2013-02-03 Sun
■ #1378. 英語史のインフォグラフィック [timeline][hel_education][link]
昨日の記事「#1377. Gelderen 版,英語史略年表」 ([2013-02-02-1]) も含め,ここ最近,英語史年表にこだわってきた(##777,1368,1369,1377 ほか,timeline の各記事も参照).
取り上げてきたのは,年代と文字だけの伝統的で散文的な年表ばかりだが,絵入りの年表のようなものがあるとおもしろい.ウェブ上で探してみたところ,Infographic Showing the History of the English Language なるページを見つけた.画像による英語史の概説だ.画像は縦長で1.5MBと重いので,以下のようにクリックによるズームと移動を可能にした(あるいはこちらのページへ).
このインフォグラフィック作成に当たっては,画像の下部にあるように以下のサイトを情報源として利用したという.ウェブ上には,あちらこちらに年表のページが転がっているようだ.
・ BBC British History in Depth: The Ages of English: 「#18. 英語史をオンラインで学習できるサイト」 ([2009-05-16-1]) で紹介したのと同じサイト内
・ Key Events in the History of the English Language: これ自身も英語史略年表.割りに詳しい説明がついている
・ Chronology of Events in the History of English: コメント付きの英語史略年表
・ Language Timeline: 数十年単位での説明つきの英語史略年表
2013-02-02 Sat
■ #1377. Gelderen 版,英語史略年表 [timeline][history][historiography]
[2011-06-13-1]の Crystal 版,[2013-01-24-1]の Fennel 版,[2013-01-25-1]のフィシャク版に引き続き,英語史年表シリーズ.今回は,Gelderen の英語史概説書 (313--17) より抜き書き.概説書にしてもそうだが,年表も,何度も同じもの,違うものを眺めていると,発見があるものである.
| 8000 BC | Hunter-gatherers move across Europe also into what is now the British Isles | |
| 6500 BC | Formation of English Channel | |
| 6000 BC | Shift to farming | |
| 3000 BC | Stonehenge culture | |
| 2500 BC | Bronze Age in Britain | |
| 1000 BC | Migrations of Celtic people to Britain begins | |
| 600 BC | Iron Age | |
| 55 BC--54 BC | Expeditions by Caesar | |
| 43 | Invasion by Claudius | |
| 43--47 | South and East England brought under Roman control | |
| 50 | London founded | |
| 70--84 | Wales, Northern England, and Scotland under Roman control | |
| 100--200 | Uprisings in Scotland | |
| 122 | Hadrian Walls begun | |
| 150 | Small groups of settlers from the continent | |
| 410 | Romans withdraw | |
| 450 | Hengest and Horsa come to Kent ('invited' to hold back the Picts) | |
| 455 | Hengest rebels against Vortigern | |
| 477 | Saxons in Sussex | |
| 495 | Saxons in Wessex | |
| 527 | Saxon kingdoms in Essex and Middlesex | |
| 550 | Anglian kingdoms in Mercia, Northumbria, and East Anglia | |
| 560 | Æthelberht becomes King of Kent | |
| 597 | Augustine missionaries land in Kent and conversion to Christianity starts | |
| 794 | Scandinavian attacks on Lindisfarne, Jarrow, Iona and subsequent conquest of Northumbria | |
| 865 | Scandinavian conquest of East Anglia | |
| 871--899 | Rule of King Alfred and establishment of the Danelaw | |
| 1016--1042 | Rule of King Cnut and his heirs | |
| 1042--1066 | Rule of King Edward (January 1066) | |
| 1066 | Death of King Edward (January 1066) | |
| 1066 | King Harold's defeat at Hastings and William of Normandy takes over (December 1066) | |
| 1066 | William (of Normandy) becomes king (December 1066) | |
| 1095 | First Crusade | |
| 1162 | Becket is murdered | |
| 1169--1172 | Conquest of Ireland | |
| 1204 | King John loses Normandy to the French | |
| 1282--1283 | Conquest of Wales | |
| 1290 | Expulsion of Jews from England | |
| 1315--1316 | Great Famine | |
| 1337--1453 | The 100-year War | |
| 1349--1351 | The Black Death, i.e. plague, kills one-third of the population | |
| 1362 | Statute of Pleadings (legal proceedings in English) | |
| 1381 | The Peasants' revolt | |
| 1382 | Condemnation of Wycliff | |
| 1476 | Introduction of the printing press by Caxton | |
| 1492 | Columbus reaches the 'New World' | |
| 1497 | Cabot reaches Newfoundland, Canada | |
| 1504 | St John's, Newfoundland, established as the first British colony in North America | |
| 1509--1547 | Reign of Henry VIII | |
| 1534 | Act of Supremacy, English monarch becomes head of the Church of England | |
| 1536 | Monasteries dissembled | |
| 1539 | English bible in every church | |
| 1550 | Population of England reaches 3 million | |
| 1558--1603 | Queen Elizabeth I | |
| 1600 | The East India Company is granted a charter | |
| 1607 | Settlement at Jamestown | |
| 1611 | The King James Bible (KJV) | |
| 1612 | English presence in Bermuda and in India | |
| 1620 | Pilgrim fathers establish colony in Plymouth | |
| 1624--1630 | War between England and Spain | |
| 1626--1629 | War between England and France | |
| 1627--1647 | Settlements on Barbados and the Bahamas | |
| 1629 | Charles I dissolves parliament | |
| 1642--1648 | First and Second Civil War | |
| 1649 | Charles I beheaded | |
| 1649 | Charles II becomes king | |
| 1649 | Jews officially admitted | |
| 1649--1655 | Cromwell conquers Ireland | |
| 1655 | English presence in Jamaica | |
| 1653--1660 | Cromwell is 'Lord Protector' | |
| 1660 | Charles II 'restored'' | |
| 1660 | Royal Society founded, to promote science | |
| 1670 | Hudson Bay Company active | |
| 1670--1679 | Colonization of West Africa | |
| 1688 | The Glorious Revolution | |
| 1689--1702 | Rule of William and Mary | |
| 1700 | Population of England is 5 million | |
| 1707 | Act of Union, uniting England and Scotland as the UK | |
| 1746 | Battle of Culloden; subsequent repression of Scottish Gaelic | |
| 1755 | Johnson's Dictionary | |
| 1759 | Wolfe takes Quebec for England | |
| 1760--1850 | Highland Clearances in Scotland, with resulting emigration and loss of Celtic | |
| 1763 | Trading in Basra, Iraq | |
| 1765--1947 | British rule over India | |
| 1773 | Boston Tea Party | |
| 1775--1783 | American War of Independence | |
| 1776 | American Declaration of Independence | |
| 1780--1789 | Colonies (of convicts) in Australia | |
| 1789 | French Revolution | |
| 1789 | George Washington first American president | |
| 1791 | British colonies in Upper and Lower Canada | |
| 1803 | Louisiana Purchase | |
| 1806 | British take over the Cape Colony in South Africa | |
| 1806 | Webster's Dictionary | |
| 1819--1824 | Malacca and Singapore occupied by the British | |
| 1820--1829 | Railroads in the US | |
| 1821--1823 | Irish famine | |
| 1830--1839 | Settlement of New Zealand | |
| 1834 | Slavery abolished in the British Empire | |
| 1842 | China cedes Hong Kong | |
| 1844 | First telegraph | |
| 1837--1901 | Reign of Queen Victoria | |
| 1853 | Gadsden Purchase | |
| 1853 | Japan opened to Western trade | |
| 1858 | Decision to start the OED | |
| 1861--1865 | American Civil War | |
| 1861 | British colony in Nigeria | |
| 1862 | British colony in Honduras | |
| 1865 | Abolition of slavery in the United States of America | |
| 1869 | Suez Canal opened | |
| 1876 | Telephone invented | |
| 1884 | Berlin Conference determines colonial power in Africa | |
| 1886 | Annexation of Burma | |
| 1890--1899 | Rhodesia and Uganda colonized in an attempt to control the Cape-to-Cairo corridor | |
| 1880--1902 | Boer Wars and British conquest of South Africa | |
| 1898 | American control over Hawaii, Philippines, and Puerto Rico | |
| 1898 | Hong Kong and Territories leased to Britain for 99 years | |
| 1901 | Death of Queen Victoria | |
| 1907 | Hollywood becomes a filmmaking center | |
| 1914--1918 | First World War | |
| 1916 | Easter Uprising, leading to Irish independence in 1921 | |
| 1918 | Women (over 30) get the vote in Britain | |
| 1920 | Kenya as British colony | |
| 1922 | BBC starts | |
| 1928 | OED appears (with supplement in 1933) | |
| 1931 | Statute of Westminster (former British Dominions de fact independent); British Commonwealth | |
| 1939 | photocopying invented | |
| 1939--1945 | Second World war | |
| 1942 | First computers | |
| 1945 | United Nations founded | |
| 1946 | Philippines independent | |
| 1947 | The independence of India and Pakistan; and New Zealand | |
| 1948 | Burma and Ceylon (Sri Lanka) independent | |
| 1949 | NATO founded | |
| 1950--1953 | Korean War | |
| 1951 | First computers | |
| 1960 | Nigeria becomes independent | |
| 1960 | World population reaches 3 billion | |
| 1961--1975 | Vietnam War | |
| 1963 | Kenya becomes independent | |
| 1973 | Britain joins European Union (confirmed in a 1975 referendum) | |
| 1980 | CNN starts | |
| 1984 | Apple PC | |
| 1990 | Native American Languages Act | |
| 1990--1991 | Gulf War | |
| 1990--1999 | Internet becomes major communication tool | |
| 1999 | World population reaches 6 billion | |
| 2000 | OED online | |
| 2003 | Iraq War | |
| 2003 | In Wales, 20% speak Welsh, up 2.4% in 10 years |
(後記 2013/03/18(Mon):同じ年表は Gelderen のコンパニオンサイトより,"Timeline" から閲覧できる.)
・ Gelderen, Elly van. A History of the English Language. Amsterdam, John Benjamins, 2006.
2013-01-25 Fri
■ #1369. フィシャク版,英語史略年表 [timeline][history][historiography]
昨日の記事「#1368. Fennell 版,英語史略年表」 ([2013-01-24-1]) に引き続き,今日はフィシャク版の年表を再現する.日本語での英語史年表もあると便利だと思い,和訳に従った (207--10) .同じ英語史の年表といっても,作成者によって力点が異なるものであり,それぞれに特徴がある.年表も確かに1つの歴史記述の方法であるということを認識させられる.
| 55, 54 BC | ユーリウス・カエサルが軍隊を率いてブリテン島に上陸 | |
| 43 BC | ローマ帝国による組織的なブリテン島征服が始まる | |
| end of C3 | ゲルマン人諸部族による最初のブリテン島攻撃 | |
| 367 | スコット人(アイルランドから),ピクト人(北から),サクソン人(東から)が,ローマ支配下のブリテン島を攻撃 | |
| 375 | フン族の西進を逃れようと西ゴート族がドナウ川を渡りローマ領内に侵入し,ゲルマン民族の大移動が始まる.ローマ帝国が大打撃を受ける | |
| 383 | ローマ軍がローマに召喚される | |
| 410 | 最後のローマ軍団がブリテン島から撤退 | |
| 449 | ゲルマン人部族がブリテン島に侵入し,征服を始める | |
| c500 | 「バドニクス丘」の戦いで侵入者ゲルマン人が敗れ,ブリテン島征服は南部において一時中断 | |
| 547? | ハンバー川以北にアングル族が王国を建てる | |
| 597 | 聖アウグスティヌスがケント王国に到着し,ブリテン島南部に住んでいたゲルマン人にキリスト教の布教を始める | |
| 634 | アイルランドの修道僧がノーサンブリアのキリスト教化に乗り出す | |
| 655 | マーシアのキリスト教改宗がノーサンブリアとアイルランドの宣教師たちの手により完了 | |
| 664 | ノーサンブリアにおいて,ホイットビー教会会議が開かれる.ブリテン島やアイルランドのキリスト教がローマ教会に統一される契機となる | |
| c725 | 口承による『ベーオウルフ』がこの頃完成される | |
| 787 | デーン人の侵攻が始まる | |
| 865 | デーン人侵攻の第2期 | |
| 871--899 | アルフレッド大王の治世 | |
| 879 | アルフレッド大王と(グスルムが率いる)デーン人との間でウェドモアの協定.デーンロー地域の確定 | |
| 886 | アルフレッド大王がロンドンを占領.グスルムの王国を除く全イングランドがその統治権を認める | |
| 964 | 修道院の改革が始まり,英語の標準化に影響を与える | |
| 973 | エドガーがバースにおいて,初めてキリスト教の儀式による戴冠式を挙げ,(デーンロー地域を含む)全イングランドの最初の王となる | |
| 991 | オラフ・トリュグヴァソンがイギリスに侵攻.デーン人侵攻の第3期が始まる | |
| 1066 | ウィリアム征服王がヘースティングズの戦いで勝利をおさめ,ノルマン人の英国征服が始まる.フランス語とラテン語が英語に代わって公用語となる | |
| 1154 | 『ピーターバラ年代記』と呼ばれる写本の記録はこの年で終結する.(一般に『アングロ・サクソン年代記』と呼ばれる.写本は7つあり,カエサルの侵入から始まっている.) | |
| 1204 | ジョン王がフランス国王フィリップ2世に敗れ,ノルマンディーがフランス王の手に渡る.イギリスの民族主義が高まり始める | |
| 1250 | 英国貴族の二重忠節が終結し,フランス語を重んずる必要がなくなる | |
| 1258 | ヘンリー3世が,ノルマン人の英国征服以降初めて英語で布告を出す | |
| 1295 | チェルムズフォードの裁判所で,文書が英語とフランス語の両語で読まれる | |
| 1337--1453 | 百年戦争.この戦争により,イギリス人はフランスのあらゆるものに対して敵愾心を抱くようになる | |
| 1344 | 大法官宛の請願書が初めて英語で書かれる | |
| 1348--1350 | 黒死病のため,イギリス社会に大規模な住民の移動がおこる | |
| 1362 | 国会が初めて英語で開会される.議会は「訴答手続法」を制定し,1363年1月以降はすべての訴訟手続,審議は英語で行なうことに決められる | |
| 1381 | 農民一揆がおこり,社会的変動の進行を加速する | |
| c1385 | 英語がイングランド全域の学校で用いられるようになる | |
| 1413 | ヘンリー4世が英国王として初めて英語で遺書を残す | |
| 1422 | 英語による最初の玉璽文書 | |
| 1423 | 国会の議事録が英語で書かれ始める | |
| c1430 | 町や同業組合の公文書に英語を用い始める | |
| 1476 | ウィリアム・キャクストンがイングランドに戻り,ウエストミンスターに最初の印刷所をつくる | |
| 1499 | キャクストンの後継者ピンソンが,英語・ラテン語の二言語語彙集,『子供のための言葉の宝庫』を出版する(書かれたのは1440年).辞書編纂への一歩となる | |
| 1534 | ヘンリー8世がローマ教会との関係を絶ち,英国国教会が成立 | |
| 1564--1616 | ウィリアム・シェークスピアの生涯 | |
| 1586 | ウィリアム・ブローカ著『文法のための小冊子』(同著者による現存しない文法書の簡易版)が出版される.最初の英文法書 | |
| 1588 | スペインの無敵艦隊に勝利.英語が世界に広がる端緒となる | |
| 1604 | ロバート・コードリー著『アルファベット順語彙一覧』の出版.最初の英語の一言語辞典(英英辞典) | |
| 1607 | アメリカに英語がもたらされる.今日のヴァージニア州に,入植者によってジェームズタウンが建設される | |
| 1611 | 欽定英訳聖書(ジェームズ王聖書)の出版 | |
| 1639--1686 | インド(マドラス,カルカッタ,ボンベイ)に英国の入植地が建設される | |
| 1642--1660 | 市民革命 | |
| 1664 | 王立教会が「英語を改良するための」委員会を設置 | |
| 1712 | J. スウィフトによるオックスフォード伯への手紙が『英語の矯正,改良,確定のための提案』として出版され,アカデミーの設立を促す | |
| 1713 | ノヴァスコシアがフランスからイギリスに譲渡される | |
| 1755 | サミュエル・ジョンソン著『英語辞典』が出版される.19世紀末まで正しい英語の揺るぎない権威的存在となる | |
| 1759 | ウルフ将軍がケベックの戦いでフランス軍に勝利 | |
| 1761 | インドがイギリスの植民地となる | |
| 1769--1777 | キャプテン・クックが,南太平洋への航海途上で,オーストラリア,ニュージーランド,タスマニアをイギリス王領と宣言する | |
| 1775--1783 | アメリカ独立戦争により,アメリカ合衆国の誕生 | |
| 1788 | オーストラリアのニューサウスウェールズに最初の流刑地植民地が建設される.ケープタウン(南アフリカ)にあるオランダ植民地がイギリス領有となる | |
| 1805 | トラファルガーの海戦においてイギリス軍がフランス軍に勝利する.イギリスが海上覇権を掌握し植民地拡大への道を開く | |
| 1816 | イギリスで最初の安価な新聞が発行され,英語に影響を与えるマスメディア時代が始まる | |
| 1840 | ニュージーランドにおいて,イギリス植民地が建設される.イギリスの安価な郵便制度が文字通信の発達を促し,さらに英語が普及する | |
| 1858 | 『新英語辞典』(後に『オックスフォード英語辞典』と称される)の編集作業が始まる | |
| 1890--1910 | 数多くの発明や科学上の発見が,英語に前例のない大きな影響を与える | |
| 1899--1901 | 南アフリカのブール戦争において初期オランダ入植者の子孫が敗北.イギリスの覇権が確立 | |
| 1914--1918 | 第1次世界大戦.英語の威信が高まる.フランス語は教育言語として,また外交言語としてさえ,その地位を失い始める(ヴェルサイユ条約がフランス語と英語で書かれる) | |
| 1939--1945 | 第2次世界大戦がさらに,英語の普及を押し進め,その威信を高める |
・ ヤツェク・フィシャク著,小林 正成・下内 充・中本 明子 訳 『英語史概説 第1巻外面史』 青山社,2006年.
2013-01-24 Thu
■ #1368. Fennell 版,英語史略年表 [timeline][history][historiography]
「#777. 英語史略年表」 ([2011-06-13-1]) では,Crystal 版の英語史略年表を掲載したが,今回は Fennell 版を再現する.Fennell では各章の最初に対象となっている時代に関する年表が載せられており,以下はそれをほぼ忠実に編集したまでで,細かくは整理していない.Fennell の著書の題名から予想されるとおり,社会史的な側面が強く反映されている年表である.
| 8000 BC | Hunter groups move into Lapland | |
| 7000 BC | Wheat, barley and pulses cultivated from Anatolia to Pakistan; goats and pigs domesticated | |
| 7000 BC | Farming developed on Indian subcontinent; barley main crop | |
| 6500 BC | Adoption of farming in Balkan region; beginning of the European Neolithic spread of domestic animals, probably from Anatolia | |
| 6200 BC | Farming villages established in the west and central Mediterranean | |
| 5200 BC | First farmers of central Europe spread northwest as far as the Netherlands | |
| 4500 BC | Cattle used as plough animals in lower Danube region | |
| 4500 BC | First megalithic tombs built in western Europe | |
| 4400 BC | Domestication of horse on Eurasian Steppes | |
| 4200 BC | Earliest copper mines in eastern Europe | |
| 4200 BC | Agriculture begins south of the Ganges | |
| 3800 BC | Ditched enclosures around settlements in western Europe, forming defended villages | |
| 3500 BC | New faming practices: animals increasingly used for traction, wool and milk; simple plough (ard) now used in northern and western Europe | |
| 3250 BC | Earliest writing from western Mesopotamia: pictographic clay used for commercial accounts | |
| 3200 BC | First wheeled vehicles in Europe (found in Hungary) | |
| 3100 BC | Cuneiform script developed in Mesopotamia | |
| 3000 BC | Construction of walled citadels in Mediterranean Europe and development of successful metal industry | |
| 2900 BC | Appearance of Corded Ware pottery in northern Europe | |
| 2500 BC | Bell beakers found in western Europe, often associated with individual burials | |
| 2500 BC | Development of urban civilization in the Indian Plain | |
| 2500 BC | Earliest syllabic script used in Sumerian literature | |
| 2300 BC | Beginning of full European Bronze Age | |
| 2000 BC | Fortified settlements in east and central Europe point to increasing social and economic pressures | |
| 1900 BC | Cretan hieroglyphic writing | |
| 1850 BC | Horses used for the first time to pull light carts in the western Steppes | |
| 1650 BC | Linear A script (Crete and the Cyclades) | |
| 1650 BC | City-states of central Anatolia unified to form the Hittite kingdom with a strongly fortified capital at Boğazköy | |
| 1400 BC | Linear B script (mainland and islands of Greece) | |
| 1400 BC | Development of pastoral nomadism on the Steppes: cattle herded from horseback | |
| 1300 BC | Westward spread of urnfield cemeteries | |
| 1200 BC | Collapse of Hittite empire | |
| 1000 BC | Hillforts in Western Europe | |
| 1000 BC | Full nomadic economy on the Steppes based on rearing horses, cattle and sheep | |
| 850 BC | First settlement at Rome; cluster of huts on Palatine Hill | |
| 800 BC | Establishment of culture north and east of Alps --- first stage of Celtic Iron Age (Hallstatt) | |
| 800 BC | Rise of Etruscan city-states in central Italy | |
| 800 BC | Rise of cities and states in Ganges Valley supported by rice farming | |
| 750 BC | First Greek alphabetic inscription | |
| 750 BC | Ironworking spreads to Britain | |
| 750 BC | Earliest Greek colonies set up from western Mediterranean to the eastern shores of the Black Sea | |
| 690 BC | Etruscan script developed from Greek | |
| 600 BC | Trade between Celts north west of Alps and Greek colonies of the west Mediterranean; rich wagon burials attest to wealth and power of Celtic elite | |
| 600 BC | Latin script | |
| 600 BC | Central lowlands of northern Europe first settled | |
| 600 BC | First Greek coins | |
| 480 BC | 2nd stage of European Bronze Age (La Tène) | |
| 480 BC | Emergence of classical period of Greek arts and architecture | |
| 480 BC | City-states reach height of importance | |
| 460 BC | Parchment replaces clay tablets for Aramaic administrative documents | |
| 450 BC | Athens, the greatest Greek city-state, reaches the peak of its power | |
| 400 BC | Carthage dominates the west Mediterranean | |
| 390 BC | Celts sack Rome | |
| 334 BC--329 BC | Alexander the Great invades Asia Minor, conquers Egypt and Persia and reaches India; Hellenism established in Asia | |
| 331 BC | Alexandria founded | |
| 250 BC | Brahmin alphabetic script in India | |
| 250 BC | All of peninsular Italy controlled by Rome | |
| 206 BC | Rome gains control of Spain | |
| 146 BC | Romans destroy the Greek states but Greek culture still important and Greek artists brought to Rome | |
| 146 BC | Roman destruction of Carthage | |
| 55 BC | Julius Caesar attempts to invade Britain | |
| 27 BC | Augustus sole ruler of Roman empire | |
| 43--50 | Emperor Claudius invades Britain | |
| 50 | Rome largest city in the world --- population 1 million | |
| 117 | Roman empire reaches its greatest extent | |
| 125 | Hadrian's Wall built | |
| 285 | Administrative separation of eastern and western halves of Roman empire | |
| 313 | Edict of Milan: toleration of Christianity in Roman empire | |
| 330 | Constantine founds Constantinople as new eastern capital of the Roman empire | |
| 410 | Sack of Rome by Visigoths leading to collapse of western Roman empire | |
| 410 | Romans withdraw from Britain | |
| 429 | German (Vandal) kingdom in north Africa | |
| 449 | Angles, Saxons and Jutes invade Britain | |
| 597 | St Augustine introduces Christianity to the English | |
| 787 | Scandinavian invasions begin | |
| 793 | Sacking of Lindisfarne | |
| 878 | King Alfred defeats the Danes at Eddington | |
| 878 | Treaty of Wedmore | |
| 899 | King Alfred dies | |
| 1016 | Danish King Cnut rules England | |
| 1042 | Accession of Edward the Confessor to the English throne | |
| 1066 | Battle of Hastings; Norman Conquest | |
| 1095 | First Crusade | |
| 1170 | Assassination of Thomas à Becket | |
| 1204 | King John loses lands in Normandy | |
| 1259--1265 | The Barons' War | |
| 1337--1453 | The Hundred Years War | |
| 1340--1400 | Geoffrey Chaucer | |
| 1346 | Battle of Crecy | |
| 1346 | Battle of Poitiers | |
| 1348--1351 | The Black Death | |
| 1362 | Parliament opened in English | |
| 1362 | The Statute of Pleading (English becomes the official language of legal proceedings) | |
| 1381 | The Peasants' Revolt | |
| 1415 | Battle of Agincourt | |
| 1476 | Caxton introduces the printing press | |
| 1489 | French no longer used as the language of Parliament | |
| 1509 | Henry VIII ascends the throne | |
| 1534 | Act of Supremacy | |
| 1536 | Small monasteries dissolved | |
| 1536 | Statute incorporates all of Wales with England | |
| 1539 | English translation of Bible in every church | |
| 1547 | Edward VI | |
| 1553 | Mary Tudor | |
| 1554 | Mary marries Philip of Spain | |
| 1558 | Elizabeth I | |
| 1559 | Act of Supremacy restores laws of Henry VIII | |
| 1574 | First company of actors; theatre building begins | |
| 1577 | Sir Francis Drake plunders west coast of South America | |
| 1584 | Colonists at Roanoke | |
| 1600 | British East India Company founded | |
| 1600 | Population of England c.2.5 million | |
| 1603 | James I | |
| 1605 | Barbados, West Indies, claimed as English colony | |
| 1606 | Virginia Company of London sends 120 colonists to Virginia | |
| 1607 | Jamestown, Virginia, is established by London Co. as the first permanent English settlement in America | |
| 1611 | King James Bible | |
| 1616 | Death of Shakespeare | |
| 1620 | The Pilgrims arrive at Plymouth Rock on the Mayflower | |
| 1621 | English attempt to colonize Newfoundland and Nova Scotia | |
| 1625 | Charles I | |
| 1627 | Charles I grants charter to the Guiana Company | |
| 1633 | English trading post established in Bengal | |
| 1637 | English traders established in Canton | |
| 1639 | English established at Madras | |
| 1642--1646 | Civil War | |
| 1646 | English occupy the Bahamas | |
| 1648 | Second Civil War | |
| 1649 | Cromwell invades Ireland | |
| 1649 | Charles I beheaded | |
| 1649 | Charles II | |
| 1649 | Commonwealth established | |
| 1653 | Cromwell becomes Lord Protector | |
| 1655 | English capture Jamaica | |
| 1660 | Charles II restored to throne | |
| 1663 | Charles II grants charter to Royal African Company | |
| 1668 | British East India Company gains control of Bombay | |
| 1670 | English settlement in Charles Town, later Charleston, South Carolina | |
| 1680--1689 | Welsh Quakers settle in large numbers in Pennsylvania | |
| 1680--1689 | First German immigrants in America | |
| 1684 | Bermudas become Crown Colony | |
| 1689 | William and Mary proclaimed king and queen in England and Ireland | |
| 1690 | Calcutta founded | |
| 1690 | Population of England c.5 million | |
| 1700 | Population of England and Scotland 7.5 million | |
| 1707 | Union of England and Scotland as Great Britain | |
| 1707 | British land in Acadia, Canada | |
| 1710 | English South Sea Company founded | |
| 1727 | George II | |
| 1729 | North and South Carolina become Crown Colonies | |
| 1729 | Benjamin and James Franklin publish 'The Pennsylvania Gazette' | |
| 1744 | Robert Clive arrives at Madras | |
| 1756--1763 | The French and Indian War in North America | |
| 1759 | British take Quebec from the French | |
| 1760 | George III | |
| 1762 | British capture Martinique, Grenada, Havana and Manila | |
| 1765--1947 | British Raj in India | |
| 1770 | James Cook discovers Botany Bay, Australia | |
| 1774 | Parliament passes the Stamp Act, unifying the colonies against the British | |
| 1775 | The East India, or Tea, Act prompts the Boston Teat Party | |
| 1775--1783 | American War of Independence | |
| 1776 | American Declaration of Independence | |
| 1776 | The Revolutionary War begins | |
| 1778 | Cook discovers Hawaii | |
| 1783 | The Treaty of Paris successfully ends the Revolution | |
| 1783 | British recognize US independence | |
| 1784 | Pitt's India Act: East India Company under government control | |
| 1786 | Penang ceded to Great Britain | |
| 1789 | George Washington inaugurated as first US President | |
| 1790 | The first penal colony established in Sydney, Australia | |
| 1795, 1806 | British forces occupy Cape of Good Hope | |
| 1800 | British capture Malta | |
| 1803 | The Louisiana Purchase doubles the size of US territory | |
| 1810 | British seize Guadeloupe | |
| 1811 | British occupy Java | |
| 1812--1814 | War of 1812 between the USA and Britain | |
| 1819 | Florida purchased by the USA from Spain | |
| 1819 | British settlement established in Singapore by East India Company | |
| 1822 | English becomes the official language of the Eastern Cape of South Africa | |
| 1822 | Liberia founded --- Africa's oldest republic | |
| 1824 | Erie Canal opens, strengthening east-west trade, but increasing the isolation of the south | |
| 1824 | British take Rangoon, Burma | |
| 1828 | The Baltimore and Ohio Railway opens | |
| 1832 | Britain occupies the Falkland Islands | |
| 1837 | Queen Victoria | |
| 1837 | The electric telegraph demonstrated by Samuel Morse | |
| 1840 | New Zealand becomes an official colony | |
| 1840 | Penny post introduced in Britain | |
| 1842 | Hong Kong ceded to Great Britain | |
| 1848 | Gold discovered in California | |
| 1849 | Gold Rush | |
| 1851 | Victoria, Australia, proclaimed separate colony | |
| 1852 | New constitution for New Zealand | |
| 1858 | Powers of East India Company transferred to British Crown | |
| 1860 | Kowloon added to British territories in South-East Asia | |
| 1861 | Civil War begins with the Confederate attack on Fort Sumter | |
| 1861 | British Colony founded in Lagos, Nigeria | |
| 1863 | Emancipation of the slaves is proclaimed, as of 1 January | |
| 1865 | General Lee surrenders to Grant at Appomattox | |
| 1865 | President Lincoln is assassinated, five days later | |
| 1867 | Alaska is purchased from Russia, becoming the 49th state in 1959 | |
| 1867 | Federal Malay States become a Crown Colony | |
| 1869 | The first transcontinental railroad is completed | |
| 1876 | Alexander Graham Bell patents the telephone | |
| 1877 | Edison invents the phonograph | |
| 1878 | David Hughes invents the microphone | |
| 1879 | London opens its first telephone exchange | |
| 1884 | Papua New Guinea becomes British protectorate | |
| 1885 | Britain established protectorate over Northern Bechuanaland, Niger River Region and southern New Guinea, and occupies Port Hamilton, Korea | |
| 1886 | First Indian National Congress meets | |
| 1887 | First Colonial Conference opens in London | |
| 1888 | Cecil Rhodes granted mining rights by King of Matabele | |
| 1890 | Rhodes becomes Premier of Cape Colony | |
| 1893 | Uganda united as British protectorate | |
| 1893 | USA annexes Hawaii | |
| 1895 | Marconi invents radiotelegraphy | |
| 1895 | Auguste and Louis Lumière invent the motion-picture camera | |
| 1895 | British South Africa Company territory south of the Zambezi River becomes Rhodesia | |
| 1898 | America receives Guam and sovereignty over the Philippines | |
| 1898 | New Territories leased by Britain from China for 99 years | |
| 1899 | First magnetic sound recordings | |
| 1899--1902 | Boer War | |
| 1900 | R. A. Fessenden transmits the human voice via radio waves | |
| 1900 | British capture Bloemfontein, relieve Mafeking, annex Orange Free State and Transvaal and take Pretoria and Johannesburg Commonwealth of Australia created | |
| 1901 | Marconi transmits radiotelegraph messages from Cornwall to New Zealand | |
| 1901 | End of Queen Victoria's reign | |
| 1903 | Ford Motor Company founded | |
| 1903 | Orville and Wilbur Wright make the first successful manned flight at Kitty Hawk, North Carolina | |
| 1903 | British conquer northern Nigeria | |
| 1907 | New Zealand becomes a dominion within the British Empire | |
| 1908 | Union of South Africa established | |
| 1908 | Henry Ford introduces the mass-produced Model T | |
| 1914 | Panama Canal opened | |
| 1914--1918 | World War I | |
| 1916 | USA purchases Danish West Indies (Virgin Islands) | |
| 1917 | USA purchases Dutch West Indies | |
| 1919 | League of Nations founded | |
| 1920 | Gandhi emerges as leader of India | |
| 1920 | Kenya becomes British colony | |
| 1921 | British Broadcasting Corporation founded | |
| 1921 | First Indian Parliament meets | |
| 1924 | The National Origins Act marks the official end of large-scale immigration to America; from this point on numbers are restricted and quotas are introduced | |
| 1924 | British Imperial Airways founded | |
| 1925 | John Logie Baird transmits a picture of a human face via television | |
| 1928 | John Logie Baird demonstrates first colour television | |
| 1929 | Teleprinters and teletypewriters first used | |
| 1929 | First scheduled TV broadcasts in Schernectedy, New York | |
| 1929 | First talking pictures made | |
| 1936 | BBC London television service begins | |
| 1938 | Lajos Biró invents the ball-point pen | |
| 1939--1945 | World War II | |
| 1942 | First computer developed in the United States | |
| 1942 | Magnetic recording tape invented | |
| 1944 | First telegraph line used between Washington and Baltimore | |
| 1945 | United Nations founded | |
| 1946 | Chester Carlson invents Xerography | |
| 1946 | Philippines become independent from the United States | |
| 1947 | Transistor invented at Bell Laboratories | |
| 1947 | India proclaimed independent | |
| 1948 | Peter Goldmark invents the long-playing record | |
| 1951 | Colour TV introduced into USA (15 million TV sets in USA) | |
| 1952 | Accession of Queen Elizabeth II | |
| 1957 | Common Market established by Treaty of Rome | |
| 1957 | Malaysian independence | |
| 1958 | First stereophonic recordings | |
| 1962--1975 | Uganda, Kenya, Zambia (Northern Rhodesia), Malawi, Malta, Gambia, Southern Rhodesia (Zimbabwe), Guyana, Mauritius, Nigeria, Bahamas, Papua New Guinea all become independent of Great Britain | |
| 1965 | Atlantic cable completed | |
| 1968 | Intelsar communication satellite launched | |
| 1989 | South Africa desegregated | |
| 1997 | Hong Kong rule returns to China |
・ Crystal, David. The English Language. 2nd ed. London: Penguin, 2002.
・ Fennell, Barbara A. A History of English: A Sociolinguistic Approach. Malden, MA: Blackwell, 2001.
2012-12-20 Thu
■ #1333. 中英語で受動態の動作主に用いられた前置詞 [preposition][passive][timeline]
中英語で動作主を示すのに用いられた前置詞には,by, from, mid, of, with があった.すべてが同じような頻度で用いられていたわけではなく,時代により盛衰が見られた.
古英語では,主として from が,またしばしば of が動作主を表わすのに用いられていた.このうち from は14世紀まで使用されたが,後に廃れていった.一方,of は古英語の終わりから中英語にかけて著しく伸張し,1600年辺りまでは最も広く用いられた.次に現代英語に連なる by をみてみると,動作主を示す用法は,古英語でもそれらしき例があったと指摘されてはいるが,はっきりしない(下の Mustanoja からの3番目の引用を参照).動作主の by が中英語で例証されるようになるのは14世紀終わりからであり,15--16世紀にかけて拡大し,of と肩を並べるほどになる.そのほか,動作主の前置詞としてはそれほど目立たないが,13世紀より文証される with や初期中英語で散見される mid の例もある.
それぞれが廃用になった時期や各時代の相対頻度などの詳細は未調査だが,大雑把に時系列に並べてみると次のようになるだろう.
1000 1100 1200 1300 1400 1500 1600 1700
from :************************************** - - -
of :*************************************************************** - - -
bi : - - - *******************************
with : - - *** - -
mid : - - *** - -
Mustanoja より,各前置詞の関連する記述箇所を引用しておこう.
From its function to indicate a person as a source of an action, first as a giver or sender, from develops into a preposition of agency in OE. In this function it occurs down to the 14th century: --- he wæs gehalgod to biscop fram þone ærcebiscop Willelm of Cantwarabyri (OE Chron. an. 1129); --- I . . . am sett king from hym upon Sion (Wyclif Ps. ii 6; am maad of hym a kyng, Purvey). (385--86)
To express agency of is used less frequently than from in OE, but it begins to gain ground towards the end of this period and becomes the most popular preposition expressing agency in connection with a passive verb down to c 1600. It is possible that this use of of has been promoted by the influence of OF de. Examples: --- ich wolde þet heo weren of alle alse heo beoþ of ou iholden (Ancr. 21); --- is alle biset of helle muchares (Ancr. 67); --- if he wolde be slayn of Symkyn (Ch. CT A Rv. 3959); --- enformed whan the kyng was of that knyght (Ch. CT F Sq. 335). (397)
Wülfing II, p. 338, quotes a doubtful OE instance of be denoting agency with a passive verb, and R. Gottweiss (Anglia XXVIII, 1905, 353--4) calls attention to what he calls 'signs of the use of be with the passive' in Ælfric's homilies. BTS, be 20, quotes an example from the OE Gospel of St Luke (þa þing þe be him wærun gewordene 'quae febant ab eo,' ix 7). Cf. active cases like þat was agan þære bi þan kaisere (Lawman A 27982). Unambiguous ME instances where by indicates the agent of a passive verb occur from the end of the 14th century on (I praye Jhesu shorte hir lyves That wol nat be governed by hir wyves, Ch. CT D WB 1262; --- ne hadde he ben holpen by the steede of brass, Ch. CT F Sq. 666). This use becomes increasingly common in the 15th and 16th centuries. In the Cloud (MSS of the early 15th---early 16th century) of is a little more frequently used to denote agency than by. It may be assumed that the use of by to indicate the agent of a passive expression is promoted by the influence of French par. (374--75)
With begins to occur as a preposition of agency in the 13th century: --- heder was þat mayde brouȝt With marchaundes þat hur had bouȝt (Flor. & Bl. 408); --- he was with þe prestes shrive (Havelok 2489); --- and with twenty knyghtes take, O persone allone, withouten mo (Ch. CT A Kn. 2724). (420)
. . . instrumental mid is occasionally used to express agency in early ME: --- a lefdi was þet was mid hire voan biset at abuten (Ancr. 177). (394)
・ Mustanoja, T. F. A Middle English Syntax. Helsinki: Société Néophilologique, 1960.
2012-11-02 Fri
■ #1285. FLASHで英語史略年表 [timeline][history][flash][web_service][world_languages][loan_word][link]
マンチェスター大学の発信する,子供向け教育コンテンツを用意しているこちらのサイトのなかに,Timeline of English Language なるFLASHコンテンツを発見した.粗い英語史年表で,あくまで導入的な目的での使用を念頭に置いたものだが,話の種には使えるかもしれないので紹介しておく.
言語に関する他のコンテンツへのリンクは,こちらにある.次のものなどは,結構おもしろい.
・ World Language Map
・ Borrowing Game
簡易年表ということでいえば,A brief chronology of English なるものを見つけた.本ブログ内では,timeline を参照.
2011-06-13 Mon
■ #777. 英語史略年表 [timeline][history][historiography]
英語史年表は,どの概説書にも記載があるしオンラインでも見つけられる(例えば英語の歴史年表―前史・古英語期)が,本ブログとしての版も作成してゆこうと考えている.たたき台として,Crystal (298--300) の略年表を再現したものを掲げておく.その他,直接間接に英語史に関連する年表は timeline を参照.
| 449 | Invasion by Angles, Saxons, and Jutes | |
| 450--480 | Earliest runic inscriptions in Old English | |
| 597 | Augustine brings Christianity to Kent | |
| 680 | Approximate earliest date for the composition of Beowulf | |
| 700 | Approximate dating of earliest Old English manuscripts | |
| 735 | Death of the Venerable Bede | |
| 787 | Viking raids begin | |
| 871 | Alfred becomes King of Wessex | |
| 886 | Danelaw boundaries settled | |
| 950--1000 | Approximate dates of the main Old English poetry collections | |
| 1016--1042 | Cnut and his sons reign | |
| 1066 | Norman Conquest | |
| 1150--1200 | Earliest texts in Middle English | |
| 1171 | Henry II's invasion of Ireland | |
| 1204 | France reconquers Normandy | |
| 1250--1300 | Edward I's campaigns against the Welsh and Scots | |
| 1362 | English first used at the opening of Parliament | |
| 1375--1400 | Chaucer's main works written | |
| 1384 | Wyclif's translation of the Bible | |
| 1400--1450 | The Great Vowel Shift | |
| 1400--1600 | Main period of older Scots literature | |
| 1476 | Introduction of printing | |
| 1475--1650 | Renaissance loan words into English | |
| 1549 | Book of Common Prayer written | |
| 1560--1620 | English plantation settlements in Ireland | |
| 1584 | Roanoke settlement in America | |
| 1590--1616 | Shakespeare's main works written | |
| 1600 | East India Company established trading posts in India | |
| 1603 | Act of Union of the crowns of England and Scotland | |
| 1604 | Publication of Robert Cawdrey's A Table Alphabeticall | |
| 1607 | First permanent English settlement in America | |
| 1609 | First English settlement in the Caribbean | |
| 1611 | Authorized Version of the Bible | |
| 1619 | Arrival of first African slaves in North America | |
| 1620 | Arrival of the Pilgrim Fathers in America | |
| 1623 | First Folio of Shakespeare's plays published | |
| 1627 | British established in Barbados | |
| 1655 | British acquire Jamaica from Spain | |
| 1707 | Union of the Parliaments of England and Scotland | |
| 1712 | Jonathan Swift's proposal for an English Academy | |
| 1713 | British control in eastern Canada recognized | |
| 1721 | Publication of Nathaniel Bailey's Universal Etymological English Dictionary | |
| 1755 | Publication of Samuel Johnson's Dictionary of the English Language | |
| 1762 | Publication of Robert Lowth's Short Introduction to English Grammar | |
| 1765--1947 | British Raj in India | |
| 1776 | American independence declared | |
| 1780--1800 | First wave of emigration to Canada from the USA | |
| 1783 | Loss of American colonies of Britain | |
| 1788 | Establishment of first penal colony in Australia | |
| 1791 | Establishment of Upper and Lower Canada | |
| 1794 | Publication of Lindley Murray's English Grammar | |
| 1800--1910 | Main period of European emigration to the USA | |
| 1802 | Ceylon and Trinidad ceded to Britain | |
| 1803 | Act of Union between Britain and Ireland | |
| 1806 | British control established in South Africa | |
| 1808 | Sierra Leone made colony | |
| 1814 | Tobago, Mauritius, St Lucia and Malta ceded to Britain | |
| 1816 | Colony of Bathurst (Gambia) established | |
| 1819 | British established Singapore | |
| 1828 | Publication of Noah Webster's American Dictionary of the English Language | |
| 1840 | Official colony established in New Zealand | |
| 1842 | Hong Kong ceded to Britain | |
| 1861 | Lagos (Nigeria) established as colony | |
| 1865--1900 | Movement of blacks to northern parts of the USA after the American Civil War | |
| 1867 | Independence of Canada | |
| 1874 | Gold Coast (Ghana) established as colony | |
| 1884--1928 | Publication of the Oxford English Dictionary | |
| 1888--1894 | British protectorates established in Kenya, Zanzibar, Uganda | |
| 1901 | Independence of Australia | |
| 1907 | Independence of New Zealand | |
| 1910 | Union of South Africa established | |
| 1919 | Tanganyika ceded to Britain | |
| 1922 | Partition of Northern Ireland and Eire | |
| 1922 | Establishment of the BBC | |
| 1925 | Afrikaans given official status in South Africa | |
| 1931 | British Commonwealth recognized | |
| 1947 | Independence of India | |
| 1948 | Independence of Ceylon (Sri Lanka) | |
| 1957 | Independence of Ghana | |
| 1957--63 | Independence of Malaysia | |
| 1960 | Independence of Nigeria | |
| 1940--1975 | Main period of immigration to Britain from Europe, Caribbean and Asia | |
| 1961 | Independence of Sierra Leone and Cyprus | |
| 1962 | Independence of Jamaica, Trinidad and Tobago, Uganda | |
| 1963 | Independence of Kenya | |
| 1964 | Independence of Tanzania, Malawi, Malta, Zambia | |
| 1965 | Independence of The Gambia, Singapore | |
| 1966 | Independence of Guyana, Botswana, Lesotho, Barbados | |
| 1968 | Independence of Mauritius, Swaziland, Nauru | |
| 1970--1984 | Independence of possessions in Caribbean and Pacific | |
| 1972 | Independence of Bangladesh | |
| 1972 | First network e-mail sent | |
| 1975 | Independence of Papua New Guinea | |
| 1977 | Voyager spacecraft leaves with English message | |
| 1984 | Independence of Brunei | |
| 1986 | Independence of Marshall Islands | |
| 1988 | CD-ROM of the Oxford English Dictionary | |
| 1990 | Independence of Namibia | |
| 1991 | Independence of the Federated States of Micronesia | |
| 1991 | Implementation of the World Wide Web | |
| 1994 | Independence of Palau | |
| 2000 | Oxford English Dictionary goes online |
・ Crystal, David. The English Language. 2nd ed. London: Penguin, 2002.
・ 寺澤 芳雄,川崎 潔 編 『英語史総合年表?英語史・英語学史・英米文学史・外面史?』 研究社,1993年.
2011-05-18 Wed
■ #751. 地球46億年のあゆみのなかでの人類と言語 [timeline][writing][homo_sapiens][anthropology][origin_of_language][grammatology]
[2009-06-08-1]の記事「言語と文字の歴史は浅い」では,人類のあゆみにおいて言語の歴史がいかに浅いかを示した.今回は,タイムスパンを地質学的次元にまで引き延ばし,地球のあゆみ46億年における人類と言語の歴史の浅さを強調したい.直感でとらえられるように,46億年を1年間というスケールに縮めて表現してみた.
1秒は約146年に相当する.大晦日は黄色表示にし,秒単位まで示した.人類の誕生は600万年前,ホモサピエンスの誕生は20万年前,言語の発生は10万年前とする説をもとに計算してある.より詳しい表はこのページのHTMLソースを参照.
| 月日(時分秒) | 出来事 |
|---|---|
| 01/01 | 太陽と地球が生まれる |
| 01/08 | 月ができる |
| 01/16 | 海ができる |
| 02/17 -- 03/04 | 巨大ないん石が地球に落ちて海が蒸発,その後ふたたび海ができる |
| 03/04 | 最古の生命があらわれる |
| 05/30 | ???????????????????????í????????????????? |
| 06/24 -- 07/09 | この間のどこかで,大規模な氷河時代 |
| 07/17 | 真核生物(細胞の中の遺伝子が膜で包まれている生物)が登場 |
| 08/02 | ヌーナ超大陸ができる |
| 09/27 | 多細胞生物が発展 |
| 09/27 -- 10/29 | ロディニア超大陸の時代 |
| 10/30 -- 11/13 | この間のどこかで,大規模な氷河時代 |
| 11/14 | エディアカラ生物群が登場 |
| 11/19 | 無せきつい動物の種類が爆発的に増える |
| 11/25 -- 11/27 | 植物の上陸 |
| 11/30 | 昆虫が登場 |
| 12/11 | ペルム期末期の大量絶滅 |
| 12/15 -- 12/26 | 恐竜の繁栄 |
| 12/26 | 白亜紀末期の大量絶滅 |
| 12/31 12:34:26 | 人類の誕生 |
| 12/31 23:37:08 | ホモサピエンスの誕生 |
| 12/31 23:48:34 | 言語の発生 |
| 12/31 23:58:03 | ラスコーの壁画 |
| 12/31 23:59:18 | 印欧祖語の時代 |
| 12/31 23:59:22 | インダス文字の起源 |
| 12/31 23:59:23 | エジプト文字の起源 |
| 12/31 23:59:25 | メソポタミア文字の起源 |
| 12/31 23:59:36 | 漢字,ヒッタイト文字の起源 |
| 12/31 23:59:42 | マヤ文字,古代ペルシャ文字の起源 |
| 12/31 23:59:44 | 古代インド文字の起源 |
| 12/31 23:59:48 | 英語の起源 |
| 12/31 23:59:56 | 近代英語の始まり |
言語の登場は,大晦日の夜11時48分34秒.英語が世界進出の兆しを示した近代英語期の幕開けは年越しの4秒前のことである.英語史や英語の未来を語るといっても,地球の歴史ではせいぜい数秒のことなのだなと実感.
小学館の図鑑『地球』で「地球のあゆみをふりかえる」 (8--9) を眺めていて,この中に言語の歴史を入れたらどうなるかと戯れにこの年表を作ってみたにすぎないのだが,結果として考えさせられる教訓的な年表となった.
・ 丸山 茂徳 他(監修) 『地球』 小学館の図鑑 NEO 第10巻,小学館,2007年.
2009-09-05 Sat
■ #131. 英語の復権 [me][history][reestablishment_of_english][timeline][monarch]
ノルマン人の征服 ( Norman Conquest ) 以降,中英語の前半は,イングランドはフランス語の支配に屈していた.庶民の言語である英語はいわば地下に潜っていたが,13世紀辺りから徐々に英語の復活劇が始まる.だが,フランス語支配の時代に蓄えられた多くの遺産をすべてひっくり返すには,相当な時間とエネルギーが必要だった.例えば,法的文書の英語義務化は18世紀になってようやく施行された.英語の復権は,実に長い道のりだったわけである.
以下の年表は,英語の復権に関連する出来事に絞ってまとめた年表である.
| 1066年 | ノルマン人の征服 |
| 12--13世紀 | 英語の文学作品などが現れ始める( Layamon's Brut, The Owl and the Nightingale, Ancrene Wisse, etc. ) |
| 1258年 | Simon de Monfort の反乱(政府機関へのフランス人の登用に対する抗議.英語の回復も強く要求される.その結果,Henry III は布行政改革の宣言書をラテン語,フランス語だけでなく英語でも出すこととなった.) |
| 1272年 | Edward I がイングランド王として初めて英語を使用する |
| 1337年 | Edward III,フランスの王位継承権を主張し百年戦争が始まる( ? 1453年 ) |
| 1348--50年 | 最初のペストの流行( 1361--62, 1369, 1375年にも流行.黒死病については[2009-08-24-1]を参照.) |
| 1350年代 | Higden's Polychronicon で,上流貴族の子弟にとってもすでに英語が母語となっていたことが示唆される |
| 1356年 | 地方裁判所の記録が英語になる |
| 1362年 | 議会の開会が英語で宣言される |
| 1363年 | 法廷での使用言語が英語となる (ただし,記録はラテン語) |
| 1380年代 | ロンドンのギルドが記録に英語を使い始める |
| 1381年 | Peasants' Revolt |
| 1384年 | ロンドンのシティーが英語で布告を出す |
| 1399年 | 英語を母語とする最初の王 Henry IV 即位 |
| 1414年 | Henry V がイングランド王として初めて英語で手紙を書く(政府内でも英語の使用が奨励される) |
| 1422年 | ロンドンの醸造業者が手続きをラテン語から英語にする |
| 1453年 | 百年戦争の終結 |
| 1488年 | 英語が法的文書の書き言葉として認められる |
| 1539年 | Great Bible が王により初めて公認される(保守的な宗教の世界でも英語の使用が認められるようになる) |
| 1628年 | 英語で書かれた最初の法典が編纂される |
| 1731年 | 法的文書が英語でなければならなくなる |
2009-06-08 Mon
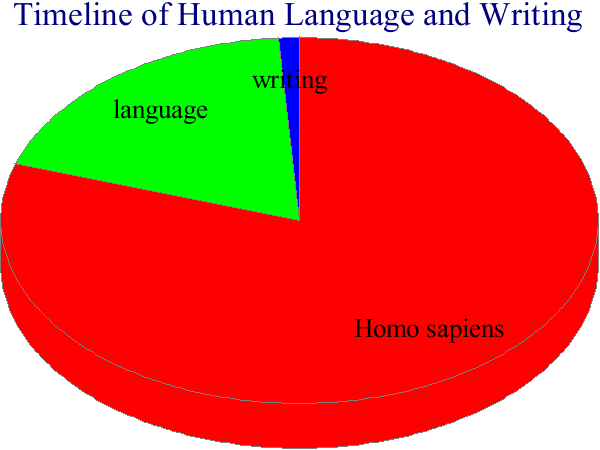
■ #41. 言語と文字の歴史は浅い [timeline][writing][homo_sapiens][anthropology][origin_of_language][grammatology]
数百万年に及ぶ人類の歴史の中では,言語の発生はかなり最近のことであるし,文字の発生はさらに最近である.
約50万年前に Homo erectus から Homo sapiens が分かれたが,頭蓋骨の形状から,彼らは言語を話さなかったようだ.約10万年前から,頭蓋骨の形状が現代の我々のものに類似してきたようで,恐らく言語の発生もこのくらいだろうと考えられる.一方,文字の発生は,現在確認されている最も古いもので,ようやく5500年ほどを遡れるくらいである.
上記の人類史の観点から,主だった古代文字の年代を時系列に整理してみよう.
| 出来事 | 約?年前 |
|---|---|
| 人類の発生 | 5,000,000? |
| Homo erectus の発生 | 2,000,000 |
| Homo sapiens の発生 | 500,000 |
| 言語の発生 | 100,000 |
| インダス文字の起源 | 5,500 |
| エジプト文字の起源 | 5,300 |
| メソポタミア文字の起源 | 5,100 |
| 漢字の起源 | 3,500 |
| ヒッタイト文字の起源 | 3,500 |
| マヤ文字の起源 | 2,500 |
| 古代ペルシャ文字の起源 | 2,500 |
| 古代インド文字の起源 | 2,250 |
以下の円グラフは,Homo sapiens の歴史50万年における言語と文字の歴史の長さの割合を示したものである.文字の歴史は何とも浅い.
2009-05-16 Sat
■ #18. 英語史をオンラインで学習できるサイト [link][timeline][hel_education]
今回はちょっとしたサイトの紹介だけ.BBC の Ages of English Timeline は,FLASH により遊び感覚で英語史の要点を学べる.
Powered by WinChalow1.0rc4 based on chalow