぜ?」』(ナツメ社)を記念し,ホームグラウンドである YouTube 「いのほた言語学チャンネル」にて本書を紹介する回を配信しました.「#384. いのほた本は,世に問いたい言語学のひとつのかたち --- 『言語学でスッキリ解決!英語の「なぜ?」』(ナツメ社)」です(16分半ほどの動画).ぜひご覧ください.
本書は,2人が3年半にわたり YouTube 上で対談してきた内容が凝縮されており,お陰様で発売早々から大きな反響をいただいています.本書の特設HPも開設していますので,こちらよりぜひご訪問ください.また,SNS などで,ハッシュタグ #いのほたなぜ を添えて,本書に関するご意見やご感想などをお寄せいただけますと幸いです.
さて,「いのほた」の最新回では,本書の構成について言及しつつ,私が担当した「超ざっくり英語史年表」 (pp. 6--9) の制作舞台裏を披露しました.これまでも英語史の略年表は様々な形で作ってきましたが,年表制作という作業には常に悩みがつきまといます.単なる年号の羅列以上の,厄介な問題を含んでいるのです.この点について掘り下げてみます.
年表を作るにあたり,まず歴史的な出来事には「線」を引きやすいものと,そうでないものとがあります.政治史や軍事史における事件,例えば1066年のノルマン征服 (norman_conquest) のようなものは,年号(そして日付まで)が明確に記録されており,年表に掲載する際に悩みはありません.「1066年,ノルマン征服」とズバッと書き込めばよいだけです.
ところが,言語変化を多く扱う英語史年表では,そうは単純にいかないことが多いのです.例として,英語史の最たる音変化の1つ,大母音推移 (gvs) を考えてみましょう.一般にこの変化は1400年頃から1700年頃にかけて,じっくり,ゆっくり起こったと説明されることが多いです.ここでの問題は,この変化の始まりと終わりが,特定の何年とは決められないことです.実際は1400年の元旦に始まったわけでも,1700年の大晦日に終わったわけでもありません.年表という2次元のレイアウトの制約の中で,どこに始まりと終わりを置くのか,あるいはどれくらいの時間幅で矢印を引くかというのは,その都度,苦渋の選択を迫られる作業となります.レイアウト上は,書き込む文字やイラストとの兼ね合いもあり,さらに問題は複雑化します.
年表制作における恣意性のもっと顕著な例として,英語史の開始年をどこに置くかという大きな問題があります.この問題の根深さは,hellog の periodisation のタグのついた各記事で見てきたとおりですが,年表に反映させるとなると,明示的に年号を示すことが要求されているようで,プレッシャーが大きいのです.伝統的に英語史の始まりは449年とされてきました.これは,アングロサクソン人と呼ばれる西ゲルマン人の一派が,ブリテン島へ本格的に来襲した年とされているからです.これをもって,アングロサクソン王国の始まり,ひいてはイギリスの始まり,そして英語の始まりと了解されてきたわけです.
しかし,言語プロパーの歴史を論じる立場からすると,この449年開始説はきわめて眉唾ものです.なぜならば,アングロサクソン人がまだ大陸にいたとされる448年と,ブリテン島に上陸したとされる449年とで,彼らの話していた言語自体は何ら変わっていないはずだからです.
言語は,社会的な事件によって急にその姿を変えるものではなく,あくまでゆっくりと変容していく連続体として存在しています.極論をいえば,英語の歴史は,印欧祖語まで(少なくともある程度は)地続きで繋がっていると理解できますし,さらに突き詰めれば,人類の言語の始まりにも繋がっている可能性があります.つまり,「○○語史の始まり」という区切りは,純粋な言語学的な考慮ではなく,その言語を話す集団の社会的な歴史,すなわち国史や政治史とシェアさせてもらう形で,便宜的に設定されているにすぎないのです.
ただ,とりわけ入門的な書籍に掲載する年表で「449年」などと明記しないと,「では,英語史はいつ始まったのですか?」という素朴な疑問にサラッと答えられなくなるため,伝統的な区切りをひとまず採用しているにすぎない,ということなのです.年表に書かれている年号は,学習の便宜という実用的な要請に応えるための妥協の産物といってよいものです.文章であれば「~年頃」などといった表現で逃げることができるのですが,年表という形式では,どうしても数直線の上にピンポイントで明示的に配置するといったデジタルな感覚が強く,それゆえに悩ましいのです.言語の歴史は,革命のような劇的な断絶ではなく,ゆっくりと変化していくファジーな世界です.そのことを理解した上で,本書の「超ざっくり英語史年表」に目を通していただけると,より深く英語史というものに思いを馳せることができるかと思います.
新刊書「いのほたなぜ」に関する話題は,引き続き「いのほた言語学チャンネル」や hellog その他の媒体で繰り広げていくつもりです.関連情報はすべて特設HPにまとまっていますので,日々そちらをご覧ください.よろしくお願い致します.
・ 井上 逸兵・堀田 隆一 『言語学でスッキリ解決!英語の「なぜ?」』 ナツメ社,2025年.
2025-01-14 Tue
■ #5741. ウェブメディアでのhel活タイムライン [helkatsu][hellog][twitter][voicy][heldio][helwa][youtube][inohota][instagram][heltube][heltalk][note][link][timeline]
*
私が主なウェブメディア上で展開している英語史に関する主な情報発信プラットフォームを,タイムラインでまとめてみました.上記のインフォグラフィックのなかから,リンクで直接飛べます.以下にリストの形でも挙げておきます.
- 2009年5月1日~,hellog~英語史ブログ
- 2010年1月~,X/@chariderryu
- 2021年6月2日~,Voicy: 英語の語源が身につくラジオ (heldio)
- 2022年2月26日~,YouTube: いのほた言語学チャンネル
- 2022年6月4日~,Instagram/@chariderryu
- 2022年7月3日~,YouTube: heltube --- 英語史チャンネル
- 2022年7月21日~,note
- 2023年6月2日~,Voicy: プレミアム限定配信 英語史の輪 (helwa)
- 2023年10月5日~,stand.fm: 英語史つぶやきチャンネル (heltalk)
本ブログは15年半以上前のスタートでしたが,それ以外はおおよそ2021年以降に立ち上げられています.2022年が建設ラッシュ(?)だったのかと感慨深く思いました.いずれの発信媒体についても,引き続きよろしくお願いいたします.
2024-12-10 Tue
■ #5706. 人類史上の画期的な出来事の一覧 [timeline][anthropology][homo_sapiens][writing]

『世界の人物大年表(ビジュアル版)』をパラパラと眺めている.2020年に英語で出版された Timelines of Everone を翻訳したもので,めくっているだけで楽しい世界史の人物年表・事典である.
冒頭にほど近い pp. 10--11 に「人類の歴史」と題する見開きのインフォグラフィックがある.ここから小見出しのみを抜き出してみる.人類史上の15件の画期的な出来事が選び出されている.
| 250万年前ごろ | 最初の道具 |
| 80万年前ごろ | 火 |
| 40万年前ごろ | 槍で狩る |
| 4万4000年前ごろ | 洞窟壁画 |
| 4万年前ごろ | 世界中で(石器や衣服) |
| 2万年前ごろ | 陶器 |
| 1万5000年前ごろ | 寒さをしのぐ住居 |
| 1万4000年前ごろ | 犬とヒト |
| 1万2000年前ごろ | 農業 |
| 9000年前ごろ | 金属の利用 |
| 8009年前ごろ | 都市生活 |
| 紀元前3400年前ごろ | 文字 |
| 1500年ごろ | 大洋横断 |
| 1750年ごろ | 新技術 |
| 1990年ごろ | コンピュータ時代 |
ここでは著者らによる人類史上ベスト15が掲げられているわけだが,ベスト15のリストは,歴史家の数だけ候補があるはずだ.もし私が作ったら,言語贔屓なだけに,言語史上の出来事が多く挙がってくるのだろうな,などと妄想した.上記の一覧では,紀元前3400年前ごろの文字(の発明)が言語周りの出来事としてエントリーされている.
・ 定延 由紀・李 聖美・中村 左千江・伊藤 理子(訳)『世界の人物大年表(ビジュアル版)』 創元社,2022年.
[ 固定リンク | 印刷用ページ ]
2023-10-06 Fri
■ #5275. 19世紀のイングランド英語という時代区分とさらなる下位区分 [periodisation][lmode][prescriptivism][prescriptive_grammar][sociolinguistics][timeline][history]
昨日の記事「#5274. 19世紀のイングランド英語を研究する意義」 ([2023-10-05-1]) で取り上げた,英語史の大家 Görlach による19世紀イングランド英語の入門書の冒頭には,19世紀という英語史上の区切りには,特に社会的・言語的な根拠があるわけではないと述べられている.別の論者 (DeKeyser) によれば,規範主義の1つのピークである1795年の Murray による文法書と,もう1つのピークである1906年の Fowler による King's English に挟まれた時代として理屈づけられてはいるようだが牽強付会の気味はある (Görlach 5) .
とはいえ,Görlach 自身も,19世紀のイングランド英語を研究する際に念頭においておくべき下位区分を提示しているし,関連する社会文化的な出来事も指摘している.下位区分として「長い19世紀」を4期に分けている (6) .
1776--1800 William Pitt's coalitions; the beginnings of the Industrial Revolution; the separation of the United States; the colonization of Australia and occupation of Ceylon and Malta; the start of the Romantic Movement; th end of Irish independence; 1800--1830 The final phase of the Hanoverian reign, predating the great reforms; Napoleonic wars and the Regency; Romantic poetry; 1830--1870 The great reforms; the Chartist movements; the heyday of capitalist industrialism; the expansion of literacy and printed matter; increased mobility as a consequence of railways; 1870--1914 Late Victorian imperialism and the last phase of global 'stability'; general education; modern communication.
上記の下位区分とは別に,19世紀中に起こった,社会言語学的な含意のある出来事も略年表の形で示されている (6) .こちらも参考までに挙げておこう.
1824 the repeal of the Combination Acts; 1828 the emancipation of the Nonconformists; 1832 the First Reform Bill, which can be seen as a triumph of the middle class; 1833 the first important Factory Act restricting child work; 1834 the abolition of slavery; 1834 the Poor Law Amendment Act; 1838--48 the Chartist movement; publication of the People's Charter; 1846 the repeal of the Corn Laws; 1855 the final repeal of the Stamp Act of 1712 (making cheap newspapers available); 1867 the Second Reform Bill (1 million new voters) and Factory Acts; 1870 the Elementary Education Act (establishing compulsory education in the 1870s); 1884--5 the Third Reform Bill (2 million new voters)
このように略年表を眺めると19世紀イングランドは自由化の世紀だということが改めてよく分かる.この時代は,英語という言語が世界的に拡大していく時期であるとともに,イングランド内でも大衆化が進展していった時期ととらえてよいだろう.
・ Görlach, Manfred. English in Nineteenth-Century England: An Introduction. Cambridge: CUP, 1999.
2023-02-20 Mon
■ #5047. 「大航海時代略年表」 --- 『図説大航海時代』より [timeline][history][age_of_discovery][me][emode][renaissance][link]
世界史上,ひときわきらびやかに映る大航海時代 (age_of_discovery) .広い視野でみると,当然ながら英語史とも密接に関わってくる(cf. 「#4423. 講座「英語の歴史と語源」の第10回「大航海時代と活版印刷術」を終えました」 ([2021-06-06-1])).
以下,『図説大航海時代』の巻末 (pp. 109--10) の略年表を掲載する.大航海時代の範囲についてはいくつかの考え方があるが,1415年のポルトガル軍によるセウタ占領に始まり,1648年のウェストファリア条約の締結に終わるというのが1つの見方である.しかし,下の略年表にみえるように,その前史は長い.
| 紀元前5世紀 | スキュラクス,インダス河口からスエズ湾まで航海 |
| 4世紀後半 | ネアルコス,インダス地方からティグリス河口まで探検 |
| 111 | 漢の武帝,南越を併合 |
| 1世紀 | カンボジヤ南部に扶南国興る |
| 60--70頃 | 『エリュトラ海案内記』 |
| 1世紀前半 | 「ヒッパロスの風」によるアラビア海航海がさかんになる |
| 2世紀 | 扶南とローマ,インドと中国の交易がおこなわれる |
| 166 | 大秦王安敦(マルクス・アウレリウス)の支社日南郡に至る |
| 207 | 南越国建国 |
| 4--5世紀 | 東南アジアのインド化進む |
| 399--412 | 東晋の法顕のインド,セイロン旅行.『仏国記』を書く |
| 7世紀前半 | 扶南,真臘に併合される |
| 618 | 唐建国 |
| 639 | アラブ人のエジプト侵入 |
| 7世紀後半 | シュリーヴィジャヤ王国マラッカ海峡の交易を支配 |
| 671--95 | 唐の仏僧義浄インド滞在.『南海寄帰内法伝』 |
| 750 | バグダートにアッバース朝おこる.インド洋貿易に進出 |
| 875 | チャンパ(占城)興る |
| 907 | 唐滅亡.五代十国時代に入る |
| 960 | 宋建国.海外貿易の隆盛 |
| 969 | ファーティマ朝カイロに移る.紅海を通じてのアジア貿易.以後エジプトは紅海経由のインド洋貿易を主導する |
| 1096 | 第1次十字軍 (--99) .イタリア港市の台頭 |
| 1127 | 南宋興る |
| 1147 | 第2次十字軍 (--48) |
| 1169 | エジプトにアイユーブ朝成立 |
| 1245--47 | プラノ・カルピーニ,教皇の命によりカラコルムに至る旅行記を著わす |
| 1254 | リュブリュキ,教皇の命によりカラコルムまで旅行.旅行記を書く |
| 1258 | モンゴル軍バグダート占領.アッバース朝滅亡.ただしモンゴル軍はシリア,エジプトに侵入できず |
| 1271--95 | マルコ・ポロのアジア旅行と中国滞在.旅行記を口述 |
| 1291 | ジェノヴァのヴィヴァルディ兄弟西アフリカ航海 |
| 1293 | ジャヴァにマジャパヒト王国成立.モンゴル軍ジャヴァに侵攻 |
| 1312 | ジェノヴァのランチェローテ・マロチェーロ,カナリア諸島に航海 |
| 1349(ママ) | イブン・バトゥータ,24年にわたるアフリカ,アジア旅行からタンジールに帰る |
| 1336 | 南インドにヴィジャヤナガル王国興る |
| 1345 | マジャパヒト,全ジャヴァに勢力拡大 |
| 1351--54 | イブン・バトゥータ西アフリカ旅行.『三大陸周遊記』を書く |
| 1360 | マンデヴィルの『東方旅行記』この頃成立 |
| 1368 | 明建国 |
| 1372 | 明,海禁政策をとる |
| 1403 | スペインのクラビーホ,中央アジアに旅行しティムールに謁す.ラ・サルとベタンクール,カナリア諸島に航海 |
| 1405 | 鄭和の大航海.1433年まで7回にわたる |
| 1415 | ポルトガル軍セウタ占領.間もなく西アフリカ航路の探検が始まる |
| 1434 | ジル・エアネス,ボジャドール岬回航 |
| 1453 | オスマン軍によるコンスタンティノープル攻略 |
| 1455 | ヴェネツィア人カダモストの西アフリカ航海 |
| 1475 | ヴィチェンツァでプトレマイオスの『地理学』刊行 |
| 1479 | スペイン,ポルトガル間にアルカソヴァス条約 |
| 1482 | ポルトガルの西アフリカの拠点エルミナ建設.ポルトガル人コンゴ王国と接触 |
| 1488 | ディアスによる喜望峰発見.大航海時代 |
| 1492 | コロンブス第1回航海 (--93) |
| 1493 | コロンブス第2回航海 |
| 1494 | スペイン,ポルトガル間にトルデシリャス条約 |
| 1498 | ガマのインド航海.コロンブス第3回航海.南米本土に達する |
| 1500 | カブラル,インドへの途次ブラジルに漂着 |
| 1501 | アメリゴ・ヴェスプッチ南アメリカの南緯52°まで航海 |
| 1502 | コロンブス第4回航海.中米沿岸航海 |
| 1505 | トロ会議.西回りで香料諸島探検を議決 |
| 1508 | ブルゴス会議で同様な趣旨の議決 |
| 1509 | アルメイダ,ディウ沖で,エジプト,グジャラート連合艦隊撃破 |
| 1510 | ポルトガル,ゴア完全占領 |
| 1511 | ポルトガル,マラッカ攻略 |
| 1512 | ポルトガル人香料諸島に到着 |
| 1513 | バルボア,パナマ地峡を横断して太平洋岸に達する |
| 1519--21 | コルテスのメキシコ(アステカ王国)征服 |
| 1520 | マゼラン,地峡を発見し,太平洋を横断してフィリピンに至る |
| 1522 | エルカノ以下18人,最初の世界回航をとげてセビリャ着 |
| 1527 | モンテホのユカタン探検 |
| 1528--33 | ピサロのインカ帝国征服 |
| 1529 | サラゴッサ条約により香料諸島のポルトガル帰属決定 |
| 1534 | カルティエのカナダ探検 |
| 1535 | アルマグロのチリ探検 |
| 1537 | ケサーダのムイスカ(チブチャ)征服 |
| 1538 | 皇帝・教皇・ジェノヴァ連合艦隊プレヴェザでトルコ人に敗北 |
| 1541 | ゴンサーロ・ピサロのアマゾン探検.部下のオレリャーナ,河口まで航海 (1542) |
| 1543 | 三人のポルトガル人,種子島着 |
| 1545 | ボリビアのポトシ銀山発見,翌年メキシコでも大銀山発見 |
| 1553 | ウィロビーの北東航路探検 |
| 1565 | ウルダネータ,大圏航路によりフィリピンからメキシコまで航海 |
| 1567 | メンダーニャの太平洋航海.翌年ソロモン諸島発見 |
| 1568 | ジョン・ホーキンズ,サン・ファン・デ・ウルアでスペインの奇襲をうけて脱出 |
| 1570 | ドレイクのカリブ海スペイン基地の掠奪 |
| 1571 | レガスピ,マニラ市建設.キリスト教徒の海軍レパントでオスマン艦隊に勝利 |
| 1575 | フロビッシャー,北西航路探検の勅許を得る |
| 1577--80 | ドレイク,掠奪の世界周航をおこなう |
| 1578 | アルカサルーキヴィルでポルトガル軍モロッコ軍に大敗 |
| 1584--85 | ウォルター・ローリのヴァージニア植民計画 |
| 1586--88 | キャベンディシュの世界周航 |
| 1595 | ローリの第1次ギアナ探検.メンダーニャの太平洋探検,マルケサス諸島発見 |
| 1598 | ファン・ノールト,オランダ人として最初の世界周航 |
| 1599 | オランダ人ファン・ネック東インド航海 |
| 1600 | イギリス東インド会社設立.この頃ブラジルに砂糖産業が興り,アフリカ人奴隷の輸送始まる |
| 1605 | キロスの航海.ニュー・ヘブリデスまで |
| 1606 | キロク帰国後,あとに残されたトレス,ニュー・ギニア,オーストラリア間の海峡を発見し,マニラに向かう |
| 1610 | ハドソン,アニアン海峡を求めて行方不明になる |
| 1614 | メンデス・ピントの東洋旅行記『遍歴記』刊行 |
| 1615 | オランダ人スホーテンとル・メールの航海.ホーン岬発見 |
| 1617 | ローリ第2回ギアナ探検 |
| 1620 | メイフラワー号ニュー・イングランドに到着 |
| 1622 | インド副王の艦隊,モサンビケ沖でオランダ船隊の攻撃を受け壊滅 |
| 1623 | アンボイナ事件.オランダ人によるイギリス人,日本人の殺害.これ以後イギリス人は東インドの香料貿易から撤退し,インドに集中 |
| 1637 | オランダ人西アフリカのエルミナ奪取 |
| 1639 | マカオの対日貿易,鎖国のため不可能になる.タスマンの太平洋航海 |
| 1641 | オランダ人マラッカ奪取 |
| 1642--43 | タスマン,オーストラリアの輪郭を明らかにする |
| 1645 | オランダ人セント・ヘレナ島占領 |
| 1647 | オランダ,アンボイナ島完全占領.カサナーテのカリフォルニア探検 |
| 1648 | セミョン・デジニョフ,アジア最北東端の岬(デジニョフ岬)に到達.ただしベーリング海峡の存在には気がつかなかった.ウェストファリア条約の締結による三十年戦争の終わり.オランダの独立承認される |
hellog ではこれまでも関連する年表を多く掲載してきた.大航海時代との関連で,以下のリンクを挙げておこう.
・ 「#2371. ポルトガル史年表」 ([2015-10-24-1])
・ 「#3197. 初期近代英語期の主要な出来事の年表」 ([2018-01-27-1])
・ 「#3478. 『図説イギリスの歴史』の年表」 ([2018-11-04-1])
・ 「#3479. 『図説 イギリスの王室』の年表」 ([2018-11-05-1])
・ 「#3487. 『物語 イギリスの歴史(上下巻)』の年表」 ([2018-11-13-1])
・ 「#3497. 『イギリス史10講』の年表」 ([2018-11-23-1]) を参照.
・ 増田 義郎 『図説大航海時代』 河出書房新社,2008年.
2022-12-04 Sun
■ #4969. splendid の同根類義語のタイムライン [cognate][synonym][lexicology][inkhorn_term][emode][borrowing][loan_word][renaissance][oed][timeline]
すでに「#3157. 華麗なる splendid の同根類義語」 ([2017-12-18-1]) で取り上げた話題ですが,一ひねり加えてみました.splendid (豪華な,華麗な;立派な;光り輝く)というラテン語の動詞 splendēre "to be bright or shining" に由来する形容詞ですが,英語史上,数々の同根類義語が生み出されてきました.先の記事で触れなかったものも含めて OED で調べた単語を列挙すると,廃語も入れて13語あります.
resplendant, resplendent, resplending, splendacious, †splendant, splendent, splendescent, splendid, †splendidious, †splendidous, splendiferous, †splendious, splendorous
OED に記載のある初出年(および廃語の場合は最終例の年)に基づき,各語の一生をタイムラインにプロットしてみたのが以下の図です.とりわけ16--17世紀に新類義語の登場が集中しています.
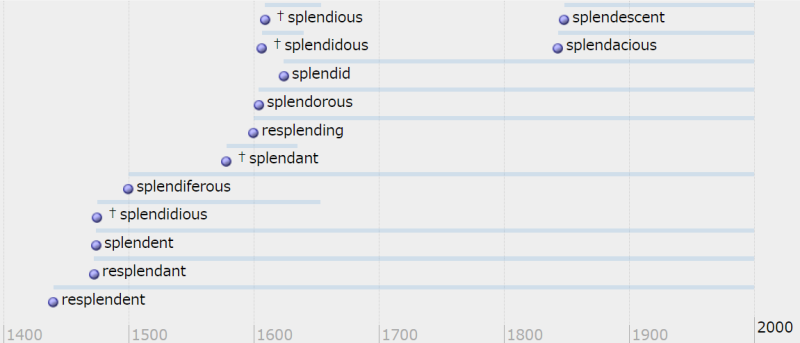
ほかに1796年に初出の resplendidly という副詞や1859年に初出の many-splendoured という形容詞など,合わせて考えたい語もあります.いずれにせよ英語による「節操のない」借用(あるいは造語)には驚かされますね.
2022-07-13 Wed
■ #4825. 英米史略年表 --- 『英語の教養』より [review][toc][timeline]
昨年出版された大井光隆(著)『英語の教養』(ベレ出版)をパラパラ眺めて楽しんでいる.文化的なキーワードを挙げつつ1テーマを1ページで解説する,手軽に読める英米文化誌の本となっている.どこから読んでもためになる.章立てを示そう.
第1章 英米の歴史
第2章 年中行事と祝日
第3章 ギリシャとローマの神話
第4章 聖書とキリスト教
第5章 伝説と民間伝承
第6章 生活のことば
第7章 スポーツの文化
第8章 架空の人物と民間のヒーロー
第9章 動物の世界
第10章 植物の世界
第1章を開いたところに「英米史略年表」が掲げられている (10--11) .英米史の全体像を大づかみするには,細かい年表よりも,このくらいの略年表が便利である.要点だけを押さえた英米史年表として以下に記しておきたい.
| (紀元前) | |
| 600年頃 | ブリテン島に大陸からケルト人が移住 |
| 55年~4 | ローマの将軍カエサル,ブリテン島に侵攻(~54) |
| このころ,イエス・キリスト誕生 | |
| (紀元後) | |
| 43 | ローマによるブリテン島支配が始まる |
| 409 | ローマ軍,ブリテン島より撤退 |
| 597 | ローマの宣教師アウグスティヌスによるキリスト教の布教始まる |
| 800 | このころからバイキングの侵攻が始まる |
| 871 | アルフレッド王即位 |
| 1016 | デンマーク王クヌート (Canute) がイングランドを征服,王位に就く |
| 1066 | 「ノルマン征服」で,ウィリアム1世即位 |
| 1215 | ジョン王,マグナカルタを認める |
| 1337 | 英仏間の「百年戦争」始まる (~1453) |
| 1348 | 黒死病,猛威を振るう |
| 1455 | 「ばら戦争」始まる (~85) |
| 1509 | ヘンリー8世即位 (~47) |
| 1534 | 国教会 (Church of England) 成立,ローマ・カトリック教会と絶縁 |
| 1558 | エリザベス1世即位 (~1603) |
| 1588 | ドレイク,スペインの無敵艦隊を破る |
| このころ,劇作家シェイクスピアが活躍 | |
| 1600 | 東インド会社が設立され,東洋との直接貿易始まる |
| 1607 | イギリス人が初めてアメリカに入植し,現在のバージニアに植民地ジェームズタウン (Jamestown) を設立 |
| 1620 | ピルグリム・ファーザーズがアメリカに移住 |
| 1640 | ピューリタン革命 (~60) |
| 1649 | チャールズ1世が処刑され,イングランド共和国成立 |
| 1660 | 王政復古 (the Restoration) で,チャールズ2世即位 (~85) |
| 1665 | ロンドンで黒死病が大流行 |
| 1666 | ロンドン大火で,市街の80%が消失 |
| 1688 | 名誉革命 (the Glorious Revolution) 始まる (~89) |
| 1707 | イングランドとスコットランドが合同し,グレートブリテン連合王国が成立 |
| 1775 | アメリカ独立戦争始まる |
| 1776 | アメリカ独立宣言が採択される |
| 1789 | フランス革命勃発 |
| 1801 | イギリス,アイルランドと合同 |
| 1815 | ウェリントン,ワーテルローの戦いでナポレオン軍を破る |
| 1830 | リバプール・マンチェスター間に鉄道が開業し,鉄道時代がスタート |
| 1837 | ビクトリア女王即位 (~1901) |
| 1840 | アヘン戦争勃発 (~42) |
| 1845 | アイルランドで大飢饉 (~46) |
| 1851 | ロンドンで第1回万博(ロンドン大博覧会)開催 |
| 1861 | アメリカで南北戦争始まる |
| 1914 | 第一次世界大戦始まる (~18) |
| 1939 | 第二次世界大戦始まる (~45) |
| 1952 | エリザベス2世即位 |
| 1960 | アメリカで公民権運動 |
| 1965 | ベトナム戦争 (~75) |
| 1989 | 「ベルリンの壁」崩壊 |
| 2019 | 世界各地で「新型コロナウィルス感染症」 (COVID-19) が発生 |
・ 大井 光隆 『英語の教養』 ベレ出版,2021年.
2022-05-05 Thu
■ #4756. アングロサクソン時代の略年表 [timeline][anglo-saxon][oe][literature]
新学期の古英語の授業も少しずつ軌道に乗ってきた.時代背景を理解するために,この辺りでアングロサクソン時代の略年表を掲げたい.すでに「#2526. 古英語と中英語の文学史年表」 ([2016-03-27-1]),「#2871. 古英語期のスライド年表」 ([2017-03-07-1]),「#3193. 古英語期の主要な出来事の年表」 ([2018-01-23-1]) で類似の年表を掲げているが,バリエーションがあったほうがよいと考えているので今回は Godden and Lapidge (xii--xiii) からの略年表を再現する.
Chronological table of the Anglo-Saxon period
| from c. 400 | Germanic peoples settle in Britain |
| c. 540 | Gildas in De excidio Britanniae laments the effects of the Germanic settlements on the supine Britons |
| 597 | St Augustine arrives in Kent to convert the English |
| 616 | death of Æthelberht, king of Kent |
| c. 625 | ship-burial at Sutton Hoo (mound 1) |
| 633 | death of Edwin, king of Northumbria |
| 635 | Bishop Aidan established in Lindisfarne |
| 642 | death of Oswald, king of Northumbria |
| 664 | Synod of Whitby |
| 669 | Archbishop Theodore and Abbot Hadrian arrive in Canterbury |
| 674 | monastery of Monkwearmouth founded |
| 682 | monastery of Jarrow founded |
| 687 | death of St Cuthbert |
| 689 | death of Cædwalla, king of Wessex |
| 690 | death of Archbishop Theodore |
| c. 700 | 'Lindisfarne Gospels' written and decorated |
| 709 | deaths of Bishops Wilfrid and Aldhelm |
| 716--57 | Æthelbald king of Mercia |
| 731 | Bede completes his Ecclesiastical History |
| 735 | death of Bede |
| 754 | death of St Boniface, Anglo-Saxon missionary in Germany |
| 757--96 | Offa king of Mercia |
| 781 | Alcuin of York meets Charlemagne in Parma and thereafter leaves York for the Continent |
| 793 | Vikings attack Lindisfarne |
| 802--39 | Ecgberht king of Wessex |
| 804 | death of Alcuin |
| 839--56 | Æthelwulf king of Wessex |
| 869 | Vikings defeat and kill Edmund, king of East Anglia |
| 871--99 | Alfred the Great king of Wessex |
| 878 | Alfred defeats the Viking army at the battle of Edington, and the Vikings settle in East Anglia (879--80) |
| 899--924 | Edward the Elder king of Wessex |
| 924--39 | Athelstan king of Wessex and first king of All England |
| 937 | battle of Brunanburh: Athelstan defeats an alliance of Scots and Scandinavians |
| 957--75 | Edgar king of England |
| 859--88 | Dunstan archbishop at Canterbury |
| 963--84 | Æthelwold bishop at Winchester |
| 964 | secular clerics expelled from the Old Minster, Winchester, and replaced by monks |
| 971--92 | Oswald archbishop at York |
| 973 | King Edgar crowned at Bath |
| 978--1016 | Æthelred 'the Unready' king of England |
| 975--7 | Abbo of Fleury at Ramsey |
| 991 | battle of Maldon: the Vikings defeat an English army led by Byrhtnoth |
| c. 1010 | death of Ælfric, abbot of Eynsham |
| 1011 | Byrhtferth's Enchiridion |
| 1013 | the English submit to Swein, king of Denmark |
| 1016--35 | Cnut king of England |
| 1023 | death of Wulfstan, archbishop of York |
| 1042--66 | Edward the Confessor king of England |
| 1066 | battle of Hastings: the English army led by Harold is defeated by the Norman army led by William the Conqueror |
・ Godden, Malcolm and Michael Lapidge, eds. The Cambridge Companion to Old English Literature. Cambridge: CUP, 1986.
[ 固定リンク | 印刷用ページ ]
2021-11-17 Wed
■ #4587. 「日本英語受容史略年表」 [timeline][english_in_japan][elt]
「#4578. 朝ドラ『カムカムエヴリバディ』が始まっています」 ([2021-11-08-1]) で述べたように,日本における英語受容の歴史は,広い意味での英語史の1側面とみることができる.英語の進出と受容とでは視座が異なるものの,英語の拡大の一部であることは間違いない.
もちろん日本の英語教育や英語学習の歴史にも直結する問題であり,英語関係者の間でもっと関心が広まってしかるべき話題だと思っている.斎藤 (198--99) が以下のように述べているとおりである.
英語をめぐる最近の議論を聞いていると,(とくに「コミュニケーション」能力を中心とした)英語力を高めるための学習法だけが問題視されているような気がしてならない.たしかに,効果的な英語学習法が研究・開発されれば,それはそれで喜ぶべきことであろう.だが,日本の英語学習法をめぐる議論は,つねに日本人にとって英語とは何なのかとの問いを踏まえていなければならない.そしてその問いは,日本人にとって英語とは何だったのかとの問いの延長線上にあるものなのである.
以下,斎藤 (195--97) より「日本英語受容史略年表」を掲げよう.英語受容史を体現する3名の偉人,福沢・新渡戸・漱石(紙幣の肖像画でもある)の動きと連動させているのがユニークである.関連して「#3695. 日本における英語関係史の略年表」 ([2019-06-09-1]) も参照.
| 年号 | 年 | 日本英語受容史上の重要事項 | 福沢・新渡戸・漱石の動き | 世界の動き |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 江戸 | 1600(慶長5) | ウィリアム・アダムズ豊後に漂着.(関ヶ原の戦いが起こる) | イギリスの東インド会社ができる. | |
| 1776 | アメリカが独立宣言をする. | |||
| 1808(文化5) | フェートン号事件 | |||
| 1811(文化8) | 日本初の英語手引き書『諳厄利亜興学小筌』成る. | |||
| 1834(天保5) | 福沢,大阪に生まれる. | |||
| 1840 | アヘン戦争が起こる. | |||
| 1841(天保12) | ジョン万次郎,アメリカ船に救出されてアメリカに渡る. | |||
| 1848(嘉永元) | ラナルド・マクドナルド利尻島に上陸. | |||
| 1853(嘉永6) | 黒船が浦賀に来航. | |||
| 1854(安政元) | 日米和親条約締結. | |||
| 1856(安政3) | 蕃書調所が開設される. | |||
| 1859(安政6) | 横浜開港 | 福沢,横浜を見学し,英学に転向. | ||
| 1860(万延元) | 福沢,咸臨丸でアメリカへ. | |||
| 1861 | アメリカで南北戦争が起こる. | |||
| 1862(文久2) | 日本初の印刷の英和辞書『英和対訳袖珍辞書』が出版される. | 新渡戸,盛岡に生まれる. | ||
| 1867(慶応3) | 漱石,江戸に生まれる. | |||
| 明治 | 1868 | 福沢,私塾を慶應義塾と改称. | ||
| 1874 | 7つの官立の外国語学校が英語学校と改称. | |||
| 1876 | 札幌農学校開校. | |||
| 1877 | 東京と大阪の英語学校を除き官立の英語学校が廃校となる. | 新渡戸,札幌農学校入学. | ||
| 1884 | 新渡戸,渡米. | |||
| 1894 | (日清戦争が起こる.) | |||
| 1896 | 斎藤秀三郎,正則英語学校を創設. | |||
| 1900 | 津田梅子,女子英学塾創立. | 漱石,渡英. | ||
| 1901 | (日英同盟締結.) | 福沢,死去. | ||
| 1903 | 漱石,第一高等学校校長となる. | |||
| 大正 | 1914 | (第一次世界大戦に参戦.) | 第一次世界大戦が始まる. | |
| 1916 | 漱石,死去. | |||
| 1922 | ハロルド・パーマー来日 | |||
| 1923 | (関東大震災が起こる.) | |||
| 1924 | 英語存廃論が盛んとなる. | アメリカで排日移民法が成立. | ||
| 昭和 | 1933 | 新渡戸,死去. | ||
| 1939 | 第二次世界大戦が始まる. | |||
| 1941 | (太平洋戦争が始まる.) | |||
| 1945 | (終戦.) | |||
| 1946 | 「カムカム英語会話」放送開始. | |||
| 1951 | (サンフランシスコ講和条約調印.) | |||
| 1954 | 高校生のAFS留学始まる. | |||
| 1963 | 日本英語検定協会発足. | |||
| 1972 | 中学校学習指導要領改訂,「週3時間」全面実施. | |||
| 平成 | 1990 | 湾岸戦争が起こる. | ||
| 1994 | 「オーラル・コミュニケーション」A・B・Cが科目に加わる. | |||
| 1999 | 学習指導要領改訂. | |||
| 2000 | 小渕内閣の諮問機関「21世紀日本の構想」懇談会が「英語第二公用語化」を提言. | |||
| 2002 | 文科省「『英語が使える日本人』の育成のための戦略構想」. | |||
| 2002 | 文科省「『英語が使える日本人』の育成のための行動計画」. | |||
| 2009 | 高校学習指導要領告示(2013施行).「授業は英語で行うことを基本とする」と規定. | |||
| 2013 | 文科省「グローバル化に対応した英語教育改革実施計画」. |
・ 斎藤 兆史 『英語襲来と日本人 --- 今なお続く苦悶と狂乱』 中央公論新社,2017年.
2020-03-06 Fri
■ #3966. 英語統語論の主要な歴史的変化の一覧 [syntax][language_change][word_order][timeline]
Fischer et al. (4--6) に英語統語論の主要な歴史的変化の一覧表がある.参照用に便利なので,"Overview of syntactic categories and their changes" と題されたこの一覧を再現しておきたい.左欄を縦に眺めるだけでも,英語歴史統語論にどのような話題があり得るのかがつかめる.
| Changes in: | Old English | Middle English | Modern English | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| case form and function: | genitive | various functions | genitive case for subjective/poss.; of-phrase elsewhere | same |
| dative | various functions/PP sporadic | increase in to-phrase; impersonal dative lost | same | |
| accusative | main function: direct object | accusative case lost, direct object mainly marked by position | same | |
| determiners: | system | articles present in embryo form, system developing | articles used for presentational and referential functions | also in use in predicative and generic contexts |
| double det. | present | rare | absent | |
| quantifiers: | position of | relatively free | more restricted | fairly fixed |
| adjectives: | position | both pre- and postnominal | mainly prenominal | prenominal with some lexical exceptions |
| form/function | strong/weak forms, functionally distinct | remnants of strong/weak forms; not functional | one form only | |
| as head | fully operative | reduced; introduction of one | restricted to generic reference/idiomatic | |
| 'stacking' of | not possible | possible | possible | |
| adjectival or relative clause | relative: se, se þe, þe, zero subject rel. | new: þæt, wh-relative (except who), zero obj. rel. | who relative introduced | |
| adj. + to-inf. | only active infinitives | active and passive inf. | mainly active inf. | |
| aspect-system: | use of perfect | embryonic | more frequent; in competition with 'past' | perfect and 'past' grammaticalized in different functions |
| form of perfect | BE/HAVE (past part. sometimes declined) | BE/HAVE; HAVE becomes more frequent | mainly HAVE | |
| use and form of progressive | BE + -ende; function not clear | BE + -ing, infrequent, more aspectual | frequent, grammaticalizing | |
| tense-system: | 'present' | used for present tense, progressive, future | used for present tense and progr.; (future tense develops) | becomes restricted to 'timeless' and 'reporting' uses |
| 'past' | used for past tense, (plu)perfect, past progr. | still used also for past progr. and perfect; new: modal past | restricted in function by grammaticalization of perfect and progr. | |
| mood-system: | expressed by | subjunctive, modal verbs (+ epistemic advbs) | mainly modal verbs (+ develop. quasi-modals); modal past tense verbs (with exception features) | same + development of new modal expressions |
| category of core modals | verbs (with exception features) | verbs (with exception features) | auxiliaries (with verbal features) | |
| voice-system: | passive form | beon/weorðan + (inflected) past part. | BE + uninfl. past part | same; new GET passive |
| indirect pass. | absent | developing | (fully) present | |
| prep. pass. | absent | developing | (fully) present | |
| pass. infin. | only after modal verbs | after full verbs, with some nouns and adject. | same | |
| negative system | ne + verb (+ other negator) | (ne) + verb + not; rare not + verb | Aux + not + verb; (verb + not) | |
| interrog. system | inversion: VS | inversion: VS | Aux SV | |
| DO as operator | absent | infrequent, not grammaticalized | becoming fully grammaticalized | |
| subject: | position filled | some pro-drop possible; dummy subjects not compulsory | pro-drop rare; dummy subjects become the norm | pro-drop highly marked stylistically; dummy subj. obligat. |
| clauses | absent | that-clauses and infinitival clauses | new: for NP to V clauses | |
| subjectless/impersonal constructions | common | subject position becomes obligatorily filled | extinct (some lexicalized express.) | |
| position with respect to V | both S (...) V and VS | S (...) V; VS becomes restricted to yes/no quest. | only S (adv) V; VS > Aux SV | |
| object: | clauses | mainly finite þæt-cl., also zero/to-infinitive | stark increase in infinitival cl. | introduction of a.c.i. and for NP to V cl. |
| position with respect to V | VO and OV | VO; OV becomes restricted | VO everywhere | |
| position IO-DO | both orders; pronominal IO-DO preferred | nominal IO-DO the norm, introduction of DO for/to IO | IO-DO with full NPs; pronominal DO-IO predominates | |
| clitic pronouns | syntactic clitics | clitics disappearing | clitics absent | |
| adverbs: | position | fairly free | more restricted | further restricted |
| clauses | use of correlatives + different word orders | distinct conjunctions; word order mainly SVO | all word order SVO (exc. some conditional clauses) | |
| phrasal verbs | position particle: both pre- and postverbal | great increase; position: postverbal | same | |
| preposition stranding | only with pronouns (incl. R-pronouns: þær, etc.) and relative þe | no longer with pronouns, but new with prep. passives, interrog., and other relative clauses | no longer after R-pronouns (there, etc.) except in fixed expressions | |
・ Fischer, Olga, Hendrik De Smet, and Wim van der Wurff. A Brief History of English Syntax. Cambridge: CUP, 2017.
[ 固定リンク | 印刷用ページ ]
2019-10-28 Mon
■ #3836. フランス語史の年表 [timeline][hfl][french][anthropology][indo-european][hfl]
フランス語史は専門ではないものの,英語史を掘り下げて理解するためには是非ともフランス語史の知識がほしい.ということで,少なからぬ関心を寄せている.今回は Perret (179--81) よりフランス語史の年表 "Chronologie" を掲げよう.イタリックの行は,仮説的な年代・記述という意味である.
[ Préhistoire des langues du monde ]
Il y a 4 ou 5 millions d'années: apparition de l'australopithèque en Afrique.
Il y a 1,6 million d'années: homo erectus colonise l'Eurpope et l'Asie.
Il y a 850 000 ans: premiers hominidés en Europe.
Avant - 100 000: Homo sapiens en Europe (Neandertal) et en Asie (Solo).
- 100 000: un petit groupd d'Homo sapiens vivant en Afrique (ou au Moyen-Orient) se met en marche et recolonise la planète. Les autres Homo sapiens se seraient éteints. (Hypothèse de certains généticiens, les équipes de Cavalli-Sforza et de Langaney, dite thèse du «goulot d'étranglement»).
- 40 000: première apparition du langage?
[ Préhistoire des Indo-Européens ]
- 10000: civilisation magdalénienne en Dordogne. Premier homme en Amérique.
- 7000: les premières langues indo-européennes naissent en Anatolie (hypothèse Renfrew).
Entre - 65000 et - 5500: les Indo-Européens commencent leur migration par vagues (hypothèse Renfrew).
- 4500: les Indo-Européens occupent l'ouest de l'Europe (hypothèse Renfrew).
- 4000 ou - 3000: les Indo-Européens commencent à se disperser (hypothèse dominante).
- 3500: civilisation dite des Kourganes (tumuluss funéraires), débuts de son expansion.
- 3000: écriture cunéiforme en Perse, écriture en Inde. Première domestication du cheval en Russie? (- 2000, premières représentations de cavaliers).
[ Préhistoire du français ]
- 4000 ou - 3000: la civilisation des constructeurs de mégalithes apparaît en Bretagne.
- 3000: la présence des Celtes est attestée en Bohème et Bavière.
- 2500: début de l'emploi du bronze.
- 600: premiers témoignages sur les Ligure et les Ibères.
- 600: des marins phocéens s'installent sur la cõte méditerranéenne.
- 500: une invasion celte (précédée d'infiltrations?): les Gaulois.
[ Histoire du français ]
- 1500: conquête de la Provence par les Romains et infiltrations dans la région narbonnaise.
- 59 à - 51: conquête de la Gaule par les Romains.
212: édit de Caracalla accordant la citoyenneté à tous les hommes libres de l'Empire.
257: incursions d'Alamans et de Francs jusqu'en Italie et Espagne.
275: invasion générale de la Gaule par les Germains.
312: Constantin fait du christianisme la religion officielle de l'Empire.
Vers 400: traduction en latin de la Bible (la Vulgate) par saint Jérôme.
450--650: émigration celte en Bretagne (à partir de Grande-Bretagne): réimplantation du celte en Bretagne.
476: prise de Rome et destitution de l'empereur d'Occident.
486--534: les Francs occupent la totalité du territoire de la Galue (496, Clovis adopted le christianisme).
750--780: le latin cesse d'être compris par les auditoires populaires dans le nord du pays.
800: sacre de Charlemagne.
813: concile de Tours: les sermons doivent être faits dans les langues vernaculaires.
814: mort de Charlemagne.
842: les Serments de Strasbourg, premier document officiel en proto-français.
800 à 900: incursions des Vikings.
800--850: on cesse de comprendre le latin en pays de langues d'oc.
880: Cantilène de sainte Eulalie, première elaboration littéraire en proto-français.
911: les Vikings sédentarisés en Normandie.
957: Hugues Capet, premier roi de France à ignorer le germanique.
1063: conquête de l'Italie du Sud et de la Sicile par des Normands.
1066: bataille de Hastings: une dynastie normande s'installe en Angleterre où on parlera français jusqu'à la guerre de Cent Ans.
1086: la Chanson de Roland.
1099: prise de Jérusalem par les croisés: début d'une présence du français et du provençal en Moyen-Orient.
1252: fondation de la Sorbonne (enseignement en latin).
1254: dernière croisade.
1260: Brunetto Latini, florentin, compose son Trésor en français.
1265: Charles d'Anjou se fait couronner roi des deux Siciles, on parlera français à la cour de Naples jusqu'au XIVe siècle.
1271: réunion du Comté de Toulouse, de langue d'oc, au royaume de France.
1476--1482: Louis XI rattache la Bourgogne, la Picardie, l'Artois, le Maine, l'Anjou et la Provence au royaume de France.
1477: l'imprimerie. Accélération de la standardisation et de l'oficialisation du français, premières «inventions» orthographiques.
1515: le Consistori del Gai Saber devient Collège de rhétorique: fin de la littérature officielle de langue d'oc.
1523--1541: instauration du français dans le culte protestant.
1529: fondation du Collège de France (rares enseignements en fançais).
1530: Esclarcissment de la langue française, de Palsgrave, la plus connue des grammaires du français qui parassient à l'époque en Angleterre.
1534: Jacques Cartier prent possession du Canada au nom du roi de France.
1539: ordonnace de Villers-Cotterêts, le français devient langue officielle.
1552: la Bretagne est rattachée au royaume de France.
1559: la Lorraine est rattachée au royaume de France.
1600: la Cour quitte les bords de Loire pour Parsi.
1635: Richelieu officialise l'Académie française.
1637: Descartes écrit en français Le Discours de la méthode.
1647: Remarques sur la langue française de Vaugelas: la norme de la Cour prise comme modèle du bon usage.
1660: Grammaire raisonnée de Port-Royal.
1680: première traduction catholique de la Bible en français.
1685: révocation de l'édit de Nantes: un million de protestants quittent la France pour les pays protestants d'Europe, mais aussi pour l'Afrique et l'Amérique.
1694: première parution du Dictionnaire de l'Académie.
1700: début d'un véritable enseignement élémentaire sans latin, avec les frères des écoles chrétiennes de Jean-Baptiste de la Salle.
1714: traité de Rastadt, le français se substitue au latin comme languge de la diplomatie en Europe.
1730: traité d'Utrecht: la France perd l'Acadie.
1739: mise en place d'un enseignment entièrement en français dans le collège de Sorèze (Tarn).
1757: apparition des premiers textes en créole.
1762: explusion des jésuites, fervents partisans dans leur collèges de l'enseignement entièrement en latin; une réorganisation des collèges fait plus de place au français.
1763: traité de Paris, la France perd son empire colonial: le Canada, les Indes, cinq îles des Antilles, le Sénégal et la Lousinane.
1783: la France recouvre le Sénégal, la Lousiane et trois Antilles.
1787: W. Jones reconnaît l'existence d'une famille de langues regroupant latin, grec, persan, langues germaniques, langues celte et sanscrit.
1794: rapport Barrère sur les idiomes suspect (8 pluviôse an II); rapport Grégoire sur l'utilité de détruire les patois (16 prairial an II).
1794--1795: la Républic s'aliène les sympathies par des lois interdisant l'usage de toute autre langue que le français dans les pays occupée.
1797: tentative d'introduire le français dans le culte (abbé Grégoire).
1803: Bonaparte vend la Louisiane aux Anglais.
1817: la France administre le Sénégal.
1827: Préface de Cromwell, V. Hugo, revendication de tous les registres lexicaux pour la langue littéraire.
1830: début de la conquête de l'Algérie.
1835: la sixième édition du Dictionnaire de l'Académie accepte enfin la graphie -ais, -ait pour les imparfiat.
1879: invention du phonographe.
1881: Camille Sée crée un enseignment public à l'usage des jeunes fille.
1882: lois Jules Ferry: enseignement primaire obligatoire, laïquie et gratuie (en français).
1885: l'administration du Congo (dit ensuite de Belge) est confiée au roi des Belges.
1901: arrêté proposant une certaine tolérance dans les règles orthographiques du français.
1902: l'enseignement secondaire moderne sans latin ni grec est reconnu comme égal à la filière classique.
1902--1907: publication de l'Atlas linguistique de la France par régions de Gilliéron et Edmont.
1950: autorisation de soutenir des thèses en français.
1919: traité de Versalles, le français perd son statue de langue unique de la diplomatic en Europe.
1921: début de la diffusion de la radio.
1935: invention de la télévision.
1951: loi Deixiome permet l'enseignement de certaines langues régionales dans le second cycle.
1954--1962: les anciennes colonies de la France deviennent des états indépendents.
1962--1965: concile de Vatican II: la célébration do la messe, principal office du culte catholique, ne se fait plus en latin.
1987: un créole devient langue officielle en Haïti.
1990: un «rapport sur les rectifications de l'orthographe» propose la régularisation des pluriels de mots composés et la suppression de l'accent circonflexe.
1994: première création d'un organism de soutien à la francophonie.
・ Perret, Michèle. Introduction à l'histoire de la langue française. 3rd ed. Paris: Colin, 2008.
2019-10-26 Sat
■ #3834. 『図説フランスの歴史』の年表 [timeline][history]
先日の「#3828. 『図説フランスの歴史』の目次」 ([2019-10-20-1]) に引き続き,同書の巻末 (177--79) にある「フランス史略年表」を掲げたい.イギリス史の年表については,「#3478. 『図説イギリスの歴史』の年表」 ([2018-11-04-1]),「#3479. 『図説 イギリスの王室』の年表」 ([2018-11-05-1]),「#3487. 『物語 イギリスの歴史(上下巻)』の年表」 ([2018-11-13-1]),「#3497. 『イギリス史10講』の年表」 ([2018-11-23-1]) を参照.
| 前9世紀頃 | ケルト人,ガリアへ移住 |
| BC121 | ローマ軍,ガリア南部を征服 |
| BC52 | カエサル,ガリア全土を征服 |
| 372 | トゥールのマルティヌス,マルムティエ修道院を設立 |
| 418 | 西ゴート族,アキテーヌ地方に定住 |
| 476 | 西ローマ帝国滅亡 |
| 486 | ソワソンの戦い.クローヴィス,メロヴィング朝を開く |
| 496 | トルビアックの戦い.クローヴィス,カトリックに改宗 |
| 575頃 | トゥール司教グレゴリウス『フランク人の歴史』 |
| 732 | トゥール・ポワティエ間の戦い.カール・マルテル,イスラム勢力を撃破 |
| 751 | ピピン3世(小ピピン),カロリング朝を開く |
| 800 | 教皇レオ3世,シャルルマーニュを西ローマ皇帝に戴冠 |
| 843 | ヴェルダン条約,帝国の三分割 |
| 987 | パリ伯ユーグ・カペー,フランス王に即位.カペー朝始まる (--1328) |
| 1154 | アンリ・プランタジネット,イングランド王に即位(ヘンリ2世).アンジュー帝国成立 |
| 1190 | フィリップ2世,第3回十字軍に出発 |
| 1202 | フィリップ2世,英王ジョンの大陸所領没収を宣言 |
| 1209 | 教皇イノケンティウス3世,南仏のカタリ派を攻撃,アルビジョワ十字軍始まる |
| 1214 | ブーヴィーヌの戦い |
| 1226 | ルイ9世即位,母后ブランシュ・ド・カスティーユ摂政 (--34) |
| 1229 | トゥルーズ伯降伏,アルビジョワ十字軍終わる |
| 1248 | ルイ9世,第6回十字軍に参加 |
| 1270 | ルイ9世,第7回十字軍に出発.テュニスで病死 |
| 1302 | フィリップ4世,最初の全国三部会をパリにて招集 |
| 1303 | アナーニ事件,教皇ボニファティウス8世憤死 |
| 1305 | フィリップ4世,ボルドー大司教を教皇に擁立(クレメンス5世) |
| 1307 | フィリップ4世,テンプル騎士団員を一斉逮捕 |
| 1309 | 教皇クレメンス5世,教皇庁をアヴィニョンに移す |
| 1328 | シャルル4世没,カペー朝断絶.フィリップ6世即位,ヴァロア朝の開始 (--1589) |
| 1337 | 百年戦争始まる |
| 1348 | 黒死病がフランス全土で流行 |
| 1358 | エティエンヌ・マルセルのパリ革命 |
| 1415 | 英王ヘンリ5世,ノルマンディに上陸 (8.12) .アザンクールの戦い (10.25) |
| 1420 | トロワの和約 |
| 1429 | ジャンヌ・ダルク,オルレアンを解放.シャルル7世ランスで戴冠 |
| 1431 | ジャンヌ・ダルク火刑 |
| 1453 | カスティヨンの戦い,百年戦争終了 |
| 1477 | ブルゴーニュ公シャルル突進公戦死,ブルゴーニュ公国解体へ |
| 1494 | シャルル8世,イタリアへ侵入.イタリア戦争始まる (--1559) |
| 1516 | ボローニャの政教協約 |
| 1525 | パヴィアの戦い,フランソワ1世捕虜に |
| 1530 | フランソワ1世,王立教授団を創設 |
| 1534 | 檄文事件.プロテスタントへの弾圧開始 |
| 1539 | ヴィレル・コトレ王令.公文書におけるフランス語使用,小教区帳簿の作成を義務づける |
| 1559 | カトー・カンブレジ条約,イタリア戦争終了.アンリ2世没 |
| 1562 | ヴァシーでプロテスタントを虐殺,宗教戦争始まる (--98) |
| 1572 | サン・バルテルミの虐殺 |
| 1576 | ギーズ公アンリ,カトリック同盟(リーグ)を結成 |
| 1589 | アンリ3世暗殺,ヴァロア朝断絶.アンリ4世即位,ブルボン朝始まる (--1792) |
| 1593 | アンリ4戦,サン・ドニでカトリックに改宗 |
| 1594 | アンリ4世,シャルトルで成聖式.国王,巴里に入城 |
| 1598 | ナント王令 |
| 1604 | ポーレット法,官職の世襲・売買を年税の支払いを条件に公認 |
| 1624 | リシュリュー,宰相に就任 |
| 1629 | アレス王令,プロテスタントの武装権を剥奪 |
| 1630 | 「欺かれた者たちの日」,マリ・ド・メディシス失脚 |
| 1635 | フランス,三十年戦争に参戦 |
| 1639 | ノルマンディで反税蜂起「ニュ・ピエ(裸足党)の乱」 |
| 1648 | フロンドの乱勃発 (--53) |
| 1659 | ピレネー条約 |
| 1661 | マザラン没.ルイ14世,親政を開始 |
| 1665 | コルベール,財務総監に就任 |
| 1667 | パリに警視総監職を設置.フランドル戦争始まる (--68) |
| 1672 | オランダ戦争始まる (--78) |
| 1685 | ナント王令の廃止 |
| 1688 | アウクスブルク同盟戦争始まる (--97) .国王民兵制導入 |
| 1695 | カピタシオン(人頭税)導入 |
| 1701 | スペイン継承戦争始まる (--13) |
| 1710 | ディジエーム(十分の一税)導入 |
| 1715 | ルイ14世没.ルイ15世即位,オルレアン公摂政 |
| 1720 | 「ローのシステム」破綻 |
| 1733 | ポーランド継承戦争始まる (--35) |
| 1740 | オーストリア継承戦争始まる (--48) |
| 1756 | 七年戦争始まる (--63) |
| 1771 | 大法官モプーによる司法改革 |
| 1775 | 小麦粉戦争 |
| 1786 | カロンヌ,全身分を対象とする新たな税を提唱 |
| 1789 | 国民議会成立 (6.17),封建制の廃止 (8.4),人権宣言 (8.26),ヴェルサイユ行進 (10.5) |
| 1790 | 聖職者民事基本法 |
| 1791 | ヴァレンヌ事件 (6.20),「1791年憲法制定」 (9.3) |
| 1792 | オーストリアに宣戦布告 (4.20),8月10日事件(王権の停止),ヴァルミの戦い (9.20),共和制の開始 (9.21) |
| 1793 | ルイ16世処刑 (1.21),山岳派独裁,恐怖政治,総最高価格法 (9.29) |
| 1794 | テルミドールの反動 (7.27),山岳派失脚 |
| 1796 | ナポレオン,イタリア遠征 |
| 1799 | ブリュメール18日のクーデタ.ナポレオン,政権を掌握 |
| 1800 | フランス銀行設立 |
| 1804 | ナポレオン法典(民法典).ナポレオン,皇帝に即位 |
| 1806 | ベルリン勅令(大陸封鎖令) |
| 1814 | ナポレオン,皇帝を退位.エルバ島へ.ルイ18世パリに帰還 |
| 1815 | ナポレオン「百日天下」 |
| 1824 | ルイ18世没,シャルル10世即位 |
| 1830 | 七月革命,ルイ・フィリップ即位(七月王政の開始) |
| 1847 | 最初の「改革宴会」 |
| 1848 | 二月革命勃発 (2.23),第二共和制の成立,ルイ・ナポレオン大統領に (12.10) |
| 1852 | ルイ・ナポレオン,皇帝に即位.第二帝政 (--70) |
| 1855 | 第1回パリ万国博覧会開催 (--56) |
| 1870 | 普仏戦争勃発,第二帝政崩壊 |
| 1871 | パリ・コミューン |
| 1881--82 | ジュール・フェリー法制定.初等教育の無償・義務化 |
| 1884 | ヴァルデック・ルソー法制定.労働組合を合法化 |
| 1889 | ブーランジェ事件 |
| 1898 | ゾラ,「私は弾劾する」 |
| 1901 | 結社法制定 |
| 1905 | 政教分離法,反教権主義が確立 |
| 1914 | 第一次世界大戦勃発 |
| 1918 | コンピエーニュの森で連合軍とドイツとの休戦協定 |
| 1919 | ヴェルサイユ条約調印 |
| 1924 | フランス,ソ連を承認 |
| 1928 | ケロッグ・ブリアン条約(パリ不戦条約)締結 |
| 1933 | スタヴィンスキー事件(金融スキャンダル).右翼の攻撃強まる |
| 1936 | ブルム人民戦線内閣成立 |
| 1939 | 第二次世界大戦勃発 |
| 1940 | パリ陥落 (6.14),ヴィシー政権成立 (7.10),ユダヤ人排斥法 (10.3) |
| 1943 | ジャン・ムーラン,レジスタンス全国評議会 (CNR) 結成.国内のレジスタンスの統一 |
| 1944 | パリ解放 (8.25).ドゴール臨時政府成立 (9.9) |
| 1945 | 婦人参政権採択 |
| 1947 | マーシャル・プランに参加 |
| 1954 | ディエン・ビエン・フー陥落 (5.7) .ヴェトナムより撤退.アルジェリア戦争始まる (11.1) |
| 1957 | ヨーロッパ経済共同体 (EEC) 条約調印 |
| 1958 | アルジェリアでコロンと軍の反乱 (5.13),ドゴール内閣成立 (6.1),第五共和制開始.ドゴール,大統領に当選 (12.21) |
| 1962 | エヴィアン協定.アルジェリア戦争終結 |
| 1966 | フランス,NATO の軍事機構から脱退 |
| 1967 | ヨーロッパ共同体 (EC) 成立 |
| 1968 | 5月革命 |
| 1969 | ドゴール,大統領を辞任 (4.28) .ポンピドゥーが大統領に |
| 1974 | ジスカールデスタン,大統領に当選 |
| 1981 | ミッテラン,大統領に当選 |
| 1986 | シラク,首相に就任.保革共存政権(コアビタシオン)成立 |
| 1992 | ヨーロッパ連合条約(マーストリヒト条約)に調印 |
| 1993 | EU 成立 |
| 1995 | シラク,大統領に当選 |
| 1999 | EU 単一通貨「ユーロ」導入 |
| 2003 | イラク戦争に反対,派兵せず |
| 2005 | 国民投票で EU 憲法拒否,パリ郊外暴動事件 |
| 2007 | サルコジ,大統領に当選 |
| 2012 | オランド,大統領に当選 |
・ 佐々木 真 『図説フランスの歴史』増補新版 河出書房新社,2016年.
[ 固定リンク | 印刷用ページ ]
2019-09-08 Sun
■ #3786. ローマン・ブリテンの略年表と地図 [roman_britain][timeline][history][map]
「#3784. ローマン・ブリテンの言語状況 (1)」 ([2019-09-06-1]) と「#3785. ローマン・ブリテンの言語状況 (2)」 ([2019-09-07-1]) で,ローマン・ブリテンの話題を取り上げた.君塚や指のイギリス史概説書を参照して,この時代を中心とする略年表を作成してみた(イギリス史全体の年表については,「#3478. 『図説イギリスの歴史』の年表」 ([2018-11-04-1]),「#3487. 『物語 イギリスの歴史(上下巻)』の年表」 ([2018-11-13-1]),「#3497. 『イギリス史10講』の年表」 ([2018-11-23-1]) などを参照).
| 81万年前頃 | ブリテン付近に人類が居住 |
| 紀元前1万年頃 | 狩猟採集民が居住(旧石器時代末期) |
| 前7--6千年頃 | ブリテン島が大陸から分離 |
| 前4千年頃 | 農耕・牧畜の開始(新石器時代の開始) |
| 前22--20世紀頃 | ビーカー人が渡来(青銅器時代の開始) |
| 前18世紀頃 | ストーンヘンジの建造 |
| 前6世紀頃 | ケルト系のベルガエ人の渡来 |
| 前2世紀末 | ベルガエ人が高度な鉄器文化と農牧文化を築く |
| 前55--54年 | ユリウス・カエサルのブリタニア遠征 |
| 43年 | ローマ皇帝クラウディウスのブリタニア侵攻 |
| 50年頃 | ロンディニウム(ロンドン)の建設 |
| 61年 | イケニ族の女王ボウディッカの反乱 |
| 80年頃 | ローマ軍,スコットランドに到着 |
| 122--132年 | ハドリアヌスの長城の建造 |
| 140年頃 | アントニヌスの長城の建造(しかし,60年後に放棄) |
| 2世紀末 | ロンドンが中心都市として発達し,街道も整備される |
| 211年 | ブリテン,ローマと協約締結し「同盟者」に |
| 306年 | ブリタニアで即位したコンスタンティヌス,帝国の再編へ |
| 4世紀半ば | キリスト教の伝来,ヨークとロンドンに司教座 |
| 406年 | 大陸のゲルマン諸部族,ライン川を超えてガリアへ侵入 |
| 410年 | ローマ,ブリタニアから撤退 |
| 449年 | アングロ・サクソンの渡来が始まる |
| 6世紀末 | 7王国の成立 |
| 597年 | 聖アウグスティヌス,キリスト教宣教のために教皇グレゴリウス1世によってローマからケント王国へ派遣される |
| 664年 | ウィットビーの宗教会議でローマキリスト教の優位が認められる |
ローマン・ブリテンの関連地図も,君塚 (9) の「「ローマ帝国支配のブリテン島」と,Encyclopaedia Britannica からのもの (Encyclopaedia Britannica 2008 Ultimate Reference Suite. Chicago: Encyclopaedia Britannica, 2008.) を挙げておこう.
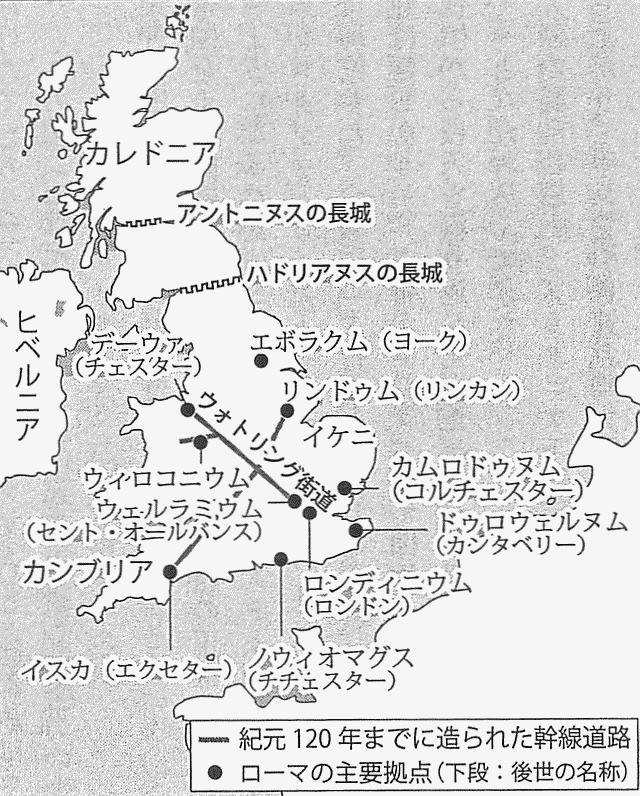
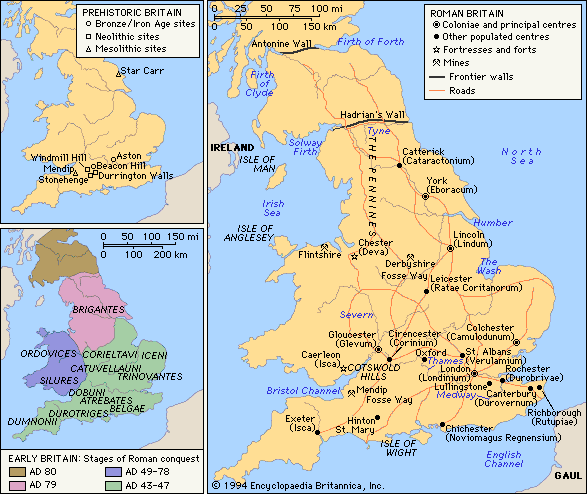
ついでに Encyclopaedia Britannica から見つけた,ローマ軍に抵抗したイケニ族の女王ボアディッカを描いた19世紀の版画も挙げておく (Queen Boudicca leading a revolt against the Romans, engraving, 19th century. The Granger Collection, New York) .

ローマン・ブリテン時代のその他の話題については「#3440. ローマ軍の残した -chester, -caster, -cester の地名とその分布」 ([2018-09-27-1]) ほか roman_britain の各記事を参照.
・ 君塚 直隆 『物語 イギリスの歴史(上下巻)』 中央公論新社〈中公新書〉,2015年.
・ 指 昭博 『図説イギリスの歴史』 河出書房新社,2002年.
[ 固定リンク | 印刷用ページ ]
2019-07-26 Fri
■ #3742. ウェールズ歴史年表 [wales][welsh][timeline][history]
「#1715. Ireland における英語の歴史」 ([2014-01-06-1]),「#2361. アイルランド歴史年表」 ([2015-10-14-1]) の記事で,アイルランドと英語の歴史を概説した.そのウェールズ版について,これまでの記事で「#1718. Wales における英語の歴史」 ([2014-01-09-1]) などは書いてきたが,「ウェールズ歴史年表」はまだ掲げていなかったので,ここに略年表を示そう.以下は,桜井(著)『物語 ウェールズ抗戦史』の巻末の年表 (249--51) より.ウェールズがイングランドに併合される1536年より前までの歴史で,かつ時期によって扱いの濃淡もあるが,簡便で有用な略年表である.
| 60?61年頃 | イケニ族の女王ボウディッカの反乱 |
| 410年 | ローマのブリテン島撤退 |
| 5世紀半ば | アングロサクソン人のブリテン島侵入始まる |
| 476年 | ローマ帝国(西ローマ帝国)滅亡 |
| 5世紀終わり?6世紀初め | アンブロシウス・アウレリアヌス率いるブリトン人がベイドンの丘でアングロサクソン人に完勝 |
| 634年 | グウィネズ王カドワロン,ノーサンブリア王国を征服 |
| 900?950年 | ハウエル善良王の治世 |
| 1057年頃 | グリフィズ・アプ・サウェリンの全ウェールズ統一 |
| 1066年 | ノルマンの征服 |
| ノルマン人のウェールズ侵攻開始 | |
| 1093年 | ノルマン人によるデハイバース王フリース・アプ・テウドゥールの殺害 |
| 1107?1111年 | フランドル人のウェールズ南西部移住 |
| 1155年 | フリース・アプ・グリフィズ(ロード・フリース),デハイバース王に即位 |
| 1174年 | ジェラルド・オブ・ウェールズ,ブレコンの副司教に就任 |
| 1176年 | ジェラルドの第1回セント・デイヴィッズ司教選挙始まる |
| 1195年 | グウェンウィンウィン,ポウィス王に即位 |
| 1198?1203年 | ジェラルドの第2回セント・デイヴィッズ司教選挙 |
| 1199 | サウェリン・アプ・ヨーワース(大サウェリン),北ウェールズ大公を名乗る |
| 1218年 | 大サウェリン,イングランドとウースター条約を結ぶ |
| 1258年 | サウェリン・アプ・グリフィズ(最後のサウェリン),ウェールズ大公を名乗る |
| 1276?1277年 | 第1次ウェールズ征服戦争 |
| 1282?1283年 | 第2次ウェールズ征服戦争.ウェールズの政治的独立終わる |
| 1400年 | オワイン・グリンドール蜂起.ウェールズ大公を名乗る |
| 1404年 | オワイン,全ウェールズ規模の議会を招集 |
| 1405年 | オワイン,フランスと同盟 |
| 1409年 | ハルレッヒ城,陥落.オワインの乱の事実上の終了 |
| 1412年 | オワイン最後の目撃譚 |
| 1457年 | ヘンリー・テューダー,南西ウェールズのペンブローク城に生まれる |
| 1461年 | ペンブローク城,陥落.4歳のヘンリー・テューダー,ヨーク派ウィリアム・ハーバートの保護下に |
| 1470年 | ウィリアム・ハーバート敗北.ヘンリー・テューダー,叔父のジャスパーと再会 |
| 1471年 | 14歳のヘンリー・テューダー,ブルターニュ公国に亡命 |
| 1485年8月 | 28歳のヘンリー・テューダー,フランスから船団を率いてウェールズに戻る.ボズワースの戦いでリチャード3世を斃す |
| 1485年10月 | ヘンリー・テューダー,ヘンリー7世としてイングランド国王に即位 |
関連して,「#1742. 言語政策としての罰札制度 (2)」 ([2014-02-02-1]),「#3292. 史上最初の英語植民地 Pembroke」 ([2018-05-02-1]),「#3303. イングランド宗教改革の荒波をくぐりぬけたウェールズ語」 ([2018-05-13-1]) の記事も参照.
・ 桜井 俊彰 『物語 ウェールズ抗戦史 --- ケルトの民とアーサー王伝説』 集英社〈集英社新書〉,2017年.
2019-06-09 Sun
■ #3695. 日本における英語関係史の略年表 [timeline][hel_education][english_in_japan]
小学館の『英語便利辞典』に,日本における英語受容史の主要な事項を年代順に列挙した略年表がある (460--61) .1600年から第2次世界大戦直後までの3世紀半に渡る日本と英語との接触の足跡を辿ろう.
| 年号 | 事項 | 解説 |
|---|---|---|
| 1600(慶長5)年 | ウィリアム・アダムズ(William Adams;三浦按針)豊後海岸に漂着. | ウィリアム・アダムズは日本に最初に来た英国人とされる.家康に重用された. |
| 1808(文化5)年 | フェートン号事件 (Phaeton Incident) . | イギリスの軍艦フェートン号が長崎港に乱入.この事件をきっかけに,蘭学から英学へ移行. |
| 1814(文化11)年 | 『暗厄利亜語林大成(あんげりあごりんたいせい)』出版. | 蘭英字書をもとに編まれた日本最初の英和辞書. |
| 1841(天保12)年 | 中浜万次郎(通称:ジョン万),米捕鯨船に保護される. | 中浜万次郎は出漁中に太平洋上の孤島で遭難.その後米捕鯨船に救助され,アメリカで教育を受け,1851年帰国. |
| 1855(安政2)年 | 洋学所設立,翌年蕃書調所となる. | 洋学所は幕府の設置する洋学研究所. |
| 1858(安政5)年 | 日米修好通商条約締結. | 日本が外国と結んだ最初の条約. |
| 1859(安政6)年 | ヘボン博士来日. | ヘボン (James Curtis Hepburn) 博士はヘボン式ローマ字で有名.辞書編纂,聖書の日本語訳その他日本文化に多大の寄与をした. |
| 1860(万延1)年 | 咸臨丸アメリカに向け出航. | 日本の軍艦咸臨丸は,日米修好通商条約批准のための遣米使節団を乗せたポウハタン号に随行したが,同船には福沢諭吉,勝海舟なども乗船していた. |
| 1862(文久2)年 | 『英和對譯袖珍(しゅうちん)辞書』出版. | 堀達乃助他編.日本最初の本格的英和辞書. |
| 1866(慶応2)年 | 『西洋事情』ベストセラーとなる. | 福沢諭吉が著し,明治開化期の文明に大きな影響を与えた. |
| 1867(慶応3)年 | 『和英語林集成』出版. | ヘボンによる最初の和英辞典.その後改訂増補された. |
| 1871(明治4)年 | 津田梅子渡米. | 津田梅子は日本初の女子留学生.1900年女子英学塾(現在の津田塾大の前身)を創設. |
| 1876(明治9)年 | クラーク博士,札幌農学校に赴任. | クラーク (William Smith Clark) 博士は札幌農学校(現北海道大学)初代教頭を務める.諸説あるが,Boys, be ambitious! で有名.同校は新渡戸稲造(にとべいなぞう),内村鑑三など優秀な人材を輩出する. |
| 1890(明治23)年 | ラフカディオ・ハーン来日. | ラフカディオ・ハーン (Patrick Lafcadio Hearn;日本名:小泉八雲)は作家,英文学者.松江中学,東京帝国大学などで教鞭をとる.主著『怪談』『心』など. |
| 1914(大正4)年 | 『熟語本意英和中辞典』出版. | 斎藤秀三郎著.独創的な内容は,その後の英和辞書に大きな影響を与える. |
| 1918(大正7)年 | 『武信和英大辞典』出版. | 日本初の本格的和英辞典で,現行の研究社『新和英大辞典』の前身.武信(たけのぶ)由太郎編. |
| 1922(大正11)年 | パーマー (Harold E. Palmer) 来日. | オーラル・メソッド(Oral Method;口頭教授法)を唱え,以後の英語教育に大きな影響を与えた. |
| 1927(昭和2)年 | 研究社『新英和大辞典』出版. | 日本初の本格的英和大辞典.現在は第6版が出されているが,初版の著者は岡倉由三郎. |
| 1945(昭和20)年 | 『日米会話手帳』ベストセラーとなる. | 戦後2か月を経ない出版で,360万部の爆発的売れ行きを示した. |
| 1946(昭和21)年 | 平川唯一,英語会話放送開始. | 平川唯一はNHK放送のいわゆる「カムカム英語」の担当者.第二次世界大戦後の英語ブームの元祖となる. |
・ 小学館外国語辞典編集部(編) 『英語便利辞典』 小学館,2006年.
2019-03-30 Sat
■ #3624. 安藤貞雄『英語史入門』の英語史年表 [timeline][history]
本ブログでいくつか掲載してきた英語史年表のコレクションに,もう1つを加えよう.安藤貞雄『英語史入門』の第1章に「英語の外面史」と題する年表 (4--17) である.古代・中世についてかなり詳しいのが特徴(特長).
| OE 外面史 (449--1100) | |
| 【先史時代】 | |
| 2500--2000BC | スペイン・フランスにも住んでいた,短身,黒髪の新石器人種である Iberia 種族,menhir (立石),dolmen (環状列石)などの巨石遺跡を残す. |
| 【ケルト族の移住】 | |
| c2000BC | ケルト族 (Celts),大陸の Armorica (=Brittany) から Britannica (=Britain) に渡る.やがて,ピクト族 (Picts),Scythia (おそらく Scandinavia)から Caledonia (=Scotland) に移住.のちに,スコット族 (Scots),Hibernia (=Ireland) から Scotland の西半分に移住する. |
| 【ローマ人による征服 (Roman Conquest)】 | |
| 55--54BC | Caesar, 2度にわたりブリテン島を侵攻. |
| AD47 | ローマ皇帝 Claudius, ブリテン島を征服,以後約350年間,ローマ帝国の支配下に置く. |
| 122--26 | Hadrianus 皇帝,スコットランド連合軍の侵略を防ぐ目的で,イングランド北部に125キロの城壁 (Hadrian's Wall) を築く. |
| 395 | ローマ帝国,東西に分裂. |
| 410 | 最後のローマ軍団,Vandal 族からローマを守ためにブリテン島から撤退. |
| 【ヴァイキングの侵入】 | |
| 449 | ブリテン王,北方の Pict 族の撃退を大陸のジュート族 (Jutes) に依頼,Pict 族,至るところで打ち破られる. |
| 455 | Jute 族,Kent に移住. |
| 477 | Saxon 族,Sussex に移住. |
| 496 | 別の Saxon 族,Wessex に定住. |
| 547 | Angle 族,Humber 川の北に Northumbria 王国を建国.6世紀末までに Anglo-Saxon Heptarchy (7王国)の時代となる. |
| 【キリスト教化】 | |
| 563 | St. Columba,アイルランドから12人の修道士を伴い,Iona [aióunə] 島に渡り,修道院を建立(アイルランド系キリスト教). |
| 597 | St. Augustine, キリスト教宣教のために教皇 Gregory I によってローマから Kent 王国へ派遣される(ローマキリスト教). |
| 604 | Kent 王,ロンドンに St. Paul's 会堂を創建. |
| 617--85 | Northumbria,イングランドを制覇,政治・文化の中心となる. |
| 635 | アイルランド生まれの St. Aidan [éidn], Northumbria に渡り,Lindisfarne に修道院を創設,宣教に努める. |
| 657--80 | Whitby の女子修道院の牛飼いであった Cædmon, 霊感を得て天地想像の賛美歌 (Hymn) を歌う. |
| 664 | Northumbria の Whitby での宗教会議,ローマキリスト教の優位が認められる. |
| c725 | ゲルマン語最古の叙事詩 Beowulf の原本成る(ただし,British Library 所蔵の唯一の現存写本は1000年ごろのもの). |
| 731 | Jarrow の修道院の司祭 St. Bede, Historia Ecclesiastica Gentis Anglorum (英国民教会史)を完成(本文ラテン語,アングロサクソン族がキリスト教化された歴史を述べる). |
| 780--850 | 詩人 Cynewulf (Elene, The Fates of the Apostles, Christ II, Juliana) . |
| 【デーン人の征服】 | |
| 793--4 | Lindisfarne,および Jarrow の修道院,デーン人 (Danes) により掠奪される. |
| 829 | Wessex 王 Egbert, Mercia を征服,7王国を統一する. |
| 851 | デーン人,イングランドで初めて越冬,London, Canterbury を占領. |
| 866--71 | デーン人,East Anglia, Northumbria, Mercia を攻略,続いて Wessex に侵入. |
| 871--99 | Alfred 大王の治世,教会の復興,僧院の建設,学問の復興に努める.教皇 Gregory, Orosius, Boethius の著作を翻訳し,Bede の教会史の OE 訳を提唱,Anglo-Saxon Chronicle の編集を指導する. |
| 878 | Wedmore 協定,Alfred 王,苦戦の末,侵入者デーン人を破り,London と Chester を結ぶ線の北側をデーンロー (Danelaw) (デーン人の法律が及び,かつ居住を許される地域)とした). |
| c890 | Englisch (= English) という語,Bede の OE 訳に初出. |
| 901--50 | ノルウェー人,アイルランドを経てデーンロー地区へ移住. |
| 937 | Brunanburh の戦い,Wessex 王 Athelstan,デーン人を破り,英国の統一を確立. |
| 978 | Ethelred,英国王となる,デーン人の攻略を防げず,"the Unready" (無策王)とあだ名される. |
| c990--98 | Ælfric, 司教のための説教集 Homilies や聖徒伝を書いて散文の発達の貢献,OE で初学者用ラテン文法書も書いた. |
| 991 | Olaf (のち Norway 王),英国に侵攻 (The Battle of Maldon (現存するのは325行)はこのさまを歌ったもの). |
| c1000 | Beowulf 写本(当時の文学語 West-Saxon 方言に基づいて筆者),West-Saxon Gospels (West-Saxon 方言による最初の本格的英訳聖書で,6種の写本が残っている). |
| 1013 | デンマーク王 Svein,英国王 Ethelred を国外に追放,王位を奪う. |
| 1016 | Svein の息子 Canute,英国王位 (--35) につく(デンマーク王 (1019--35),ノルウェー王 (1028--35) を兼ねる). |
| 1042 | Ethelred 無策王の息子 Edward,英国王 (--66) となり,デーン人より王位を回復する."the Confessor" (篤信王)と呼ばれ,聖徒に列せられる. |
| 【ノルマン人の征服】 | |
| 1066 | Wessex 伯 Harold, Edward を継いで王位につく.Normandy 公 William, Hastings の戦いで Harold を破り,英国王 William I となる (--87) .支配階級はノルマンフランス語を日常語とし,多数のフランス語,英語に流入する. |
| 1079 | 教皇 Gregory VII, Vulgata 聖書(ラテン語訳)意外の使用を禁止(他の言語への翻訳は異端とみなされた). |
| 1086 | William I の勅命により,課税のための土地台帳 Domesday Book が完成. |
| 1087 | William II 即位 (--1100) . |
| 1096 | 聖地奪還のため第1回十字軍 (--99) .以後約2世紀にわたって第8回(1270年)まで続き,イスラム世界と接触する. |
| ME 外面史 | |
| 1100 | Henry I 即位 (--35) . |
| 1106 | Henry I, 長兄の領土 Normandy をも英国王の所属とする. |
| 1135 | Blois 伯 Stephen,英国王となる (--54) . |
| 1154 | Anjou 伯 Henry,英国王 Henry II となり (--89) ,Plantagenet 王朝始まる (--1399) .この年まで Peterborough の修道院で Anglo-Saxon Chronicle (Laud Manuscript) が書きつがれ,1080年以降の部分の英語は明らかに ME の特徴を示している.(もう一つ重要な写本 Parker Manuscript は1070年で終わっている.) |
| 1162 | Thomas à Becket, Canterbury 大司教となる.教会の至上権を主張して Henry II と対立. |
| 1170 | Oxford 大学創立,Thomas à Becket,国王側に暗殺される. |
| c1175 | Poema Morale (400行からなる宗教詩,英語で初めての脚韻を用いた). |
| 1189 | Henry II の第3子 Richard (the Lion-Hearted 獅子心王),英国王となり (--99) ,第3回十字軍を率いる. |
| 1199 | Henry II の末子 John (Lackland 失地王),英国王となる (--1216) . |
| c1200 | Layamon: Brut, Ancrene Riwle 'Rule for Anchoress', Ormulum, The Owl and the Nightingale (いずれもフランス語ではなく,英語 (ie ME) で書かれている点が注目に値する). |
| 1204 | John 王,フランス王 Philip II と戦って,Normandy および大部分の大陸所領を奪われる. |
| 1215 | John 王,貴族たちの要求をいれ,Magna Carta に調印. |
| 1216 | John 王の息子 Henry III,9歳にして即位 (--72) . |
| a1225 | King Horn (英国最初の韻文ロマンス).約200のフランス借入語がある. |
| 【英語の復権】 | |
| c1250 | 英国王 Henry III とフランス王 Lous IX に対する英国貴族の二重忠誠終わる. |
| 1258 | Henry III, 悪政の抑止と政治の改革を求める「オックスフォード条項」 (Provisions of Oxford) を公布(英語とフランス語で書かれている) |
| 1264 | 「貴族の戦い」 (Baron's War) . Simon de Montfort の率いる貴族たち,Henry III を幽閉し,「オックスフォード条項」の遵守を要求する. |
| 1265 | 英国下院創設. |
| 1272 | Henry III の第1子 Edward I 即位 (--1307) .Wales を完全に征服 (-1307) . |
| 1300 | 英語再び上流階級の第1言語となる. |
| 1307 | Edward II 即位 (--27) . |
| 1314 | Edward II, Scotland 王と戦い,敗れる. |
| a1325 | Cursor Mundi 「世界を走る者」(北部方言を用い,天地創造から最後の審判までを扱う長編宗教史). |
| 1327 | Edward III 即位 (--77) |
| 1337 | 百年戦争 (Hundred Years' War) (--1453) (Edward III が母方の権利によってフランス王位を要求して侵略を開始したため,英仏間で断続的におこなわれた戦争)始まる. |
| 1348 | 黒死病 (Black Death) ,ヨーロッパ全土に広がり,多数の聖職者が死亡.その後継者養成のため,grammar school が英国各地に設けられる (--50) .労働階級の日常語である英語の重要性が増す.最高の勲位ガーター勲位 (the Order of the Garter) 制定. |
| 1350 | 英国議会,上下両院に分かれる. |
| 1356 | London, Middlesex 州法廷で英語の使用始まる. |
| 1362 | 議会開会演説,初めて英語で行なわれる.訴答法 (Statute of Pleading) により,法廷用語も英語となる. |
| c1362 | William Langland, Piers Plowman (寓意的な物語史). |
| 【宗教改革,聖書英訳】 | |
| 1374 | John Wyclif の宗教改革運動始まる. |
| 1377 | Richard II 即位 (--99) (Plantagenet 朝最後の王). |
| 1381 | Wat Tyler, John Ball らの農民一揆 (Peasants' Revolt) により,彼らの言語である英語の重要性がさらに増す. |
| 1383 | 最古の英語の遺言状書かれる. |
| c1384 | 最初の完訳英語聖書 Wycliffite Bible 完成(Wyclif の指導のもとに公認ラテン語訳聖書 Vulgate から重訳).Wyclif, そのために殉教する. |
| 1385 | 英語による教育,すべての grammar school で定着する. |
| c1387 | Geoffrey Chaucer, The Canterbury Tales (--1400) .Chaucer の全作品のロマンス語の借入語の比率は51.8%. |
| 1388 | Purvey, Wycliffite Bible を一層慣用的な英語にするべく改訂に着手. |
| c1390 | Sir Gawayne and the Grene Knight (西中部方言で書かれた,ME ロマンスの代表的傑作). |
| c1393 | John Gower, Confessio Amantis (恋する男の告解)(恋物語を集めたもの).Gower の全語彙のうち,ロマンス借用語は42.1%,本来語派54.9%,ON 借入語は1.9%である. |
| c1395 | Wycliffite Bible 後期訳成る. |
| 1399 | Lancaster 公,Richard II を破り,Henry IV となる(Lancaster 王朝始まる (--1361)). |
| 1400 | 遺言書,一般に英語で書かれ始める. |
| 1413 | Henry V 即位 (--22) . |
| 1415 | Henry V,アジャンクール (Agincourt) でフランスの大群を破り,英国人に自信を与える. |
| 1423 | 国会の議事録,英語で記される. |
| 1425 | ロンドン方言が標準的な書き言葉になり,公文書に用いられる. |
| 1431 | Jeanne d'Arc (1412--) 焚殺される. |
| 1438 | ドイツの Gutenberg,活字印刷を始める. |
| 1442 | Henry VI 即位 (--61), York 公 Edward に王位を奪われ,Scotland に亡命する. |
| 1450 | 諸都市の記録,英語で行なわれる. |
| 1455 | バラ戦争 (Wars of Roses) 勃発,王位継承をめぐって York 家と Lancaster 家の間で争われた内乱 (--85) . |
| 1461 | Edward IV 即位 (--70) .York 王朝始まる. |
| a1470 | Thomas Malory, Le Morte Darthur (散文による Arthur 王(ケルト人)伝説の集大成.近代初期散文の文体に決定的な影響を与える). |
| 1470 | Henry VI (Lancaster 家),王位回復 (--71) . |
| 1471 | Edward IV (York 家),再び王位回復 (--83) . |
| 1476 | William Caxton, Westminster で英国最初の印刷物出版を始め,標準英語を普及させる. |
| 1483 | Edward V (York 家),2ヶ月間英国を治めるが,野心家の叔父の Richard, Edward を暗殺し,Richard III (York 家)となる (--85) . |
| 1485 | Lancaster 家の血を引く Henry Tudor, Richard III と決戦してこれを殺し,Henry VII となる(Tudor 王朝始まる (--1603)). |
| 1489 | すべての法令,英語で記録される(1300年まではラテン語,それ以後はフランス語であった). |
| ModE 外面史 | |
| EModE 期 (1500--1700) | |
| 1500 | ルネッサンス (--1650) .学校教育が普及し,活字印刷の導入によって,古典作品の翻訳が盛んに行われ,正書法も徐々に確立していく.特にラテン語から約1万の語を借入するとともに,強い民族意識に支えられて,英語が学術語トしても使用されるようになった. |
| 1509 | Henry VIII 即位 (--47) . |
| 1522 | ドイツの Martin Luther,新約聖書のドイツ語訳を出版. |
| 1525 | William Tyndale [tìndl],ギリシア語原典より新約聖書を訳し,ドイツで出版.素朴にして雄渾な訳文は,のちの欽定訳英語聖書 (AV) などの手本となった. |
| 1534 | Henry VIII,ローマ教会と絶縁する.Martin Luther,旧新約聖書のドイツ語訳を完成. |
| 1535 | Henry VIII, Oxford 大学に古典文学講座を設ける.Coverdale's Bible (旧新約聖書を含むが,Luther 訳や Vulgata 聖書からの重訳であった). |
| 1536 | Henry VIII,小修道院を破戒,解散し,その土地と財産を没収する.Tyndale,絞首焚刑に処せられる. |
| 1537 | Matthew Bible (Tyndale 訳と Coverdale 訳をつなぎ合わせたもの). |
| 1539 | Henry VIII,大修道院を解体(多数の写本・文書が紛失する),The Great Bible (大きな folio 版のため,こう呼ばれた).Coverdale 主幹で完成(最初の英国国教会の公認訳). |
| 1541 | Henry VIII, King of Ireland の称号をアイルランド議会に承認させる. |
| 1543 | inkhorn terms (インク壺言葉)という用語の OED における初例.その難解さのゆえに嘲笑,非難された. |
| 1547 | Henry VIII の第1子 Edward VI, 10歳で即位 (--53) . |
| 1549 | Edward VI, The Book of Common Prayer を制定(その後,数回の改定を経て1662年版が決定版). |
| ?1552 | 詩人 Edmund Spenser 生まれる (--99) . |
| 1553 | Henry VIII と第1夫人の娘 Mary I (Bloody Mary) 即位 (--58) .母と同様カトリック教徒で,英国をカトリック教国に戻そうとして多くの新教徒を処刑する. |
| 1560 | The Geneva Bible (ジョネーヴに亡命中の Calvin 派の学者たちによる翻訳,正確な訳文は,のちの欽定訳英語聖書に大きな影響を与える). |
| 1561 | 親切の Merchant Taylors' School の校長 Richard Mulcaster,英語を古典語よりも優先する. |
| 1564 | 詩人・劇作家 William Shakespeare 生まれる (--1616) . |
| 1568 | The Bishops' Bible (Canterbury 大主教 Parker を主幹として,The Great Bible を改定したもの). |
| 1582 | The Rheims-Douai Bible (政府の弾圧を逃れて大陸に亡命中のカトリック教徒が Vulgata 聖書から新訳を重訳したもの).旧約は1609--10年に出版. |
| 1586 | Bullokar, Bref Grammar for English (最初の英文法書). |
| 1588 | Drake, Hawkins ら,スペインの無敵艦隊 (Invincible Armada) を撃退,英国の海外進出の道を開く. |
| 1590--1620 | 英国劇全盛時代. |
| 1603 | スコットランドの James VI,英国王 James I となり,Stuart 王朝始まる (--1714) .王権神授 (Divine Right) を信じ,カトリック教徒と清教徒を圧迫する. |
| 1605 | James I に失望したカトリック教徒による,告解を撃破しようとした陰謀事件 (Gunpowder Plot) ,カトリック教徒 Guy Fawkes が首謀. |
| 1611 | 『欽定訳英語聖書』 (The Authorized Version of the Bible, AV) .本来語が多用され,延語数で約90%,近代英語の文体に大きな影響を与え,引用句辞典でも Shakespeare を抜いて最大の源泉. |
| 1620 | 102名の清教徒 Pilgrim Fathers,自由の天地を求めて北栄の Cape Cod に上陸.New England の建設に乗り出す. |
| 1623 | Condell and Heminge, Shakespeare の First Folio を出版. |
| 1625 | James I の子 Charles I 即位 (--49) .フランス王女と結婚,宮廷にカトリック的・専制的傾向が浸透. |
| 1631 | 詩人・劇作家・批評家 John Dryden (--1700) 生まれる. |
| 1636 | Harvard 大学創立. |
| 1638 | Sir Henry Spelman, Cambridge 大学で Anglo-Saxon 語講座を担当(まもなく廃絶). |
| 1640 | Ben Jonson,外国人のために The English Grammar を著す. |
| 1642 | 内乱 (Civil War) が起こる (--51) .Charles I,清教徒を弾圧,専制的で議会を無視したため,全国が王党 (Cavaliers) と議会党 (Roundheads) に分かれて戦った.倫敦の劇場閉鎖. |
| 【共和制始まる】 | |
| 1649 | Charles I 処刑され,共和制 (Commonwealth) 始まる (--60) . |
| 1650 | 理性の時代 (Age of Reason) (--1714) .形式・バランス・抑制・調和・品位・秩序が重んじられる. |
| 1653 | Oliver Cromwell (1599--1658),護国卿 (Lord Protector) となる. |
| 【王政復古】 | |
| 1660 | フランスに亡命中の Charles II (「陽気な王様」 "Merry Monarch")即位,王政復古 (Restoration) 成る.劇場再開. |
| 1662 | 英国学士院 (Royal Society) 認可(会員に簡潔明晰な表現を要求したので,散文の発達にも貢献). |
| 1664 | 英国学士院,「英語改良委員会」を設置(John Dryden が最も積極的に働いた). |
| 1667 | John Milton, Paradise Lost 『楽園喪失』,荘重体を用いて人間の原罪と神の摂理を説く. |
| 1678 | John Bunyan, The Pilgrim's Progress 『天路歴程』(寓意物語),広く読まれて小説勃興の気運を促す. |
| 1685 | York 公,James II として即位 (--88) .カトリック教徒で専制的であったため,人心離反し革命を招く. |
| 1688 | 名誉革命 (Glorious Revolution) .James II は,アイルランドへ逃亡し,王女 Mary と夫 William of Orange (オランダ人)が,Mary II (--1694), William III (--1702) として,共同で王位を継ぐ. |
| LModE 期 (1700--1900) | |
| 【ジャーナリズムの勃興】 | |
| 1702 | Mary II の妹 Anne 即位 (--14) .“文芸全盛期” (Augustan Age) 始まる (--26) ,Samuel Beckley, 英国最初の日刊新聞 The Daily Courant を創刊 (--35) . |
| 1704 | Daniel Defoe, A Weekly Review of the Affairs of France and of All Europe を創刊 (--12) . |
| 1707 | Scotland の議会,England の議会と合流,連合王国 (The United Kingdom of Great Britain) が成立する. |
| 1708 | ロンドンで coffee-house が全盛期で,その数3000.文学・政治・時事問題などが論じられる. |
| 1709 | Sir Richard Steele, 週3回発行の刊行物 The Tatler を発行 (--11) . |
| 1711 | 日刊紙 The Spectator 創刊 (--14) .二人の編者 Addison と Steele の英語は,整然として平明であり,その後の英語の文体に大きく影響した. |
| 1712 | Swift, "A Proposal for Correcting, Improving and Ascertaining the English Tongue" (アカデミーの提唱). |
| 1714 | Anne 女王没.Tory 党権力を失い,Whig 党の推す James I の曾孫 Hanover 選挙公 George Louis が,George I として王位につく(今日まで続く Honaver 王朝の始まり).彼はドイツ人で全く英語が話せず,宮廷ではフランス語を使用した.閣議も欠席しがちで,ために内閣の独立性が強まった. |
| 1721 | Bailey, An Universal Etymological English Dictionary. 難語だけでなく,基本語も収録し,本格的に語源も示した最初の英語辞書.Johnson の事典の基礎となる.増補を続け,1802年まで30版を重ねた. |
| 1727 | George II 即位 (--60) . |
| 1731 | 公用語としてのラテン語を全廃する. |
| 1753 | 大英博物館 (British Museum) 創立. |
| 1755 | Samuel Johnson, A Dictionary of the English Language. 出典を明示,慣用として行なわれる綴り字を提示し,その固定化に寄与した.この辞典は,英国ではできなかったアカデミーの代わりとしたと言える. |
| 1760 | George III 即位 (--1820) . |
| 1762 | Robert Lowth [lauθ], A Short Introduction to English Grammar. 典型的な規範文法で,広く読まれ,米国でも好評を博した. |
| 1768 | Encyclopaedia Britannica (初版3巻)発刊(第4版 (1801--10) は全20巻). |
| 1776 | アメリカ合衆国,独立を宣言(7月4日). |
| 1783 | James Watt, 蒸気機関を発明.続いて産業革命起こる. |
| 1795 | Lindley Murray, English Grammar. will と shall の使い分け,二重否定,It's me の禁止など,18世紀中葉以来の規範文法の集大成で,19世紀末まで学校文法を風靡した. |
| 1805 | Nelson 提督,Trafalgar 沖海戦でフランス艦隊を破り,制海権を握る.英国は世界貿易の大部分を制し,英語の威信も高まる. |
| 1806 | Noah Webster, A Compendious Dictionary of the English Language. のちにアメリカの綴り字として定着する新綴り字法を使用.この辞書の百科辞書的編纂法はアメリカの辞書の伝統となる.最新番は Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language (1961) で,残念ながら百科辞典的傾向が失われてしまった. |
| 1820 | George IV 即位 (--30) . |
| 1832 | First Reform Bill (商工業者に選挙権). |
| 1837 | Victoria 女王即位 (--1901) . |
| 1861 | アメリカの南北戦争 (Civil Law) (--65) . |
| 1867 | Second Reform Bill (納税している中流下層部に選挙権). |
| 1881 | Revised Version (RV) の新約出版.旧約は1885年. |
| 1884 | The New English Dictionary (NED) Part I (A--Ant) 刊行される(1928年に完成,全10巻).のちに13巻に分けて The Oxford English Dictionary (OED) と改称,Supplement (1933) . |
| 1884 | Third Reform Bill (小作人に選挙権). |
| PE 期 (1900--) | |
| 1901 | Edward VII 即位 (--10) .The American Standard Version of the Bible (ASV) ,米国で出版. |
| 1910 | George V 即位 (--36) . |
| 1914 | 第一次世界大戦 (--18) . |
| 1928 | Last Reform Bill (女性に選挙権). |
| 1936 | Edward VIII 即位 (--36) .George VI 即位 (--52) . |
| 1939 | 第二次世界大戦 (--45) . |
| 1946 | ASV の改訂版 Revised Standard Version の新約,米国で出版.旧約は1952年. |
| 1952 | Elizabeth II 即位. |
| 1961 | The New English Bible (NEB) 新約出版.旧約は1970年.その英語について,各方面からきびしい批判にさらされる. |
| 1966 | The Jerusalem Bible (各書の解説と注に特色). |
| 1988 | OED 第2版(20巻)刊行. |
| 1989 | The Revised English Bible (NEB の全面改定訳).その改訂版 The New Revised English Bible (1990) では,thou, thee などが除去され,性差別表現が回避されている. |
・ 安藤 貞雄 『英語史入門 現代英文法のルーツを探る』 開拓社,2002年.
2019-03-07 Thu
■ #3601. McArthur の英語史年表 [timeline][history][world_englishes]
McArthur の英語学事典のなかに,"A chronology of English" (475--81) と題して英語史年表が掲げられている.かなり長く詳しい年表である.「#2562. Mugglestone (編)の英語史年表」 ([2016-05-02-1]) で挙げた年表も長いが,それも今回の McArthur のものに多く依拠しているようだ.とりわけ,近現代にかけての英語の世界的な拡大に注目する年表となっている.参照用にどうぞ.
| 55 BC | Roman military expedition to Britain by Julius Caesar. |
|---|---|
| AD 43 | Roman invasion of Britain under the Emperor Claudius, beginning 400 years of control over much of the island. |
| 150 | From around this date, with Roman permission, small numbers of settlers arrive from the coastlands of Germany, speaking dialects ancestral to English. |
| 297 | First mention of the Picts of Caledonia, tribes beyond Roman control, well to the north of Hadrian's Wall. |
| 419 | Goths sack Rome. |
| 436 | The end of a period of gradual Roman withdrawal. Britons south of the Wall are attacked by the Picts and by Scots from Ireland. Angles, Saxons, and other Germanic settlers come first as mercenaries to help the Britons, then take over more and more territory. |
| 449 | the traditional date for the beginning of the Anglo-Saxon settlements. |
| 450--80 | The first surviving Old English inscriptions, in runic letters. |
| 495 | The Saxon kingdom of Wessex established. |
| 500 | The kingdom of Dalriada established in Argyll by Scots from Ireland. |
| 527 | The Saxon kingdoms of Essex and Middlesex established. |
| 550 | The Angle kingdoms of Mercia, East Anglia, and Northumbria established. |
| 557 | At the Battle of Deorham, the West Saxons drive a wedge between the Britons of Wales and Cornwall. |
| 597 | Aethelberht, king of Kent, welcomes Augustine and the conversion of the Anglo-Saxons to Christianity begins. |
| 613 | At the Battle of Chester, the angles of Northumbria drive a wedge between the Britons of Wales and Cumbria. |
| 638 | Edwin of Northumbria takes Lothian from the Britons. |
| 700 | The first manuscript records of Old English from about this time. |
| 792 | Scandinavians begin to raid and settle in Britain, Ireland, and France. In 793, they sack the monastery of Lindisfarne, the centre of Northumbrian scholarship. |
| 795 | The Danes settle in parts of Ireland. |
| 815 | Egbert of Wessex defeats the south-western Britons of Cornwall and incorporates Cornwall into his kingdom. |
| 828 | Egbert of Wessex is hailed as bretwalda (lord of Britain), overlord of the Seven Kingdoms of the Angles and Saxons (the Heptarchy). England begins to emerge. |
| 834 | The Danes raid England. |
| 843 | Kenneth MacAlpin, King of Scots, gains the throne of Pictland. |
| 865 | The Danes occupy Northumbria and establish a kingdom at York. Danish begins to influence English. |
| 871 | Alfred becomes king of Wessex, translates works of Latin into English, and establishes the writing of prose in English. |
| 886 | The boundaries of the Danelaw are settled. |
| 911 | Charles II of France grants lands on the lower Seine to the Viking chief Hrolf the Ganger (Rollo the Rover). The beginnings of Normandy and Norman French. |
| 954 | The expulsion of Eric Blood-Axe, last Danish king of York. |
| 965 | The English invade the northern Welsh kingdom of Gwynedd. |
| 973 | Edgar of England cedes Lothian to Kenneth II, King of Scots. Scotland multilingual: Gaelic dominant, Norse in the north, Cumbric in the South-west, English in the south-east, Latin for church and law. |
| 992 | A treaty between Ethelred of England and the Normans. |
| 1000 | The approximate date of the only surviving manuscript of the Old English epic poem Beowulf. |
| 1007 | Ethelred the Unready pays danegeld to stop the Danes attacking England. In 1013, however, they take the country and Ethelred flees to Normandy. |
| 1014 | The end of Danish rule in Ireland. |
| 1016--42 | The reigns of Canute/Knut and his sons over Denmark, Norway, and England. |
| 1051 | Edward the Confessor, King of England, impressed by the Normans and with French-speaking counsellors at his court, names as his heir William, Duke of Normandy, but reneges on his promise before his death. |
| 1066 | The Norman Conquest. William defeats King Harold at Hastings, and sets in train the Normanization of the upper classes of the Britain Isles. England multilingual: English the majority language, Danish in the north, Cornish in the far south-west, Welsh on the border with Wales, Norman French at court and in the courts, and Latin in church and school. |
| 1150 | The first surviving texts of Middle English. |
| 1167 | The closure of the University of Paris to students from England accelerates the development of a university at Oxford. |
| 1171 | Henry II invades Ireland and declares himself its overlord, introducing Norman French and English into the island. |
| 1204 | King John loses the Duchy of Normandy to France. |
| 1209 | The exodus of a number of students from Oxford leads to the Establishment of a second university in Cambridge. |
| 1272--1307 | The reign of Edward I, who consolidates royal authority in England, and extends it permanently to Wales and temporarily to Scotland. |
| 1282 | Death of Llewelyn, last native prince of Wales. In 1301, Edward of England's son and heir is invested as Prince of Wales. |
| 1284 | The Statute of Rhuddlan establishes the law of England in Wales (in French and Latin), but retains the legal use of Welsh. |
| 1314 | Robert Bruce reasserts Scottish independence by defeating Edward II at Bannockburn, an achievement later celebrated in an epic written in Scots. |
| 1337 | The outbreak of the Hundred Years War between England and France, which ends with the loss of all England's French possessions save the Channel Islands. |
| 1343?--1400 | The life of Geoffrey Chaucer. |
| 1348 | (1) English replaces Latin as medium of instruction in schools, but not at Oxford and Cambridge. (2) The worst year of the Black Death. |
| 1362 | (1) Through the Statute of Pleading, written in French, English replaces French as the language of law in England, but the records continue to be kept in Latin. (2) English is used for the first time in Parliament. |
| 1384 | The publication of John Wycliffe's English translation of the Latin Bible. |
| 1385 | The scholar John of Trevisa notes that 'in all the gramere scoles of Engelond, children leveth Frensche and construeth and lerneth in Englische'. |
| 1400 | By this date the Great Vowel Shift has begun. |
| 1450 | Printing by movable type invented in the Rhineland. |
| 1476 | (1) The first English book printed: The Recuyell of the Historyes of Troye. translated from French by William Caxton, who printed it at Bruges in Flanders. (2) Caxton sets up the first printing press in England, at Westminster. In 1478, he publishes Chaucer's Canterbury Tales. |
| 1485 | The Battle of Bosworth, after which the part-Welsh Henry Tudor becomes King of England. Welsh nobles follow him to London. |
| 1492 | Christopher Columbus discovers the new World. |
| 1497 | Giovanni Caboto (Anglicized as 'John Cabot'), in a ship from Bristol, lands on the Atlantic coast of North America. |
| 1499 | The publication of Thesaurus linguae romanae et britannicae (Treasury of the Roman and British Tongues), the first English-to-Latin wordbook, the work of Galfridus Grammaticus (Geoffrey the Grammarian). |
| 1504 | The settlement of St John's on Newfoundland as a shore base for English fisheries. |
| 1507 | The German geographer Martin Waldseemüller puts the name America on his map of the world. |
| 1525 | The publication of William Tyndale's translation of the New Testament of the Bible. |
| 1534 | Jacques Cartier lands on the Gaspé Peninsula in North America and claims it for France. |
| 1536 and 1542 | The Statue of Wales (Acts of Union) unites England and Wales, excluding Welsh from official use. |
| 1542 | Henry VIII of England proclaims himself King of Ireland. |
| 1549 | The publication of the first version of the Book of Common Prayer of the Church of England, the work in the main of Thomas Cranmer. |
| 1558--1603 | The reign of Elizabeth I. |
| 1450--1620 | The plantation of Ireland, first by English settlers and after 1603 also by Scots, establishing English throughout the island and Scots in Ulster. |
| 1564--1616 | The life of William Shakespeare. |
| 1583 | Sir Humphrey Gilbert establishes Newfoundland as England's first colony beyond the British Isles. |
| 1584 | The settlement of Roanoke Island by colonists led by Sir Walter Raleigh. In 1587, Virginia Dare born at Roanoke, first child of English parents in North America. In 1590, the settlers of Roanoke disappear without trace. |
| 1588 | The publication of Bishop Morgan's translation of the Bible into Welsh, sering as a focus for the survival of the language. |
| 1600 | English traders establish the East India Company. |
| 1603 | The Union of the Crowns under James VI of Scotland, I of England. |
| 1604 | The publication of Robert Cawdrey's Table Alphabeticall, the first dictionary of English. |
| 1606 | The Dutch explore northern New Holland (Terra Australis). |
| 1607 | The Jamestown colony in Virginia, the first permanent English settlement and the first representative assembly in the New World. |
| 1608 | Samuel Champlain founds the city of Quebec in New France. |
| 1611 | The publication of the Authorized or King James Version of the Bible, intended for use in the Protestant services of England, Scotland, and Ireland. A major influence on the written language and in adapting Scots towards English. |
| 1612 | (1) Bermuda colonized under the charter of the Virginia Company. (2) Traders of the East India Company establish themselves in Gujarat, India. |
| 1614 | King James writes in English to the Moghul Emperor Jehangir, in order to encourage trade with 'the Orientall Indies'. |
| 1619 | At the Jamestown colony in America, the first African slaves arrive on a Dutch ship. |
| 1620 | The Mayflower arrives in the New World and the Pilgrim Fathers set up Plimoth Plantation in Massachusetts. English is now in competition as a colonial language in the Americas with Dutch, French, Spanish, and Portuguese. |
| 1622 | Publication in London of the first English newspaper, Weekly News. |
| 1623 | Publication in London of the First Folio of Shakespeare's plays. |
| 1627 | An English colony established on Barbados in the Caribbean. |
| 1637 | (1) English traders arrive on the coast of China. (2) The Académie française founded. |
| 1640 | An English trading factory established at Madras. |
| 1647 | The Bahamas colonized by settlers from Bermuda. |
| 1652 | The first Dutch settlers arrive in southern Africa. |
| 1655 | England acquires Jamaica from Spain. |
| 1659 | The East India Company annexes St Helena in the south Atlantic. |
| 1660 | John Dryden expresses his admiration for the Académie française and its work in 'fixing' French and wishes for something similar to serve English. |
| 1662 | The Royal Society of London receives its charter from Charles II. In 1664, it appoints a committee to consider ways of improving English as a language of science. |
| 1670 | The Hudson's Bay Company founded for fur trading in northern America. |
| 1674 | Charles II receives Bombay from the Portuguese in the dowry of Catherine of Braganza and gives it to the East India Company. |
| 1687 | Isaac Newton writes Principia Mathematica in Latin: see 1704. |
| 1688 | The publication of Oronooko, or the History of the Royal Slave, by Aphra Behn: one of the first novels in English, by the first woman novelist in English, based on personal experience of a slave revolt in Surinam. |
| 1690 | A trading factory established at Calcutta in Bengal. |
| 1696 | British and French colonists in North America in open conflict. |
| 1697 | The Boston clergyman Cotton Mather applies the term American to English-speaking settlers in the New World. |
| 1702 | Publication in London of the first regular daily newspaper in English, The Daily Courant. |
| 1704 | Isaac Newton writes his second major work, Opticks, in English: see 1687. |
| 1707 | The Act of Union, uniting the Parliaments of England and Scotland, creating the United Kingdom of Great Britain, but keeping separate the state religions, educations systems, and laws of the two kingdoms. |
| 1712 | (1) Jonathan Swift in Dublin proposes an English Academy to 'fix' the language and compete adequately with French. (2) In India, the Moghul Empire begins to decline. |
| 1713 | (1) At the Treat of Utrecht, France surrenders Hudson's Bay, Acadia, and Newfoundland to the British. (2) Gibraltar is ceded to Britain by Spain. |
| 1726 | Ephraim Chambers publishes his Cyclopaedia, the first encyclopedia. |
| 1731 | The abolition of Law French in England. |
| 1746 | The Wales and Berwick Act, by which England is deemed to include Wales and the Scottish town of Berwick is incorporated into England. |
| 1755 | The publication of Samuel Johnson's Dictionary of the English Language. |
| 1757 | The East India Company becomes the power behind the government of Bengal. |
| 1759 | General James Wolfe takes Quebec for the British. |
| 1759--96 | The life of Robert Burns. |
| 1762 | The publication of Robert Lowth's Short Introduction to the English Grammar. |
| 1763 | The French cede New France to Britain, retaining only St Pierre and Miquelon (islands off Newfoundland). |
| 1768--71 | The partwork publication in Edinburgh of The Encyclopaedia Britannica. |
| 1770 | Captain James Cook takes possession of the Australian continent for Britain. |
| 1770--1850 | The life of William Wordsworth. |
| 1771--1832 | The life of Sir Walter Scott. |
| 1774 | (1) The Quebec Act creates the British province of Quebec, extending to the Ohio and Mississippi. (2) The Regulating Act places Bombay and Madras under the control of Bengal and the East India Company becomes a kind of state. |
| 1776 | The Declaration of Independence by thirteen British colonies in North America and the start of the American War of Independence (1776--83) which created the United States of America, the first nation outside the British Isles with English as its principal language. |
| 1778 | Captain James Cook visits and names the Sandwich Islands (Hawaii). |
| 1780--1800 | British Empire loyalists move from the US to Canada. |
| 1785 | In London, the newspaper The Daily Universal Register founded. Renamed The Times in 1788. |
| 1786 | (1) Lord Cornwallis is appointed first Governor-General of British India. (2) A British penal colony is established at Botany Bay in Australia. In 1788, the first convicts arrive there. |
| 1791 | (1) The British colonies of Upper Canada (Ontario) and Lower Canada (Quebec) are established. (2) In London, the newspaper The Observer is founded, the oldest national Sunday newspaper in Britain. |
| 1792 | The first Europeans settle in New Zealand. |
| 1794 | The publication of Lindley Murray's English Grammar. |
| 1802 | The establishment of the British colonies of Ceylon and Trinidad. |
| 1803 | (1) The Act of Union incorporating Ireland into Britain, as the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. (2) The Louisiana Purchase, by which the US buys from France its remaining North American territories, and doubles its size. |
| 1806 | The British take control of Cape Colony in southern Africa. |
| 1808 | The establishment of the British colony of Sierra Leone. |
| 1814 | (1) The British annex Cape Colony. (2) France cedes to Britain Malta, Mauritius, St Lucia, and Tobago. |
| 1816 | The establishment of the British colony of Bathurst (the Gambia). |
| 1819 | (1) The establishment of the British colony of Singapore. (2) The US purchases Florida from Spain. |
| 1820 | Christian missionaries from the US visit Hawaii. |
| 1821 | American settlers arrive in the Mexican territory of Texas. |
| 1828 | The publication of Noah Webster's American Dictionary of the English Language. |
| 1829 | Australia becomes a British dependency. |
| 1831 | The establishment of the colony of British Guiana. |
| 1833 | (1) The abolition of slavery in the British Empire. (2) St Helena becomes a British colony. |
| 1835 | Thomas Macaulay writes the Minute on Education whereby the British rulers of India endorse English as a language of education for Indians. |
| 1835--1910 | The life of Sam Clemens (Mark Twain). |
| 1836 | Texas declares its independence from Mexico. |
| 1839 | The first Boer Republic is established in Natal, South Africa, after the Great Trek from the Cape. |
| 1840 | (1) The Treaty of Waitangi, by which the Maori of New Zealand cede all rights and powers of government to Britain. (2) The transportation of convicts to Eastern Australia is ended. |
| 1841 | (1) Upper and Lower Canada are brought together as British North America. (2) New Zealand becomes a British colony. (3) In London, the founding of the weekly magazine Punch. |
| 1842 | (1) The opening of Chinese ports other than Canton to Western traders, after the defeat of China in the Opium War. Hong Kong is ceded by China to Britain as a Crown Colony. (2) The Philological Society is formed in London. |
| 1844 | The first telegraph message transmitted, between Washington and Baltimore. |
| 1845 | Texas becomes a state of the United States. |
| 1846 | The British annex Natal but recognize the Transvaal and the Orange Free State as autonomous Boer republics. |
| 1848 | In the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, Mexico cedes vast western territories to the US. |
| 1850 | (1) Britain takes control of the Bay Islands of Honduras, an English-speaking enclave in Central America. (2) Legislative councils are established in Australia by British Act of Parliament. |
| 1852 | The publication of Roget's Thesaurus. |
| 1853 | (1) Japan is forced by Commander Matthew Perry of the US Navy to open its harbours to Western trade. (2) The transportation of convicts to Tasmania is ended. |
| 1855 | The government of the colony of New South Wales is established. |
| 1856 | The governments of the colonies of Tasmania and Victoria are established. |
| 1857 | The Sepoy Rebellion (War of Independence, Indian Mutiny) in India leads to the transfer of British India from the East India Company to the Crown. |
| 1858 | (1) The Philological Society passes a resolution calling for a new dictionary of English on historical principles. (2) Britain cedes the Bay Islands to Honduras. |
| 1861 | The establishment of the British colony of Lagos (Nigeria). |
| 1862 | The establishment of the colony of British Honduras. |
| 1863 | The establishment of the Cambridge Overseas Examinations. |
| 1865 | The abolition of slavery in the US, at the end of the Civil War. At the outbreak of the war there were over 4m slaves. |
| 1867 | (1) The Dominion of Canada is created, consisting of Quebec, Ontario, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick. (2) Alaska is purchased from Russia by the US. |
| 1868 | (1) Transportation of convicts to Western Australia is ended. (2) In the US, Christopher Latham Sholes and colleagues patent the first successful typewriter. |
| 1869 | (1) Rupert's Land and the Northwest Territories are bought by Canada from the Hudson's Bay Company. (2) Basutoland becomes a British protectorate. |
| 1870 | Manitoba becomes a province of Canada. |
| 1771 | British Columbian becomes a province of Canada. |
| 1873 | (1) The formation of the English Dialect Society (dissolved in 1896). (2) Prince Edward Islands becomes a provicen of Canada. |
| 1874 | The establishment of the British colony of the Gold Coast in West Africa. |
| 1879 | James A. H. Murray begins editing the Philological Society's New English Dictionary on Historical Principles. |
| 1882--1941 | The Life of James Joyce. |
| 1884 | (1) The Berlin Conference, in which European powers begin 'the scramble for Africa'. (2) Britain declares a protectorate over South East New Guinea. (3) The French, Germans, and British attempt to annex what shortly becomes the German colony of Kamerun. (4) Publication of the irst fascile, A--Ant, of Murray's dictionary (the OED). |
| 1886 | The aanexation of Burma into British India and the abolition of the Burmese monarchy. |
| 1888--94 | The establishment of Britisih protectorates in Kenya, Uganda, and Zanzibar. |
| 1889 | The formation of the American Dialect Society. |
| 1895 | The establishment of the British East African Protectorate, open to white settlers. |
| 1898 | (1) The annexation of Hawaii by the US. In 1900, it becomes a US territory. (2) Spain cedes the Philippines and Puerto Rico to the US. (3) Yukon Territory comes under Canadian government control. |
| 1901 | (1) The establishment of the Commonwealth of Australia as a dominion of the British Empire. (2) The first wireless telegraphy messages sent across the Atlantic by Guglielmo Marconi (Cornwall to Newfoundland). (3) The first film-show, in an arcade opened in Los Angeles, California. |
| 1903 | (1) A message from US President Theodore Roosevelt circles the world in less than 10 minutes by Pacific Cable. |
| 1903--50 | The life of George Orwell. |
| 1905 | (1) Alberta and Saskatchewan become provinces of Canada. (2) The first cartoon strip, 'Little Nemo', appears in the New York Herald. |
| 1906 | (1) The formation of the English Association. (2) The first full-length motion picture, The Story of the Kelly Gang. (3) the publication of the Fowler brothers' The King's English. |
| 1907 | (1) The establishment of New Zealand as a dominion of the British Empire. (2) The first regular studio-based radio broadcasts by the De Forest Radio Telephone Company in the US. (3) The foundation of Hollywood as a film-making centre. |
| 1910 | (1) The establishment of the Union of South Africa as a dominion of the British Empire. (2) The first radio receivers made in kit form for sale in the US. |
| 1911 | The publication of the Fowler borthers' Concise Oxford Dictionary. |
| 1913 | (1) The formation of the Society for Pure English. (2) The first crossword puzzle published, in the New York World. |
| 1914 | (1) A third Home Rule Bill for Ireland passed by the British Parliament, but prevented from coming into operation by the outbreak of the First World War. (2) The German colony of Kamerun invaded by the French and British. |
| 1915 | The death of Sir James A. H. Murray, aged 78, having finished the section Trink-Turndown in the OED. |
| 1916 | (1) The Easter Rising in Dublin, an unsuccessful armed rebellion against the British, during which an Irish Rebulic is proclaimed. (2) The Technicolor process is first used in the film The Gulf Between, in the US. |
| 1917 | The publication of Daniel Jones's English Pronoucing Dictionary. |
| 1918 | (1) The formation of the English-Speaking Union. (2) The US War Industries Board declares moving pictures an essential industry. |
| 1919 | (1) The German colony of Tanganyika ceded to Britain. (2) The German colony of Kamerun divided between France (Cameroun) and Britain (Cameroon). (3) The publication of H. L. Mencken's The American Language. |
| 1920 | (1) The Partition of Ireland. (2) Kenya becomes a British colony. (3) The first public radio station set up by Marconi in the US. |
| 1921 | (1) A treaty between the United Kingdom and the Irish Free State, which accepts dominion status within the British Empire. (2) The first full-length 'talkie' Dream Street produced by United Artists, in the US. |
| 1922 | (1) The establishment of the British Broadcasting Company, renamed the British Boradcasting Corporation (BBC). (2) The founding in the US of the monthly magazine The Reader's Digest. |
| 1923 | The founding of Time magazine in the US. |
| 1925 | (1) The borders of the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland established. (2) Afrikaans gains official status in South Africa. (3) The founding of the weekly magazine The New Yorker. |
| 1926 | The publication of Henry W. Fowler's Dictionary of Modern English Usage. |
| 1927 | (1) Fox's Movietone News, the first sound newsfilm, released in the US. (2) The first film with dialogue, They're Coming to Get Me. released in the US. |
| 1928 | The publication of Murray's Dictionary as The Oxford English Dictionaryy, 70 years after Trench's proposal to the Philological Society. |
| 1930 | (1) C. K. Ogden lauches Basic English. (2) The first television programme with synchronized sight and sound broadcast by the BBC. |
| 1931 | (1) The British Commonwealth of Nations formed. (2) South Africa becomes a dominion of the British Empire. (3) The Cambridge Proficiency Examination held outside Britain for the first time. |
| 1933 | The publication of supplement to The Oxford English Dictionary. |
| 1934 | Tghe British Council created as an arm of British cultural diplomacy and a focus for teaching English as a foreign language. |
| 1935 | (1) The Philippines become a self-governing Commonwealth in association withthe US. (2) The Publication of the first ten Penguin Paperback titles. |
| 1936 | The Republic of Ireland severs all constitutional links with Great Britain. |
| 1937 | (1) Burma is seprated from British India and granted a constitution and limited self-rule. (2) In Wales, a new constitution for the National Eisteddfod makes Welsh its official language. |
| 1938 | Photocopying invented. |
| 1942 | The publication in Japan of the Idiomatic and Syntactic English Dictionary. prepared before the war by A. S. Hornby, E. V. Gatenby, and H. Wakefield. |
| 1945 | Japan is occupied bythe Americans on behalf of the Allies. |
| 1946 | (1) The Philippines gain their independence from the US. (2) The French colony of Cameroun and the British colony of Cameroon become United Nations trusteeships. |
| 1947 | (1) British India is partitioned and India and Pakistan become independent states. (2) New Zealand gains its independence from Britain. |
| 1948 | (1) Burma and Ceylon gain their independence from Britain. (2) The dictionary of Hornby et al. is brought out by Oxford University Press as A Learner's Dictionary of Current English. |
| 1949 | (1) Newfoundland becomes a province of Canada. (2) Two New Guinea territories are combined by the United Nations as a Australian mandate: the United Nations Trust Territory of Papua and New Guinea. |
| 1951 | The launch of the first two working business computers: the LED in the UK and the UNIVAC in the US. |
| 1952 | Puerto Rico becomes a Commonwealth in association with the US. |
| 1957 | (1) The Gold Coast becomes independent from Britain as the Republic of Ghana. (2) Robert W. Burchfield is appointed editor of a new Supplement to The Oxford English Dictionary. |
| 1957--63 | The British colonies of Malaya and Borneo become independent and unite as Malaysia. |
| 1959 | Alask and Hawaii become states of the US. |
| 1960 | Nigeria and French Cameroun become independent. |
| 1961 | (1) South Africa becomes a republic, leaves the Commonwealth, and adopts Afrikaans and English as its two official languages. (2) The British colony of Cameroon divides, part joining Nigeria, part joining the ex-French colony to become the Republic of Cameroon. (3) Sierra Leone and Cyprus gain their independence from Britain. (4) The publication of Webster's Third International Dictionary. |
| 1962 | Jamaica, Trinidad and Tobago, and Uganda gain their independence from Britain. |
| 1963 | (1) Kenya gains its independence from Britain. (2) The first protests in Wales by the Cymdeithas yr Iaith Gymraeg/Welsh Language Society, aimed at achieving fuller use of Welsh. |
| 1964 | (1) Malta, Nyasaland (as Malawai), Tanganyika and Zanzibar (as Tanzania), and Northern Rhodesia (as Zambia) gain their independence from Britain. (2) The publication in Paris of René Etiemble's Parlez-vous franglais? |
| 1965 | Gambia and Singapore gain their independence from Britain. |
| 1966 | Barbados, Basutoland (as Lesotho), Bechuanaland (as Botswana), and British Guiana (as Guyana) gain their independence from Britain. |
| 1967 | The Welsh Language Act gives Welsh equal validity with English in Wales, and Wales is no longer deemed to be a part of England. |
| 1968 | Mauritius, Swaziland, and Nauru gain their independence from Britain. |
| 1969 | Canada becomes officially bilingual, with a commitment to federal services in English and French. |
| 1971 | The invention of the microprocessor, a revolutionary development in computing. |
| 1972 | (1) East Pakistan secedes and becomes its Republic of Bangladesh. (2) Two feminist magazines launched: Ms in the US and Spare Rib in the UK. |
| 1973 | The Bahamas gain their independence. |
| 1974 | Cyngor yr Iaith Gymraeg/Council for the Welsh Language set up to advise the Secretary of State for Wales on matters concerning the language. |
| 1975 | (1) Papua New Guinea gains its independence from Australia. (2) The Bas-Lauriol law is passed in France, requiring the use of the French language alone in advertising and commerce. |
| 1977 | (1) The spacecraft Voyager travels into deep space, carrying a message in English to any extraterrestrials. (2) In Quebec, Loi 101/Bill 101 is passed, making French the sole official language of the province, limiting access to English-medium school, and banning public signs in languages other than French. |
| 1978 | The government of Northern Territory in Australia is established. |
| 1980 | The British government averts a fast to the death by Gwynfor Evans, leader of Plaid Cymru (Welsh National Party), by honouring election pledges to provide a fourth television channel using both Welsh and English. |
| 1981 | British Honduras gains its independence as Belize. |
| 1982 | The patriation of Canada's constitution. The Canada Act is the last act of the British Parliament concerning Canadian affairs. |
| 1983 | The publication of The New Testament in Scots, a translation by William L. Lorimer. |
| 1984 | The launch of the Apple Macintosh personal (desktop) computer. |
| 1985 | (1) The publication by Longman of A Comprehensive Grammar of the English Language. (2) The publication by Belknap Press of the first volume of the Dictionary of American Regional English. (3) The launch by Cambridge University Press of the quarterly magazine-cum-journal English Today: The International Review of the English Language. |
| 1986 | Showing by the BBC in the UK and public television in the US of The Story of English, a television series with both British and American backers, accompanied by a book, and followed by a radio version on BBC World Service. |
| 1989 | The publication of the 2nd edition of The Oxford English Dictionary, blending the first edition and its supplements. |
・ McArthur, Tom, ed. The Oxford Companion to the English Language. Oxford: OUP, 1992.
[ 固定リンク | 印刷用ページ ]
2019-01-18 Fri
■ #3553. 大母音推移の各音変化の年代 [gvs][phonology][sound_change][timeline][chronology][vowel]
昨日の記事「#3552. 大母音推移の5つの問題」 ([2019-01-17-1]) で取り上げたように,大母音推移 (gvs) には様々な問題が立ちはだかっている.昨日挙げた5点のすべてに通底する根本的な問いは,当時の書き言葉からしか得られない情報に基づき,いかに正しく音価を復元しうるのかという文献学的な問題である.綴字の分析や解釈の仕方に応じて,各長母音・2重母音の音価や変化のタイミングに関する結論が,研究者間で異なってしまうということになりかねない.これが大母音推移研究の最大の難問なのである.
しかし,膨大な研究の蓄積により,各音変化の年代についてある程度の事実が分かってきていることも確かである.綴字以外にも,詩の脚韻の慣習,脚韻語の辞書,正音学者による記述なども音価の特定に貢献してきたし,情報を総合すればある程度の実態が浮かび上がってくるものである.Krug (249) は,主要な先行研究をまとめる形で,大母音推移の各変化の生じた年代を示す図を作成した.以下に,"Dating the changes of Middle English long vowels" と題されたその図を再現しよう.
| Middle English | c.1500 | c.1600 | c.1700 | Modern English | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c.1300 | (RP) | ||||||||
| (I) | iː | > | ɪi | > | əɪ | > | aɪ | ≈ | aɪ |
| (II) | uː | > | ʊu | > | əʊ | > | aʊ | ≈ | aʊ |
| (III) | eː | > | iː | ≈ | iː | ||||
| (IV) | oː | > | uː | ≈ | uː | ||||
| (V) | ɛː | > | e̞ː | > | eː | > | iː | ≈ | iː |
| (VI) | ɔː | > | oː | > | oʊ > əʊ | ||||
| (VII) | aː | > | æː > ɛː | > | eː | > | eɪ |
この図をみるかぎり,少なくとも (I)--(IV) の変化,すなわち母音四辺形でいうところの上半分の長母音が経た変化は,14--15世紀という比較的早い段階で生じており,しかも互いに関わりあっているかのように思われる.この4つについては「推移」を語ることは許されるだろう.
続いて,16--17世紀半ばにかけて,(V)--(VII) の下半分の長母音が変化しているようにみえるが,特に低母音の /aː/ の動きは,かなり遅い時期までずれ込んでいるようだ.これを信じるならば,低母音から始まったとする伝統的な「押し上げ推移」 (push chain) の仮説は少なくとも否定されるだろう.
しかし,/aː/ の変化が上半分の諸変化の年代から100年ほど遅れていることを考慮すると,この時間差は一連の「推移」を断ち切るほどに大きいとみるべきだろうか,あるいは十分に小さいのだろうか.この問題を巡っても様々な意見があり,議論の終着点はみえない.
・ Krug, Manfred. "The Great Vowel Shift." Chapter 14 of The History of English. 4th vol. Early Modern English. Ed. Laurel J. Brinton and Alexander Bergs. Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter, 2017. 241--66.
2019-01-09 Wed
■ #3544. 英語辞書史の略年表 [dictionary][lexicography][timeline][cawdrey][webster][johnson][mulcaster][oed]
Dixon (242--44) より,英語に関する辞書史の略年表を掲げる.あくまで主要な辞書 (dictionary) や用語集 (glossary) に絞ってあるので注意.とりわけ18世紀以降には,ここで挙げられていない多数の辞書が出版されたことに留意されたい.それぞれのエントリーは特に記載のないかぎり単言語辞書を指しており,出版年は初版の年を表わす.
| c725 | Corpus Glossary. Latin to Latin, Old English, and Old French. |
| c1000 | Aelfric's glossary. Latin to Old English. |
| 1499 | Anonymous. Promptorium Parvalorum [ms version in 1430]. English to Latin. |
| 1500 | Anonymous. Hortus Vocabularum [ms version in 1440]. Latin to English. |
| 1535 | Ambrogio Calepino. Dictionarium Latinae Linguae. Monolingual Latin. |
| 1538 | Thomas Elyot. Dictionary. Latin to English. |
| 1552 | Richard Huloet. Abecedarium Anglo-Latinum. English to Latin. |
| 1565 | Thomas Cooper. Thesaurus Linguae Romanae & Britannicae. Latin to English. |
| 1573 | John Baret. An Alvearie or Triple Dictionarie. English, Latin, and French. |
| 1582 | Richard Mulcaster. Elementarie. [List of English words with no definitions.] |
| 1587 | Thomas Thomas. Dictionarium. Latin to English. |
| 1596 | Edmund Coote. The English Schoole-maister. |
| 1604 | Robert Cawdrey. A Table Alphabeticall. |
| 1613 | Academia della Crusca. Vocabulario. Monolingual Italian. |
| 1616 | John Bullokar. An English Expositor. |
| 1623 | Henry Cockeram. The English Dictionarie. |
| 1656 | Thomas Blount. Glossographia. |
| 1658 | Edward Phillips. The New World of English Words. |
| 1676 | Elisha Coles. An English Dictionary. |
| 1694 | Académie française. Dictionnaire. Monolingual French. |
| 1702 | John Kersey. A New English Dictionary. |
| 1721 | Nathan Bailey. A Universal Etymological English Dictionary. |
| 1730 | Nathan Bailey. Dictionarium Britannicum. |
| 1749 | Benjamin Martin. Lingua Britannica Reformata. |
| 1753 | John Wesley. The Complete English Dictionary. |
| 1755 | Samuel Johnson. Dictionary. |
| 1765 | John Baskerville. A Vocabulary, or Pocket Dictionary. |
| 1773 | William Kenrick. A New Dictionary of English. |
| 1775 | John Ash. The New and Complete Dictionary. |
| 1798 | Samuel Johnson, Junr. A School Dictionary. |
| 1828 | Noah Webster. American Dictionary. |
| 1830 | Joseph Emerson Worcester. Comprehensive Dictionary. |
| 1835--7 | Charles Richardson. A New Dictionary of the English Language. |
| 1847--50 | John Ogilvie. The Imperial Dictionary. |
| 1872 | Chambers's English Dictionary. Robert Chambers and William Chambers. |
| 1888--1928 | Oxford English Dictionary. James A. H. Murray et al. |
| 1889--91 | The Century Dictionary and Cyclopedia. William Dwight Whitney. |
| 1893--5 | A Standard Dictionary. Isaac K. Funk. [Later known as Funk and Wagnalls.] |
| 1898 | Webster's Collegiate Dictionary. [No editor stated.] |
| 1898 | Austral English. Edward E. Morris. |
| 1909 | Webster's New International Dictionary. William Torey Harris and F. Sturgis Allen. |
| 1911 | The Concise Oxford English Dictionary of Current English. H. W. Fowler and F. G. Fowler. |
| 1927 | The New Century Dictionary. H. G. Emery and K. G. Brewster. |
| 1933 | The Shorter Oxford English Dictionary. C. T. Onions. |
| 1935 | The New Method English Dictionary. Michael West and James Endicott. |
| 1938--44 | A Dictionary of American English. William A. Craigie and James R. Hulbert. |
| 1947 | The American College Dictionary. Clarence Barnhart. |
| 1948 | The Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary. As. S. Hornby. |
| 1951 | A Dictionary of Americanisms. Mitford M. Mathews. |
| 1965 | The Penguin English Dictionary. George N. Garmonsway. |
| 1966 | The Random House Dictionary Unabridged. Jess Stein. |
| 1969 | The American Heritage Dictionary. Anne H. Soukhanov. |
| 1971 | Encyclopedic World Dictionary. Patrick Hanks. |
| 1978 | Longman Dictionary of Contemporary English. Paul Proctor. |
| 1979 | Collins English Dictionary. Patrick Hanks. |
| 1981 | The Macquarie Dictionary. Arthur Delbridge |
| 1987 | COBUILD English Dictionary. John Sinclair. |
| 1988 | The Australian National Dictionary. W. S. Ramson. |
| 1995 | The Oxford English Reference Dictionary. Judy Pearsall and Bill Trumble. |
| 1999 | The Australian Oxford Dictionary. Bruce Moore. |
・ Dixon, R. M. W. The Unmasking of English Dictionaries. Cambridge: CUP, 2018.
Powered by WinChalow1.0rc4 based on chalow