2022-02-25 Fri
■ #4687. 非標準英語における再帰代名詞とその用法 [reflexive_pronoun][personal_pronoun][world_englishes][variety]
再帰代名詞 (reflexive_pronoun) は英語史研究において,いくつかの観点から重要な論点となっている.例えば,形態論的には,なぜ「所有格 + self」のものと「目的格 + self」のものが混在しているのかは古典的な問題である(cf. 「#47. 所有格か目的格か:myself と himself」 ([2009-06-14-1]) や「#2376. myself, thyself における my- と thy-」 ([2015-10-29-1])).単純形と -self 形との競合や棲み分けという語法上の話題もある(cf. 「#2322. I have no money with me. の me」 ([2015-09-05-1])).また,統語意味論的な発達についても興味深い側面がある(cf. 「#2379. 再帰代名詞の外適応」 ([2015-11-01-1])).
非標準英語を見渡すと,さらにおもしろい事実がたくさんある.例えばイングランド南東部方言,アメリカ英語の口語,またその他の変種では hisself, theirselves などの形態が用いられることがあるが,この場合,再帰代名詞体系は「所有格 + self」で一貫するため,標準英語よりも規則的となる.逆に,オーストラリア英語の1変種やイングランド南東部方言では meself などが用いられることもある (Siemund 609--10) .
用法の点でも,変種によっては主語と同一指示対象を同じくする間接目的語として -self 形ではなく単純形が使われる変種がある.以下,Siemund (610) より.
・ I'm going to buy me biscuits and chocolates.(南アフリカの Cape Flats English)
・ He was looking to buy him a house for his family.(米国の Appalachian English)
次のように,直接目的語としての例も見つけることができる.これは古英語の語法の系統を引くものとも考え得る (Siemund 610) .
・ He has cut him.
・ He went to bathe him.
Irish English や Newfoundland English では,主格代名詞の代わりに再帰代名詞が用いられる次のような例がみられる (Siemund 610) .
・ I'm afraid himself [the master of the house] will be very angry when he hears about the accident to the mare.
・ Is herself [i.e. the mistress] at home yet Jenny?
このように標準英語から一歩外に出てみると,再帰代名詞の形態にも語法にもヴァリエーションがみられることがわかる.標準英語における形態と語法も,このように相対化して考えてみるとおもしろい.
・ Siemund, Peter. "Regional Varieties of English: Non-Standard Grammatical Features." Chapter 28 of The Oxford Handbook of English Grammar. Ed. Bas Aarts, Jill Bowie and Gergana Popova. Oxford: OUP, 2020. 604--29.
2022-02-07 Mon
■ #4669. he と she を区別しない世界英語の変種 [world_englishes][new_englishes][gender][category][variety][personal_pronoun][substratum_theory]
現代の世界英語 (world_englishes) の多様性を前提とすれば,標題のような特性をもつ英語変種があったとしても驚かないだろう.3人称単数代名詞の使用において形態的に男女の区別をつけない変種,つまり標準英語のように he と she (および it)の区別を明確につけない変種があるのである.
例えば,東アフリカ英語やマレーシア英語では,しばしば指示対象にかかわらず,いずれの3人称単数代名詞も用いられ得るという.Mesthrie and Bhatt (55--56) より,関係する箇所を引用する.
Gender has proved --- despite its minor role in English --- susceptible to variation in New Englishes. Some varieties use gender in pronouns differently. Platt, Weber and Ho . . . report that in some New Englishes where the background languages do not make a distinction between he, she and it, pronouns 'are often used indiscriminately'. They offer the following examples:
41. My husband who was in England, she was by then my fiancé. (East Africa)
42. My mother, he live in kampong. (Malaysia)
Since Bantu languages do not make sex-based distinction with pronouns, and the spoken forms of the Chinese languages of Singapore and Malaysia do not differentiate gender in 3rd person pronouns . . . , substrate influences may well be at work here.
標準英語のみを知っている者にとって,これは驚くべき現象のように思われるかもしれない.しかし,英語史を研究している者にとっては,まったく驚くべきことではない.中英語では,方言にもよるが,しばしば he という3人称単数の代名詞形態が男性をも女性をも指示し得るからである.さらにひどい(!)場合には,(性を問わない)複数人称代名詞も同じ he で表わされたりする.中英語の場合には,意味論的な性の区別の消失ではなく,あくまで形態的な合一という原因により区別がつかなくなったということであり,上記の東アフリカ英語やマレーシア英語のケースとは事情が異なるのだが,「現代の World Englishes は広し」と叫ぶ前に「歴史的な英語諸変種もまた広し」と叫んでおきたい.
・ Mesthrie, Rajend and Rakesh M. Bhatt. World Englishes: The Study of New Linguistic Varieties. Cambridge: CUP, 2008.
2021-12-03 Fri
■ #4603. Jamaican Creole の連続体 [jamaica][creole][post-creole_continuum][caribbean][variety][map]
昨日の記事「#4602. Barbados が立憲君主制から共和制へ」 ([2021-12-02-1]) で,カリブ海地域の英語事情の1つの典型を示すバルバドスの歴史を略述した.英語事情と関連して同地域よりもう1つ重要な国を挙げるのであれば,間違いなくジャマイカだろう.「#1680. The West Indies の言語事情」 ([2013-12-02-1]) で触れたように,バルバドスと同様にジャマイカでも英語ベースのクレオールが行なわれている.
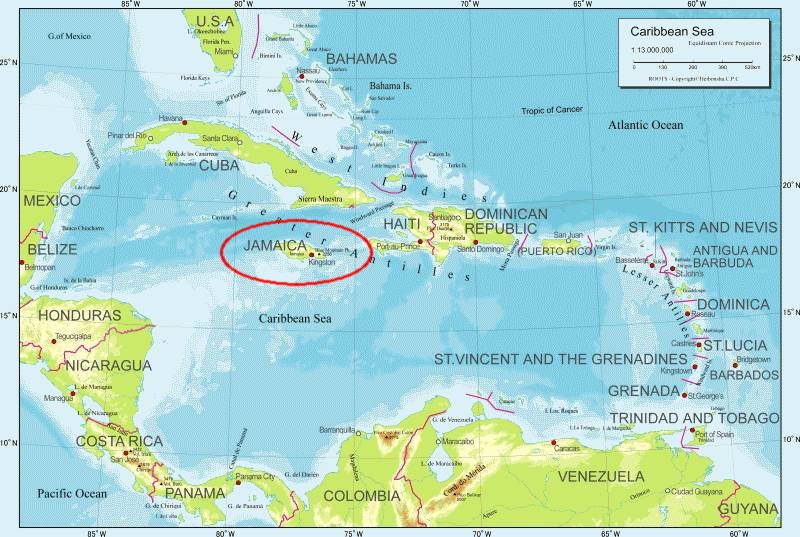
ジャマイカでは,Jamaican Creole は下層語 (basilect) として用いられており,それに対して標準(ジャマイカ)英語が上層語 (acrolect) として使われている.両者の間には中層語 (mesolect) の多数の変種が認められ,典型的な post-creole_continuum) を構成している言語社会といってよい.この連続体について,Sand (2125) を参照して見てみよう(cf. 「#385. Guyanese Creole の連続体」 ([2010-05-17-1]) とも比較).
| Standard (Jamaican) English | he went down there | ↑ | Acrolect |
| he wen dong de | | | ||
| (h)im go dong de | | | ||
| (h)im dida go dong de | | | Mesolect | |
| (h)im neva go dong de (negative only) | | | ||
| Jamaican Creole | im ben go dong de | ↓ | Basilect |
中層を構成する変種間の高低は定めがたいが,全体として連続体をなしているらしいことは分かるだろう.同一話者が場合によっては連続体のすべての変種を使いこなすというケースもあるという.また,少なくとも自分の常用する変種の近くの変種については,自らは話さずとも理解することはできるともいわれる.
数十年前のジャマイカでは公的な場面で下層・中層の変種を用いることは考えられなかったが,最近では少なくとも中層の変種はメディアや教育の場などで許容されるようになってきているという (Sand 2125) .
・ Sand, Andrea. "Second-Language Varieties: English-Based Creoles." Chapter 135 of English Historical Linguistics: An International Handbook. 2 vols. Ed. Alexander Bergs and Laurel J. Brinton. Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter, 2012. 2120--34.
[ 固定リンク | 印刷用ページ ]
2021-11-20 Sat
■ #4590. World Englishes のサンプル [world_englishes][variety][scots_english][tok_pisin][pidgin][creole][aave][south_africa][nigeria][singapore_english]
本日11月20日(土)の 13:00?14:30 に,立命館大学国際言語文化研究所の主催する「国際英語文化の多様性に関する学際研究」プロジェクトの一環として「世界の "English" から "Englishes" の世界へ」のタイトルでお話しさせていただきます(立命館大学の岡本広毅先生,これまでのご準備等,ありがとうございます).Zoom による参加も可能ですので,ご関心のある方はこちらの案内をご覧ください.
また,今朝すでにアップした私の音声ブログ Voicy の番組 「英語の語源が身につくラジオ (heldio)」 では,「立命館大学,岡本広毅先生との対談:国際英語とは何か?」と題する対談を行なっていますので,そちらもぜひ聴いてみてください.
さて,"World Englishes" に関する講演ということで,本日のブログ記事としても世界の様々な英語のサンプルを示したいと思います.ただし "Englishes" の多様性を示すために部分を切り抜いたランダムなサンプルを挙げるにすぎませんので,その点はご了承を.本日の講演では,以下の例を用いて話し始めたいと思っています.よろしくどうぞ.
・ Northern English (Yorkshire): B. Hines, Kes (1968) [qtd. in Gramley 198]
Hey up, where's tha been? They've been looking all over for thee.
・ Scots Leid: Aboot William Loughton Lorimer (2009) [qtd. in Gramley 201]
Lorimer haed aye been interestit in the Scots leid (syne he wis a bairn o nine year auld he haed written doun Scots wirds an eedioms) an his kennin o the strauchles o minority leids that he got frae his readins o the nautral press durin the Weir led him tae feel that something needit daein tae rescue the Scots laid.
・ Tok Pisin: from Mühlhäusler (1986) [qtd. in Gramley 223]
em i tok se papa i gat sik ["he said that the father was sick"]
・ Hawaiian Creole English: from Bickerton (1981) [qtd. in Gramley 226]
Jan bin go wok a hospital ["John would have worked at the hospital"]
・ Jamaican Creole: "William Saves His Sweetheart" [qtd. in Gramley 238]
nóu wants dér wáz, a úol wíč liedi lív, had wán són, níem av wiljəm. ["Once upon a time there was an old witch, who had a son whose name was William."]
・ AAVE (= African American Vernacular English): A. Walker, The Color Purple (1982) [qtd. in Gramley 269]
I seen my baby girl. I knowed it was her. She look just like me and my daddy.
・ Cape Flats SAfE: Malan (1996) [qtd. in Gramley 300]
Now me and E. speaks English. And when we went one day to a workshop --- and uh, most of the teachers there were Africaans --- and we were there; they were looking at us like that you know. And I asked E., "Why's this people staring at us?" She said, "No, I don't know."
・ Nigerian English: "Igbo Girls Like Money a Lot" (2006) (qted. in Gramley 319)
Igbo girls are hardworking, smart, successful and independent so ain't nuffin wrong in them lookin for a hardoworkin, successful man. if u ain't gats the money, they aint gon want u cos u below their level of achievement.
・ Hong Kong English: Joseph (2004) [qtd. in Gramley 321]
However, as Hong Kong is going through an economic down turn recently, we shall have to see. . . Last year we have raised more than two million Hong Kong Dollars.
・ Singapore English [qtd. in Gramley 328]
The tans [= military unit] use to stay in Sarangoon.
・ Gramley, Stephan. The History of English: An Introduction. Abingdon: Routledge, 2012.
2021-11-18 Thu
■ #4588. OED による複数形の Englishes の初例 [world_englishes][variety][oed][countability][number][plural]
普通,言語名というものは不可算名詞であり English, French, Japanese のように無冠詞で用いる.一方,日常言語生活においても言語学においても,各言語のなかに様々な変種(方言)があるということは常識的に知られており,形容詞を冠して American English, Old French, written Japanese などという表現があることは暗黙の了解事項となっている.これらは丁寧にパラフレーズするならば an American variety of English, an ancient variety of French, a written variety of Japanese などとなるだろうか.この丁寧なフレーズから,冠詞と variety of を省略したのが American English, Old French, written Japanese などの表現となっていると考えられる.
このように,あくまで表現上のショートカットととらえるのであれば,それ以上議論する余地もないかもしれない.便宜上の省略表現にすぎないからだ.しかし,Englishes のような表現は,あえてこうした発想を形式の上にも反映させようとしたところに,新しさを感じさせる.実は Englishes という複数形だけがポイントなのではなく,an English という明示的な単数形も重要なポイントなのである.要するに English の可算名詞化こそが新しいのだ.
American English と British English を合わせて two Englishes と表現できるようになった背景には,人々の英語観の転換がある.それまでも two varieties of English という言い方はできたわけで,ここから varieties of を省いて two Englishes という新しい表現を作った,ということだが,単に形式上の変化として済まされる問題ではない.認識の変化が関わっているのだ.英語を可算名詞と解釈しなおしたことのインパクトは大きい.
OED の English, adj. (and adv.) and n. の II. 2. d によると,English の可算名詞としての初例は1910年の H. L. Mencken である.この項を再現しよう.
d. As a count noun: a variety of English used in a particular context or (now esp.) a certain region of the world; (in plural) regional varieties of English considered together, often in contradistinction to the concept of English as a language with a single standard or correct form.
1910 H. L. Mencken in Evening Sun (Baltimore) 10 Oct. 6/8 (heading) The two Englishes.
1941 W. Barkley (title) Two Englishes; being some account of the differences between the spoken and the written English languages.
1964 Eng. Stud. 45 21 Many people side-step the recognition of a plurality of Englishes by such judgments as: 'Oh, that's not English, that's American.'
1978 J. Pride Communicative Needs in Learning & Use of Eng. 1 The role of literature in non-native Englishes may be focal.
1984 Eng. World-wide 5 248 An overview of some aspects of various Englishes suggesting areas of possible research.
2000 Independent (Nexis) 28 June 11 It was one of the first places to be settled in the Plantations; there's an English spoken there that's unique.
初例がアメリカ英語に関する名著 The American Language を著わしたジャーナリスト・批評家の H. L. Mencken だとは知らなかった.アメリカ英語とイギリス英語を別ものと見ていた Mencken の英語観に照らせば,彼が The two Englishes と表現したことはまったく不思議ではないが,初耳だった.
OED の例文選びのクセはあるかもしれないが,学術雑誌や新聞という堅めのメディアからの引用が多いように見受けられる.English の可算名詞としての用法が,英語研究という学術的な文脈で使い始められ,それが少しずつ一般にも広がってきたという傾向を読み取ることができそうだ.
Englishes のように複数形で用いられ得る,という英語観の変化の種が蒔かれてから,たかだか100余年.多少なりとも広く知られてきたものの,いまだ主として学術の分野で用いられるにすぎない特殊な用法とみることもできる.今後どれだけ人口に膾炙していくのか.見守っていきたい.
2021-11-15 Mon
■ #4585. 11月20日,立命館大学での講演「世界の "English" から "Englishes" の世界へ」のお知らせ [notice][world_englishes][variety][hel_education]
今週末の11月20日(土) 13:00?14:30 に,立命館大学国際言語文化研究所の主催する「国際英語文化の多様性に関する学際研究」プロジェクトの一環として「世界の "English" から "Englishes" の世界へ」のタイトルでお話しさせていただきます(立命館大学の岡本広毅先生を始め関係の方々に感謝いたします).対面と Zoom によるハイブリッド形式の講演会となっています(当日は Zoom による一般参加も可).詳しくはこちらの案内をどうぞ. *

昨今 "Englishes" や "World Englishes" という表現がよく聞かれるようになってきました."Englishes" という新表現は,英語が複数変種として存在するという事実を表わしている以上に,人々の英語に対する認識が変わってきていることを示しているのではないかと私は考えています.本講演では,英語の歴史を通じて様々な英語変種が生まれてきた過程を概観し,現在英語に作用している求心力と遠心力について議論します.英語が歴史の最初から現在に至るまで(そして,おそらく未来にかけても)常に複数形で存在してきたことを,様々な具体例とともに示していく予定です.
皆さんの英語観が,これまでの単数形の "English" から,複数形の "Englishes" へと変わっていく契機になるのではないかと期待しています.主たるオーディエンスとなる立命館大学国際コミュニケーション学域の皆さんとの議論も楽しみにしています.関心のある一般の方も,ぜひどうぞ.
2021-10-19 Tue
■ #4558. 英語史と世界英語 [hel_education][world_englishes][model_of_englishes][variety][link][heldio]
昨日の記事「#4557. 「英語史への招待:入門書10選」」 ([2021-10-18-1]) で,明治学院大学で英語史の授業を担当している泉類尚貴氏による推薦書を紹介させていただきました.その中で7番目の書籍である鳥飼玖美子(著)『国際共通語としての英語』(講談社現代新書,2011年)が意外性をもって受け取られるかもしれません.タイトルからは確かに英語を巡る重要な問題であることは分かるのですが,英語史とどのように関わるのかという疑問が浮かぶのではないでしょうか.この点を確認すべく,昨日に引き続き「英語の語源が身につくラジオ (heldio)」にて同氏と対談しました.「対談 英語史×国際英語」というお題です.以下よりどうぞ.
英語史の領域では近年,世界英語 (world_englishes) への関心が急上昇しています.私自身も食らいついていかなければと思い,にわか勉強を始めているわけですが,急激なオンライン・リソースの拡大も相まって,すでに分野を一望するのも難しい水準にまで膨張しています.関心はあってもどこから始めたらよいかと迷うのも無理もありません.
私のお勧め図書としては,唐澤一友(著)『世界の英語ができるまで』(亜紀書房,2016年)を挙げておきます.本ブログでも world_englishes や model_of_englishes にて関連する記事を多く書いてきましたが,比較的最近書いた記事をピックアップすると,次のようなラインアップになります.
・ 「#4531. 「World Englishes 入門」スライド --- オンラインゼミ合宿の2日目の講義より」 ([2021-09-22-1])
・ 「#4466. World Englishes への6つのアプローチ」 ([2021-07-19-1])
・ 「#4506. World Englishes の全体的傾向3点」 ([2021-08-28-1])
・ 「#4507. World Englishes の類型論への2つのアプローチ」 ([2021-08-29-1])
・ 「#4508. World Englishes のコーパス研究の未来」 ([2021-08-30-1])
・ 「#4169. GloWbE --- Corpus of Global Web-Based English」 ([2020-09-25-1])
・ 「#4492. 世界の英語変種の整理法 --- Gupta の5タイプ」 ([2021-08-14-1])
・ 「#4493. 世界の英語変種の整理法 --- Mesthrie and Bhatt の12タイプ」 ([2021-08-15-1])
・ 「#4501. 世界の英語変種の整理法 --- McArthur の "Hub-and-Spokes" モデル」 ([2021-08-23-1])
・ 「#4502. 世界の英語変種の整理法 --- Görlach の "Hub-and-Spokes" モデル」 ([2021-08-24-1])
世界英語を扱うオンライン・コーパスとしては,上にも触れた GloWbE (= Corpus of Global Web-Based English) を入り口としてお勧めします.このコーパスについては,専修大学文学部英語英米語学科の菊地翔太先生のHPより,こちらのページに関連情報があります.ちなみに菊地翔太先生のHPを探検し紹介するコンテンツ「菊地先生のホームページを訪れてみよう 」を大学院生が作ってくれましたので,こちらもお勧めしておきます.
2021-09-22 Wed
■ #4531. 「World Englishes 入門」スライド --- オンラインゼミ合宿の2日目の講義より [khelf][khelf_hel_intro_2021][seminar][hel_education][world_englishes][slide][variety][glowbe][khelf-conference-2021]
昨日と今日,私のゼミのオンライン合宿が行なわれています.2日目の今日は,様々な活動の間に,私の「World Englishes 入門」が挟まります.趣旨としては,次の通りです.
英語が複数形で "Englishes" として用いられるようになって久しい.現在,世界中で使われている様々な種類の英語を総称して "World Englishes" ということも多くなり,学問的な関心も高まってきている.本講演では,いかにして英語が世界中に拡散し,World Englishes が出現するに至ったのか,その歴史を概観する.そして,私たちが英語使用者・学習者・教育者・研究者として World Englishes に対してどのような態度で向き合えばよいのかについて議論する.
準備したスライドをこちらに公開します.以下にスライドの各ページへのリンクも張っておきますので,復習などにご利用ください.
1. World Englishes 入門 for khelf-conference-2021
2. World Englishes 入門 --- どう向き合えばよいのか?
3. 目次
4. 1. はじめに --- 世界に広がる英語
5. 2. イギリスから世界へ
6. 関連年表
7. 3. 様々な英語
8. ピジン語とクレオール語
9. 4. 英語に働く求心力と遠心力
10. 5. 世界英語のモデル
11. おわりに
12. 参考文献
2021-09-09 Thu
■ #4518. OALD10 の世界英語のレーベル15種 [world_englishes][variety][lexicography][dictionary]
昨年,伝統ある英語学習者用の英英辞書 Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary of Current English の第10版 (= OALD10) が出版された.私も第4版や第5版の頃から長らくお世話になっている辞書だが,冊子体のみならず CD/DVD 版で提供される時代になってきたかと思いきや,今回の第10版ではディスク媒体の配布すらなく,アクセスコード付きのオンライン版のみが提供される形となっている.時代は変わったものだ.ただ,重厚な冊子体版は相変わらず健在なので,パラパラめくっては(内容とともに)質感を楽しんでいる.
OALD は伝統的にイギリス英語を基盤とする記述に定評があるが,無視できない存在であるアメリカ英語の記述にも力を割いてきた経緯がある.さらに昨今は World Englishes の時代ということもあり,世界の諸変種の語彙を取り込んだ編纂方針が目立つようになってきた.実際,今回の第10版では,巻末に "English across the world" と題するコラムが掲載されている.小見出しとして "The spread of English" や "Englishes, not English" という文言もみえる.前者の冒頭は次の通り.
English is spoken as a first language by more than 350 million people throughout the world, and used as a second language by as many, if not more. One in five of the world's population speaks English with some degree of competence. It is an official or semi-official language in over 70 countries, and it plays a significant role in many more.
続けて世界の地域ごとに英語変種が簡単に解説されていくのだが,辞書で使用される各変種を示すレーベルも同時に紹介される.変種レーベルの一覧は見返しに記載されているが,それを再現すると次の通り15種類が確認される.BrE (= British English), NEngE (= Northern England English), ScotE (= Scottish English), WelshE (= Welsh English), IrishE (= Irish English), US (= American English), CanE (= Canadian English), NAmE (= North American English), AustralE (= Australian English), NZE (= New Zealand English), SAfrE (= South African English), WAfrE (= West African English), EAfrE (= East African English), IndE (= Indian English (the English of South Asia)), SEAsian E (= South-East Asian English) .
World Englishes の地域ベースの分類としては標準的でバランスのとれたものといってよい.伝統的イギリス系辞書も,このような配慮を示す時代になってきたのだなあ.
・ Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary of Current English. 10th ed. Ed. A. S. Hornby. Oxford: Oxford UP, 2020.
2021-09-08 Wed
■ #4517. World Englishes の研究は方言学の一種か? [world_englishes][dialectology][dialect][variety]
連日 World Englishes (英語諸変種)の記事を書いているが,世界で用いられている様々な英語の諸変種とは一般の用語でいえば英語の諸方言にほかならない.「方言」 (dialect) のことを「変種」 (variety) と呼び替えているのは,多少なりとも神経質で臆病な社会言語学の慣習というべきもので,学術的な言い分があることは理解しつつ私も常用しているが,たいていの場合は「方言」のほうが分かりやすいと本当は思っている.
では,World Englishes の研究は英語の「方言学」 (dialectology) とみてよいのかというと,理屈上は Yes だが,慣習上は No というところだろう.学術用語の常で "dialectology" という用語も,歴史を背負って手垢がついている."English dialectology" という場合には,イギリスやアメリカの内部の諸方言の研究を指すのが典型的であり,たとえばインド英語やジャマイカ英語の研究を指して "English dialectology" とは言わない.学術の伝統もあってやむを得ないところもあるのだが,英米中心主義の用語といってよい.
一方,そのような手垢を取り除いて「地域によって変異する様々な英語」のことを "dialect(s)" とみなす純粋な立場を取れば,インド英語やジャマイカ英語も各々1つの "dialect" に違いなく,それを研究することは "English dialectology" に貢献することになろう.しかし,現在,どうやらそのような見解は希薄である.インド英語やジャマイカ英語の研究は "World Englishes" の研究として言及されるのである.このような呼び替えに,英語学の伝統の「闇」が垣間見える,といってもよいかもしれない.ただし,ENL 変種と ESL 変種は様々な点で異なるのだということも,やはり一面の真実を含んでいるようにも思われるので,この問題についてこれ以上の議論は控えておく.
上記を踏まえつつも私は,伝統的な "English dialectology" と,昨今とみに注目度を増している "World Englishes" の研究は,もっと接近すべきだと考えている.現代のイギリスやアメリカの内部で細分化されている諸方言や,イギリスにおいて古英語から現代英語まで多様に存在してきた歴史的な諸方言にみられる豊富な変異が,World Englishes 間にみられる豊富な変異と比べて,質においても量においても劣っているとは思わないからである.空間的な規模でいえば,世界の一角にすぎないイギリスやアメリカの英語と世界の隅々に分布する英語とを比べることは「格違い」のように思われるかもしれないが,否,英語が世界化する以前から,例えばブリテン諸島内部だけを念頭においても,言語的変異は思いのほか豊かだったのである.
上記の私の考え方とおよそ同趣旨の Anderwald (265) の見解を引用する.
Perhaps most importantly, the recent dialectological and sociolinguistic study of non-standard varieties has shown the enormous breadth of variation that English in Britain and the United States already demonstrates. Whenever we find patterns in World Englishes that diverge from standard British or American English, it is of the utmost importance to take this internal variability into consideration. Bearing in mind Chambers's idea of vernacular universals, comparing constructions in Englishes worldwide with just the codified standard(s) is comparing apples with oranges, or, worse, with just one orange. We might find that what looks like an exotic feature of a variety of English in the southern, eastern or other hemisphere, is perhaps mirrored in an isolated dialect area in the Scottish Highlands, in a village in Ireland, or in an undocumented variety of the English Midlands. The call thus is for researchers of World Englishes to take note of the extensive dialectological work that is currently underway on varieties in non-standard 'homeland' varieties, to avoid this kind of mismatch, and ultimately misanalysis.
私の英語史研究における中心的なテーマは中英語方言学にあるのだが,一見するとかけ離れているようにみえる現代の World Englishes に関心を寄せているのは,このような理由からである.
・ Anderwald, Lieselotte. "World Englishes and Dialectology." Chapter 13 of The Oxford Handbook of World Englishes. Ed. by Markku Filppula, Juhani Klemola, and Devyani Sharma. New York: OUP, 2017. 252--71.
2021-09-04 Sat
■ #4513. indigenised Englishes と English creoles の違いは程度の問題? [esl][creole][variety][world_englishes][new_englishes][language_shift][contact]
歴史的にいえばアイルランド英語やインド英語のような "indigenised Englishes" は,基層言語と英語との言語接触および言語交替 (language_shift) の結果として生じた言語変種であり,英語との遺伝的な関係が保たれているとされる.一方,スリナムの Saramaccan のような "English creoles" は,英語との言語接触は前提とされているが,語彙提供言語である英語とは直接の遺伝的な関係のない言語変種とされる (cf. 「#463. 英語ベースのピジン語とクレオール語の一覧」 ([2010-08-03-1])) .
上記は indigenised Englishes と English creoles を対比させる際の従来の説明の仕方である.要するにクレオール語を言語接触の例外的なケースととらえる立場だ.代表的な論者として Thomason and Kaufman を挙げておこう.
しかし,近年では indigenised Englishes と English creoles の違いは,従来の見解が主張するような本質の違いではなく,程度の問題にすぎないのではないかという見方が広がってきている.そのような見方を採用する Winford (196) の説明に耳を傾けよう.
This recognition has led to a growing rapport between the study of the New Englishes and the study of English-lexicon creoles in the last couple of decades. It has given impetus to an earlier tradition of research concerned with the relationship between the two types of contact Englishes, which dates back to the 1980s . . . . The links between the two fields have more recently been reaffirmed in the work of scholars . . . . It is now generally acknowledged that the creation of the New Englishes shares a great deal in common with creole formation, with regard to both the socio-historical circumstances and the processes of change that were involved. The challenge facing us is to show how these two dimensions of language shift---the socio-historical and the linguistic---interact in the emergence of contact varieties. On the one hand, the diversity of outcomes that resulted from the spread of English to various colonies provides support for Thomason and Kaufman's claim that 'it is the sociolinguistic history of the speakers, and not the structure of their language, that is the primary determinant of the linguistic outcome of language contact' (1988: 35). At the same time, the emergence and evolution of contact Englishes supports the view that different outcomes are also constrained by the same principles and processes of change that operate in shift situations generally. All of this suggests that the division between 'indigenized English' and 'creoles' is essentially an artificial one, since we find diversity within each group and significant overlap between the two.
Winford にとっては,indigenised Englishes と English creoles の違いは程度の問題であり,引用の最後にある通り,人工的な区分にすぎないようだ.Winford はこの1節の後,Schneider の "Dynamic Model" を参照して議論を続けていく.このモデルについては「#4497. ポストコロニアル英語変種に関する Schneider の Dynamic Model」 ([2021-08-19-1]) を参照.
・ Winford, Donald. "World Englishes and Creoles." Chapter 10 of The Oxford Handbook of World Englishes. Ed. by Markku Filppula, Juhani Klemola, and Devyani Sharma. New York: OUP, 2017. 194--210.
・ Thomason, Sarah Grey and Terrence Kaufman. Language Contact, Creolization, and Genetic Linguistics. Berkeley: U of California P, 1988.
2021-08-31 Tue
■ #4509. "angloversals" --- 世界英語にみられる「普遍的な」言語項目 [world_englishes][typology][variety][terminology]
一昨日の記事「#4507. World Englishes の類型論への2つのアプローチ」 ([2021-08-29-1]) で "angloversals" という用語に触れた.世界英語 world_englishes の諸変種を見渡すと,歴史的・遺伝的関係は希薄であるにも関わらず,異なる変種間で似たような言語特徴が確認されることがある.いずれも広い意味では「英語」であるのだから,共通項が見つかること自体はさほど不思議ではないと思われるかもしれない.しかし,標準英語では認められない言語特徴が,歴史的な関係が希薄な諸変種間に広く認められるということであれば,そこには何か抜き差しならぬ理由があるのではないかと疑うのも当然である.こういった共通特徴を,仮に "Angloversals" と呼んでおこうということらしい."universals" をもじっていて少々ミスリーディングな名称だが,厳密な意味での「普遍」というよりは多くの変種に見られる「傾向」として理解しておくべきであることは,念のために指摘しておこう.
さて,この用語を作ったのは Mair である.似たような用語として,Chambers の作った "vernacular universals" というものもある.この辺りの用語を巡る経緯について,Siemund and Davydova (135) の説明を参照しよう.
Another line of research departs from the observation that World Englishes (or varieties of English) frequently exhibit identical, or at least similar, non-standard morpho-syntactic phenomena, with common ancestors of these phenomena being difficult to reconstruct in the historical dialects of the British Isles. Such observation have led to the coinage of the label 'angloversals' (Mair 2003). Another notion used with a similar extension is 'vernacular universals' (Chambers 2001, 2003, 2004).
Chambers defines vernacular universals as 'a small number of phonological and grammatical processes [that] recur in vernaculars wherever they are spoken' and views them as inherent features of unmonitored speech coming about as a result of the workings of the human language faculty (Chambers 2004: 128--29).
では,"angloversals" として,具体的にはどのような言語特徴が候補として挙げられているのだろうか.Siemund and Davydova (135--36) より,いくつか挙げてみよう.
・ 不規則動詞の水平化
・ 無標の単数形
・ 主語と動詞の不一致
・ 多重否定
・ 連結詞 (copula) の省略
・ 単位名詞の複数標示の欠如
・ yes/no 疑問文における倒置の欠如
・ 等位される主語として I ではなく me を用いる傾向
・ 副詞が形容詞と同形となる現象
・ 過去形の否定を表わすのに never が動詞に前置される現象
・ 定冠詞の過剰使用
これらは,一般にL2英語によく見られる言語特徴と同じであると言っても,さほど外れていない.一般言語学的普遍性が英語の諸変種において顕現しているもの,それが "angloversals" なのだろう.
・ Siemund, Peter and Julia Davydova. "World Englishes and the Study of Typology and Universals." Chapter 7 of The Oxford Handbook of World Englishes. Ed. by Markku Filppula, Juhani Klemola, and Devyani Sharma. New York: OUP, 2017. 123--46.
・ Mair, Christian. "Kreolismen and verbales Identitätsmanagement im geschriebenen jamaikanischen Englisch." Zwischen Ausgrenzung und Hybridisierung. Ed. E. Vogel, A. Napp and W. Lutterer. Würzburg: Ergon, 2003.
・ Chambers, J. K. "Vernacular Universals." ICLaVE 1: Proceedings of the First International Confrerence on Language Variation in Europe. Ed. J. M. Fontana, L. McNally, M. T. Turell, and E. Vallduvi. Barcelona: Universitat Pompeu Fabra, 2001.
・ Chambers, J. K. Sociolinguistic Theory: Linguistic Variation and its Social Implications. Oxford, UK/Malden, US: Blackwell.
・ Chambers, J. K. "Dynamic Typology and Vernacular Universals." Dialectology Meets Typology: Dialect Grammar from a Cross-Linguistic Perspective. Ed. B. Kortmann. Berlin/New York: Gruyter, 2004.
2021-08-30 Mon
■ #4508. World Englishes のコーパス研究の未来 [world_englishes][variety][corpus][multilingualism][methodology][ice]
連日 World Englishes に関する話題を取り上げている.比較的新しい分野であるとはいえ,この分野でのコーパスを用いた研究には少なくとも数十年ほどの実績がある.その走りは,1960年代以降,世紀末にかけて徐々に蓄積されてきた,主として英米変種に焦点を当てた各100万語からなるコーパス群,いわゆる "The Brown family of corpora" だったといってよいだろう (cf. 「#428. The Brown family of corpora の利用上の注意」 ([2010-06-29-1])) .
この "Brown family" は,次なる大型プロジェクトにもインスピレーションを与えた.「#517. ICE 提供の7種類の地域変種コーパス」 ([2010-09-26-1]) で紹介した International Corpus of English である.1990年に Sydney Greenbaum が計画を発表して以来,イギリス英語とアメリカ英語はもちろん,現在までにカナダ英語,東アフリカ英語,香港英語,インド英語,アイルランド英語,ジャマイカ英語,ニュージーランド英語,ナイジェリア英語,フィリピン英語,シンガポール英語,スリランカ英語など様々な英語変種の100万語規模のコーパスが編纂されてきた(一部のものはダウンロード可能).互いに比較可能な形でデザインされており,ICECUP という検索ソフトウェアも用意されている.本ブログの ice の記事も参照.
続いて,2013年にこの分野における近年の最大の成果である GloWbE (= Corpus of Global Web-Based English) がオンライン公開された.「#4169. GloWbE --- Corpus of Global Web-Based English」 ([2020-09-25-1]) で紹介した通り,20カ国からの英語変種を総合した19億語からなる巨大世界英語変種コーパスである.現在,このコーパスは世界英語に関する研究でよく利用されている.
このように World Englishes を巡るコーパスの編纂と使用が促進されてきたが,今後,この方面ではどのような展開が予想されるだろうか.Mair (118--19) は今後の展開(あるいは希望)として3点を挙げている.
(1) 諸変種の歴史の初期段階のコーパスの編纂が待たれる
(2) 諸変種の実態についてウェブ上のデータを利用することがますます有用となってくる
(3) 諸変種の多くについてマルチリンガルな状況で使用されているのが実態である以上,従来の英語のモノリンガル・コーパスという枠組みではなく,英語を含むマルチリンガル・コーパスというつもりで編纂されていくべきである
とりわけ (3) は,伝統的な「英語学」を学んできた私のような者にとっては,ショッキングな,目から鱗が落ちるような未来像でもある.World Englishes 研究は,すでに英語学の枠からはみ出し,"sociolinguistics of globalisation" (Mair 119) というべき目標へと踏み出していることを示唆する.そして「英語史」の研究も,世界英語を考慮に入れる以上,こうした動向と連動して,ますます開かれたものになっていくのだろう.
・ Mair, Christian. "World Englishes and Corpora." Chapter 6 of The Oxford Handbook of World Englishes. Ed. by Markku Filppula, Juhani Klemola, and Devyani Sharma. New York: OUP, 2017. 103--22.
2021-08-29 Sun
■ #4507. World Englishes の類型論への2つのアプローチ [world_englishes][variety][typology][linguistic_ideology][ecolinguistics][methodology]
昨日の記事「#4506. World Englishes の全体的傾向3点」 ([2021-08-28-1]) で触れたように,世界英語 (world_englishes) の研究はコーパスなどを用いて急速に発展してきている.Fong (88) による概括を参照すると,研究の潮流としては,世界英語の普遍性と多様性を巡る類型論 (typology) には大きく2つの方向性があるようだ.
(1) 1つは様々な英語に共通する "angloversals" を探る方向性である.ENL と ESL の英語変種を比べても,一貫して受け継がれているかのように見える不変の特徴が確認される.ここから "angloversals" と称される英語諸変種の共通点を探る試みがなされてきた.「継承」という通時的な側面はあるが,その結果としての類似性を重視する共時的な視点といってよいだろう.
(2) もう1つは,どちらかというと英語の諸変種間で共通する側面や相違する側面があることを認め,なぜそのような共通点や相違点があるのかを,歴史社会的なコンテクストに基づいて説明づけようとする視点である.主唱者の Mufwene (2001) の見方を参照すれば,諸英語の歴史的発展は接触言語の特徴や社会経済的な環境,いわゆる「言語生態系」に敏感なものであるということになる.
Fong は,世界英語研究への対し方として,このような2つの系譜があることをサラっと紹介しているが,言語イデオロギー的には,この2つは相当に異なるベルクトルをもっているものと思われる.研究者も自らがどちらの視点に立つかを自覚しておく必要があるように思われる.
・ Fong, Vivienne. "World Englishes and Syntactic and Semantic Theory." Chapter 5 of The Oxford Handbook of World Englishes. Ed. by Markku Filppula, Juhani Klemola, and Devyani Sharma. New York: OUP, 2017. 84--102.
・ Mufwene, S. S. The Ecology of Language Evolution. Cambridge: CUP, 2001.
2021-08-28 Sat
■ #4506. World Englishes の全体的傾向3点 [world_englishes][variety][medium][register]
Mair (116) によると,世界英語 (world_englishes) の研究者たちがおよそ合意している主たるトレンドが3つあるという.
1. Accent divides, whereas grammar unites (with the lexicon being somewhere in between)
2. There is divergence in speech, but convergence in writing.
3. Variation is suppressed in public and formal discourse, but pervasive in informal settings.
このように言われると,直感的にいずれもその通りなのだろうと思われ,驚きはしない.ただ,ここで指摘されている世界英語の傾向は,世界英語コーパスなどによる客観的で実証的な研究によっておよそ裏付けられるという点が重要である.大雑把にいえば,話し言葉に典型的なインフォーマルな英語使用においては,諸変種間で大きな違いがみられるが,書き言葉に典型的なフォーマルな英語使用では,標準への指向がみられるということだ.
この3点は,一見およそ似たようなことを述べているようにも思われるかもしれない.確かに互いに重なる部分があるのも事実である.しかし,各々は原則として異なる軸足に立った傾向の指摘となっていることに注意したい.1点目は,発音か文法か(語彙か)という言語部門に関するパラメータに基づいている.2点目は話し言葉か書き言葉かという媒体の問題に関係する.3点目は,社会語用論的なセッティング,端的にいえばフォーマルかインフォーマルかという言語使用の背景に注目している.
話し言葉といえば,たいていインフォーマルであり,当然ながら発音の差異に関心が向くだろう.しかし,フォーマルな話し言葉の使用は学術講演や政治演説などで普通に観察されるし,そこでは発音と比べれば相対的に目立たないだけで当然ながら文法や語彙も関与しているのである.また,書き言葉といえばフォーマルとなることが多いが,チャットや会話のスクリプトのように必ずしもそうではない書き言葉の使用はいくらでもあるし,発音の変異を反映する非標準的なスペリング使用もみられる.
3つのパラメータは,互いに重なるが原理的には独立したものとして理解しておくのが適切である.この点については「#230. 話しことばと書きことばの対立は絶対的か?」 ([2009-12-13-1]),「#2301. 話し言葉と書き言葉をつなぐスペクトル」 ([2015-08-15-1]),「#839. register」 ([2011-08-14-1]) などを参照されたい.
・ Mair, Christian. "World Englishes and Corpora." Chapter 6 of The Oxford Handbook of World Englishes. Ed. by Markku Filppula, Juhani Klemola, and Devyani Sharma. New York: OUP, 2017. 103--22.
2021-08-24 Tue
■ #4502. 世界の英語変種の整理法 --- Goerlach の "Hub-and-Spokes" モデル [model_of_englishes][world_englishes][new_englishes][variety][sociolinguistics]
昨日の記事「#4501. 世界の英語変種の整理法 --- McArthur の "Hub-and-Spokes" モデル」 ([2021-08-23-1]) に引き続き,同じ "Hub-and-Spokes" モデルではあるが Görlach が1988年および1990年に発表したバージョンを示そう.ここでは McArthur が1991年の論文 (p. 20) で図示しているものを示す.
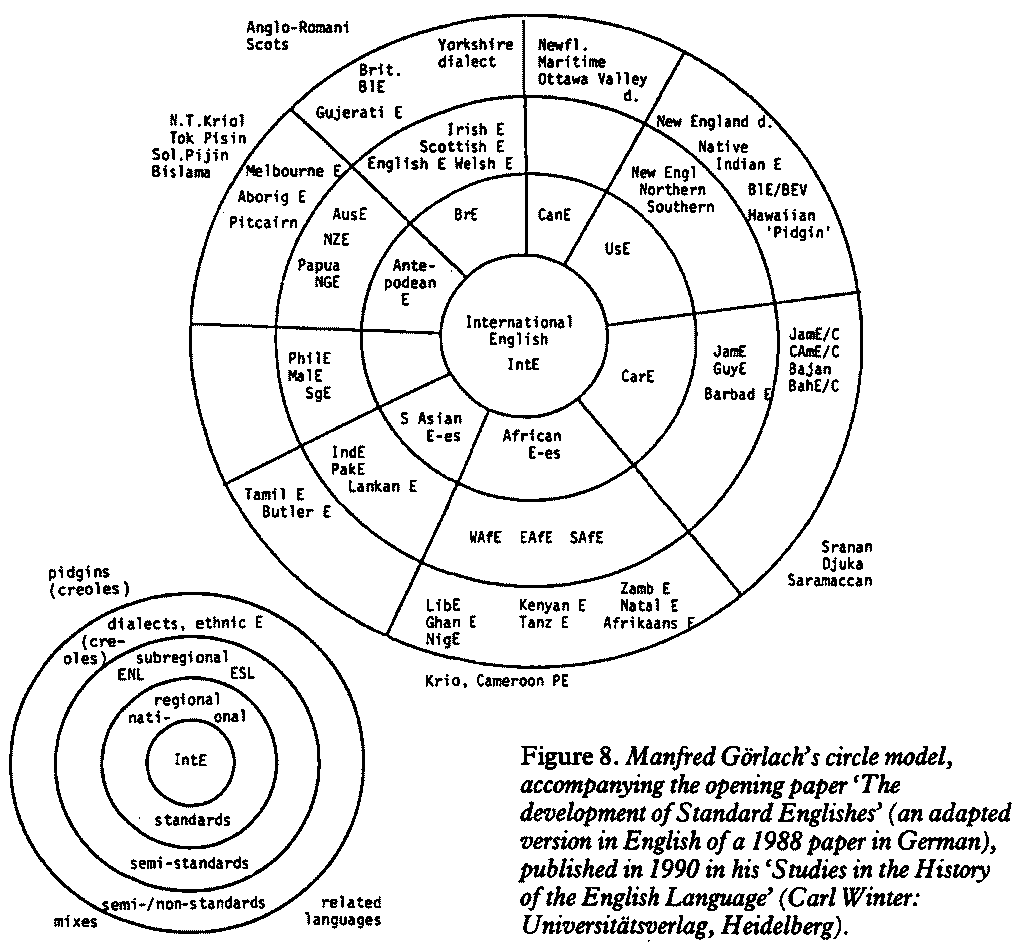
McArthur のモデルと発想は変わらないが,より細かく幾重もの同心円が描かれているのが特徴である.内側から外側に向かって,"International English", "regional/national standards", "subregional ENL---ESL semi-standards", "dialects, ethnic E (creoles), semi-/non-standards" と広がっていき,そのさらに外側に "pidgins (creoles), mixes, related languages" の領域が設けられている.
昨日見たような McArthur のモデルに向けられた批判は,およそ Görlach モデルにも当てはまる.例えば,同心円の左下辺りに Tamil E と Butler E が並んでいるが,このように地域変種と社会変種(に基づくピジン語)を並列させるのは適切なのだろうか.また,歴史的な観点が埋め込まれておらず,地政学的なモデルに終止しているきらいもある,等々.
英語変種を図式化 (model_of_englishes) してとらえようとする試みは多々あれど,いずれも一長一短あり,複雑な現実をきれいに落とし込むのは至難の業である.
・ Görlach, M. Studies in the History of the English Language. Heidelberg: Winter, 1990.
・ McArthur, Tom. "Models of English." English Today 32 (1991): 12--21.
2021-08-23 Mon
■ #4501. 世界の英語変種の整理法 --- McArthur の "Hub-and-Spokes" モデル [model_of_englishes][world_englishes][new_englishes][variety][sociolinguistics]
英語変種の整理法として比較的早くに提起されたモデルの1つに "Hub-and-Spokes" モデルがある.様々な英語変種から構成される同心円の図を車輪のハブとスポークに見立てた視覚モデルだ.このモデルにもいくつかのバージョンがあるが,McArthur が1987年の論文 ("The English Languages?", 11) で提示したものを覗いてみたい.1991年の論文 ("Models of English", 19) に再掲されている図を再現する.
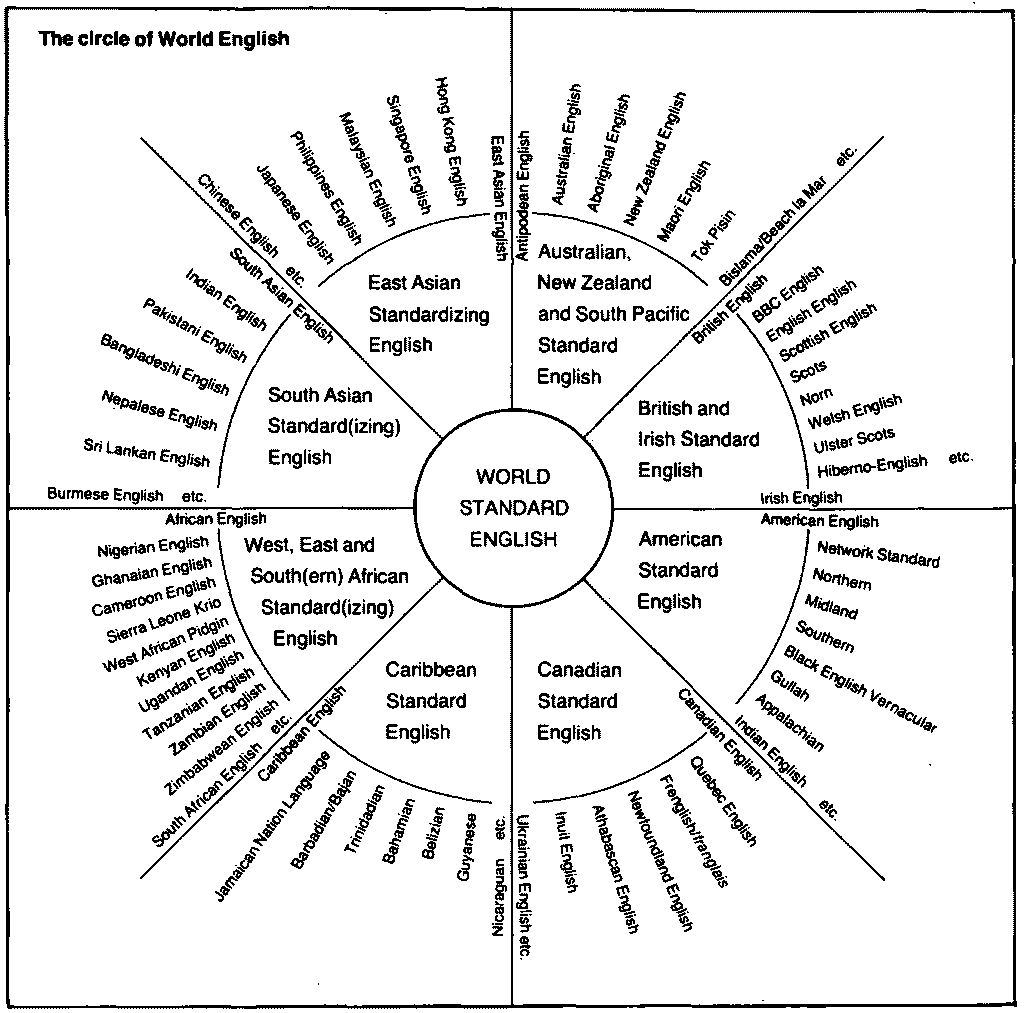
このモデルの要点について,McArthur ("The English Languages?", 11) は次のように解説している.
The purpose of the model is to highlight the broad three-part spectrum that ranges from the 'innumerable' popular Englishes through the various national and regional standards to the remarkably homogeneous but negotiable 'common core' of World Standard English.
McArthur 自身も述べているように,このモデルはあくまでたたき台として提案されたものであり,様々な問題や議論が生じることが予想される.実際,いくらでも批判的なコメントを加えることができる.個々の変種の分類はこの通りで広く受け入れられるのか,BBC English と Norn が同列に置かれているのはおかしいのではないか,また Australian English と Tok Pisin も然り.さらに本質的な問いとして,そもそも中央に据えられている "World Standard English" というものは現実に存在するのか.
この図が全体として World English を構成しているという見方については,McArthur ("The English Language", 10) は「逆説的な事実」であると評している.
Within such a model, we can talk about a more or less 'monolithic' core, a text-linked World Standard negotiated among a variety of more or less established national standards. Beyond the minority area of the interlinked standards, however, are the innumerable non-standard forms --- the majority now as in Roman times, with all sorts of reasons for being unintelligible to each other. There is nothing new in this, and it is a state of affairs that is unlikely to change in the short or even the medium term. In the distinctness of Scots from Black English Vernacular, Cockney from Krio, and Texian from Taglish, we have all the age-old criteria for talking about mutually unintelligible languages. Nonetheless, all such largely oral forms share in the totality of World English, and can be shown to share in it, however bafflingly different they may be. This is a paradox, but it is also a fact.
・ McArthur, Tom. "The English Languages?" English Today 11 (1987): 9--11.
・ McArthur, Tom. "Models of English." English Today 32 (1991): 12--21.
2021-08-19 Thu
■ #4497. Schneider の ポストコロニアル英語変種に関する "Dynamic Model" [model_of_englishes][world_englishes][new_englishes][variety][sociolinguistics][contact][accommodation][variation][dynamic_model]
先日,「#4492. 世界の英語変種の整理法 --- Gupta の5タイプ」 ([2021-08-14-1]) や「#4493. 世界の英語変種の整理法 --- Mesthrie and Bhatt の12タイプ」 ([2021-08-15-1]) で世界英語変種について2つの見方を紹介した.他にも様々なモデルがあり,model_of_englishes で取り上げてきたが,近年もっとも野心的なモデルといえば,Schneider の ポストコロニアル英語変種に関する "Dynamic Model" だろう.2001年から練り上げられてきたモデルで,今や広く受け入れられつつある.このモデルの骨子を示すのに,Schneider (47) の以下の文章を引用する.
Essentially, the Dynamic Model claims that it is possible to identify a single, underlying, fundamentally uniform evolutionary process which can be observed, with modifications and adjustments to local circumstances, in the evolution of all postcolonial forms of English. The postulate of some sort of a uniformity behind all these processes may seem surprising and counterintuitive at first sight, given that the regions and historical contexts under investigation are immensely diverse, spread out across several centuries and also continents (and thus encompassing also a wide range of different input languages and language contact situations). It rests on the central idea that in a colonization process there are always two groups of people involved, the colonizers and the colonized, and the social dynamics between these two parties has tended to follow a similar trajectory in different countries, determined by fundamental human needs and modes of behaviour. Broadly, this can be characterized by a development from dominance and segregation towards mutual approximation and gradual, if reluctant, integration, followed by corresponding linguistic consequences.
このモデルを議論するにあたっては,その背景にあるいくつかの前提や要素について理解しておく必要がある.Schneider (47--51) より,キーワードを箇条書きで抜き出してみよう.
[ 4つの(歴史)社会言語学の理論 ]
1. Language contact theory
2. A "Feature pool" of linguistic choices
3. Accommodation
4. Identity
[ 2つのコミュニケーション上の脈絡 ]
1. The "Settlers' strand"
2. The "Indigenous strand"
[ 4つの(歴史)社会言語学的条件と言語的発展の関係に関わる要素 ]
1. The political history of a country
2. Identity re-writings of the groups involved
3. Sociolinguistic conditions of language contact
4. Linguistic developments and structural changes in the varieties concerned
[ 5つの典型的な段階 ]
1. Foundation
2. Exonormative stablization
3. Nativization
4. Endonormative stabilization
5. Differentiation
Schneider のモデルは野心的かつ包括的であり,その思考法は Keller の言語論を彷彿とさせる.今後,どのように議論が展開していくだろうか,楽しみである.
・ Schneider, Edgar W. "Models of English in the World." Chapter 3 of The Oxford Handbook of World Englishes. Ed. by Markku Filppula, Juhani Klemola, and Devyani Sharma. New York: OUP, 2017. 35--57.
・ Keller, Rudi. On Language Change: The Invisible Hand in Language. Trans. Brigitte Nerlich. London and New York: Routledge, 1994.
2021-08-16 Mon
■ #4494. "South Seas Jargon" --- 南太平洋混合語 [world_englishes][variety][pidgin][tok_pisin]
昨日の記事「#4493. 世界の英語変種の整理法 --- Mesthrie and Bhatt の12タイプ」 ([2021-08-15-1]) で紹介した分類の (k) Jargon Englishes の1例として,19世紀の "South Seas Jargon" が挙げられている.「南太平洋混合語」と解釈すべき英語の変種(未満のもの?)で,他の呼び名もあるようだが,これについて McArthur の事典で調べてみた.
PACIFIC JARGON ENGLISH, also South Seas English, South Seas Jargon, Jargon. A trade jargon used by 19c traders and whalers in the Pacific Ocean, the ancestor of Melanesian Pidgin English. The whalers first hunted in the eastern Pacific but by 1820 were calling regularly at ports in Melanesia and took on crew members from among the local population. The sailors communicated in Jargon, which began to stabilize on plantations throughout the Pacific area after 1860, wherever Islanders worked as indentured labourers.
19世紀のメラネシアで,西洋および地元の貿易商人や捕鯨船員が相互のコミュニケーションのために使用していた混合語であり,後に太平洋地域のプランテーションで広く定着することになるピジン語 "Melanesian Pidgin English" の起源となった言語変種である.では,後に発達したこの "Melanesian Pidgin English" とはいかなるものだろうか.同じく McArthur の事典より.
MELANESIAN PIDGIN ENGLISH, also Melanesian Pidgin. The name commonly given to three varieties of Pidgin spoken in the Melanesian states of Papua New Guinea (Tok Pisin), Solomon Islands (Pijin), and Vanuatu (Bislama). Although there is a degree of mutual intelligibility among them, the term is used by linguists to recognize a common historical development and is not recognized by speakers of these languages. The development of Melanesian Pidgin English has been significantly different in the three countries. This is due to differences in the substrate languages, the presence of European languages other than English, and differences in colonial policy. In Papua New Guinea, there was a period of German administration (1884--1914) before the British and Australians took over. The people of Vanuatu were in constant contact with the French government and planters during a century of colonial rule (1880--1980). However, Solomon Islanders have not been in contact with any European language other than English.
"Melanesian Pidgin English" それ自体も,歴史的に詳しくみれば複数の変種の集合体というべきものだが,言語としては互いによく似ているし影響関係もあったようである.パプアニューギニアの Tok Pisin, ソロモン諸島の Solomon Pijin, バヌアツの Bislama の相互関係については「#1688. Tok Pisin」 ([2013-12-10-1]),「#1689. 南西太平洋地域のピジン語とクレオール語の語彙」 ([2013-12-11-1]) を参照されたい.
これらのメラネシアの国々では各ピジン英語が lingua_franca として広く用いられているが,その歴史はせいぜい150--200年ほどしかないということになる.「#1536. 国語でありながら学校での使用が禁止されている Bislama」 ([2013-07-11-1]) もおもしろい.
・ McArthur, Tom, ed. The Oxford Companion to the English Language. Oxford: OUP, 1992.
2021-08-15 Sun
■ #4493. 世界の英語変種の整理法 --- Mesthrie and Bhatt の12タイプ [model_of_englishes][world_englishes][new_englishes][variety][pidgin][creole][esl][efl][enl]
昨日の記事「#4492. 世界の英語変種の整理法 --- Gupta の5タイプ」 ([2021-08-14-1]) に引き続き,世界の英語変種の整理法について.今回は World Englishes というズバリの本を著わした Mesthrie and Bhatt (3--10) による12タイプへの分類を紹介したい.昨日と同様,Schneider (44) を経由して示す.
(a) Metropolitan standards (i.e. the "respected mother state's" norm as opposed to colonial offspring, i.e. in our case British English and American English as national reference forms).
(b) Colonial standards (the standard forms of the former "dominions," i.e. Australian, New Zealand, Canadian, South African English, etc.).
(c) Regional dialects (of Britain and North America, less so elsewhere in settler colonies).
(d) Social dialects (by class, ethnicity, etc.; including, e.g. Broad, General and Cultivated varieties in Australia, African American Vernacular English, and others).
(e) Pidgin Englishes (originally rudimentary intermediate forms in contact, and nobody's native tongue; possibly elaborated in complexity, e.g. West African Pidgin Englishes).
(f) Creole Englishes (fully developed but highly structured, hence of questionable relatedness to the lexifier English; e.g. Jamaican Creole).
(g) English as a Second Language (ESL) (postcolonial countries where English plays a key role in government and education; e.g. Kenya, Sri Lanka).
(h) English as a Foreign Language (EFL) (English used for external and international purposes; e.g. China, Europe, Brazil).
(i) Immigrant Englishes (developed by migrants to an English-dominant country; e.g. Chicano English in the United States)).
(j) Language-shift Englishes (resulting from the replacement of an ancestral language by English; possibly, like Hiberno English, becoming a social dialect in the end).
(k) Jargon Englishes (unstable pre-pidgins without norms and with great individual variation, e.g. South Seas Jargon in the nineteenth century)
(l) Hybrid Englishes (mixed codes, prestigious among urban youths; e.g. "Hinglish" mixing Hindi and English).
英語(使用)の歴史,地位,形式,機能の4つのパラメータを組み合わせた分類といえる.実際に存在する(した)ありとあらゆる英語変種を網羅している感がある.ただし,水も漏らさぬ分類というわけではない.この分類では,複数のカテゴリーにまたがって所属してしまうような英語変種もあるのではないか.
・ Schneider, Edgar W. "Models of English in the World." Chapter 3 of The Oxford Handbook of World Englishes. Ed. by Markku Filppula, Juhani Klemola, and Devyani Sharma. New York: OUP, 2017. 35--57.
・ Mesthrie, Rajend and Rakesh M. Bhatt. World Englishes: The Study of New Linguistic Varieties. Cambridge: CUP, 2008.
Powered by WinChalow1.0rc4 based on chalow