2025-11-10 Mon
■ #6041. 2025年度の朝カルシリーズ講座の第7回「I --- 1人称単数代名詞をめぐる物語」をマインドマップ化してみました [asacul][mindmap][notice][etymology][personal_pronoun][case][oe][indo-european][link][hel_education][sound_change][gvs]
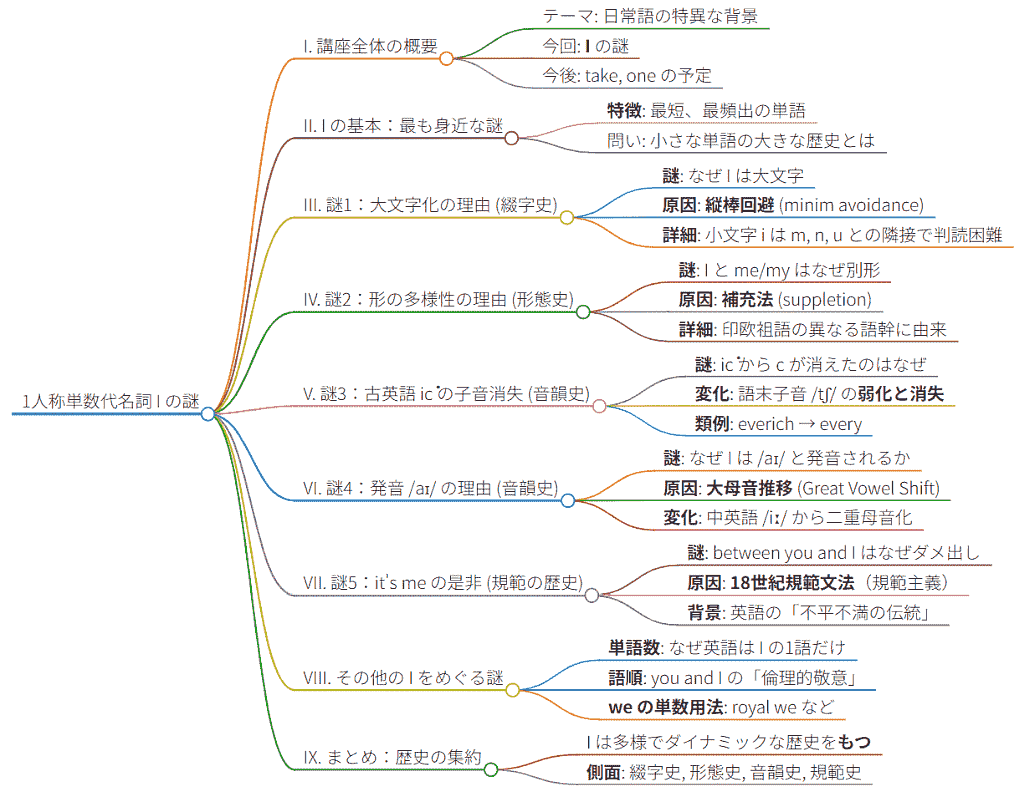
10月25日(土)に,今年度の朝日カルチャーセンターのシリーズ講座「歴史上もっとも不思議な英単語」の第7回が,秋期クールの第1回として開講されました.テーマは「I --- 1人称単数代名詞をめぐる物語」です.誰もが知る超基本語でありながら,英語史の観点から見ると,この小さな単語 I は,その短い生涯に多くのドラマを凝縮させていることが分かります.
今回の講座より,開講時間は 15:30--17:00 へと変更となり,また開講方式はオンラインのみとなりました.新しい形でのスタートとなりましたが,多数の方にご参加いただき,感謝申し上げます.
講座と関連して,事前に Voicy heldio にて「#1602. 10月25日の朝カル講座は I --- 1人称単数代名詞に注目」を配信し,また hellog にて「#6021. 10月25日(土),朝カル講座の秋期クール第1回「I --- 1人称単数代名詞をめぐる物語」が開講されます」 ([2025-10-21-1]) を投稿していました.
1人称単数代名詞 I の歴史は,まさに英語史上の音変化の縮図といえます.古英語,この単語は ic という形をとっていましたが,中英語期から近代英語期にかけて数々の音変化が起こり,現代の形に繋がっていきました.
この第7回講座の内容を markmap によりマインドマップ化して整理しました(画像をクリックして拡大).復習用にご参照ください.
なお,この朝カル講座のシリーズの第1回から第6回についてもマインドマップを作成しています.
・ 「#5857. 2025年度の朝カルシリーズ講座の第1回「she --- 語源論争の絶えない代名詞」をマインドマップ化してみました」 ([2025-05-10-1])
・ 「#5887. 2025年度の朝カルシリーズ講座の第2回「through --- あまりに多様な綴字をもつ語」をマインドマップ化してみました」 ([2025-06-09-1])
・ 「#5915. 2025年度の朝カルシリーズ講座の第3回「autumn --- 類義語に揉み続けられてきた季節語」をマインドマップ化してみました」 ([2025-07-07-1])
・ 「#5949. 2025年度の朝カルシリーズ講座の第4回「but --- きわめつきの多義の接続詞」をマインドマップ化してみました」 ([2025-08-10-1])
・ 「#5977. 2025年度の朝カルシリーズ講座の第5回「guy --- 人名からカラフルな意味変化を遂げた語」をマインドマップ化してみました」 ([2025-09-07-1])
・ 「#6013. 2025年度の朝カルシリーズ講座の第6回「English --- 慣れ親しんだ単語をどこまでも深掘りする」をマインドマップ化してみました」 ([2025-10-01-1])
シリーズの次回,第8回は,11月29日(土)に「take --- ヴァイキングがもたらした超基本語」と題して開講されます.秋期クールは引き続きオンラインのみで,開講時間は 15:30--17:00 です.ご関心のある方は,ぜひ朝日カルチャーセンター新宿教室の公式HPより詳細をご確認の上,お申し込みいただければ幸いです.
2025-10-21 Tue
■ #6021. 10月25日(土),朝カル講座の秋期クール第1回「I --- 1人称単数代名詞をめぐる物語」が開講されます [asacul][notice][personal_pronoun][person][case][indo-european][kdee][hee][etymology][sound_change][gvs][spelling][hel_education][helkatsu]

月1回,朝日カルチャーセンター新宿教室で英語史講座を開いています.今年度のシリーズは「歴史上もっとも不思議な英単語」です.英語史的に厚みと含蓄のある英単語を1つ選び,そこから説き起こして,『英語語源辞典』(研究社)や『英語語源ハンドブック』(研究社)等の参考図書の記述を参照しながら,その英単語の歴史,ひいては英語全体の歴史を語ります.
来週末の10月25日(土)の講座は秋期クールの初回となります.今回は,英語において,最も短く身近な単語の1つでありながら,その歴史に壮大な物語を秘めた1人称単数代名詞 I に注目します.誰もが当たり前のように使っているこの単語ですが,少し立ち止まって考えてみると,実に多くの謎に満ちていることに気づかされます.以下,I について思いついた謎をいくつか挙げてみます.
・ 古英語では ic 「イッチ」と発音されていました.これが,いかにして現代の「アイ」という発音に変化したのでしょうか.そもそも語末にあった c の子音はどこへ消えてしまったのでしょう.
・ なぜ I は,文中でも常に大文字で書かれるのでしょうか.
・ なぜ主語は I なのに,目的語にはまったく形の異なる me を用いるのでしょうか.
・ It's me. と It's I. は,どちらが「正しい」のでしょうか.規範文法と実用の観点から考えてみたいと思います.
・ 近年耳にすることも増えた between you and I という表現は文法的にどう説明できるのでしょうか.
・ 翻って日本語には「私」「僕」「俺」など,なぜこれほど多くの1人称代名詞があるのでしょう.英語の歴史と比較することで見えてくるものがありそうです.
このように,たった1文字の単語 I の背後には,音声変化,綴字の慣習,文法規則の変遷,そして語用論的な使い分けといった,英語史u上の重要テーマが凝縮されています.講座では,時間の許す限りなるべく多くの謎に迫っていきたいと思います.
講座への参加方法は,今期よりオンライン参加のみとなります.リアルタイムでの受講のほか,2週間の見逃し配信サービスもあります.皆さんのご都合のよい方法でご参加いただければ幸いです.また,開講時間がこれまでと異なり 15:30--17:00 となっていますので,ご注意ください.講座と申込みの詳細は朝カルの公式ページよりご確認ください.
今度の講座のご紹介は,先日の heldio でも「#1602. 10月25日の朝カル講座は I --- 1人称単数代名詞に注目」としてお話ししましたので,そちらもお聴きください.
なお,秋期クールのラインナップは以下の通りです.皆さんで「英語史の秋」を楽しみましょう!
- 第7回:10月25日(土) 15:30?17:00 「I --- 1人称単数代名詞をめぐる物語」
- 第8回:11月29日(土) 15:30?17:00 「take --- ヴァイキングがもたらした超基本語」
- 第9回:12月20日(土) 15:30?17:00 「one --- 単なる数から様々な用法へ広がった語」
・ 寺澤 芳雄(編集主幹) 『英語語源辞典』新装版 研究社,2024年.
・ 唐澤 一友・小塚 良孝・堀田 隆一(著),福田 一貴・小河 舜(校閲協力) 『英語語源ハンドブック』 研究社,2025年.
2025-07-21 Mon
■ #5929. but の前置詞と接続詞の用法,および格支配の問題 [but][preposition][conjunction][case][german][danish][prescriptive_grammar]
昨日の記事「#5928. 多義語 but」 ([2025-07-20-1]) に続き,but の話題.but には「~を除いて」を意味する前置詞および接続詞の用法がある.前置詞であれば後続するのは常に目的格であり,接続詞であれば,それが導く節内での役割に応じて格が決定される,というのが理屈である.しかし,これはあくまで理屈にとどまり,必ずしも現実の事例に反映されているわけではない.例えば,文のなかで要求されている格が何であれ,no one but me もあれば no one but I もある.これは何の問題なのだろうか.
Jespersen に "Preposition and Conjunction" と題する詳しい記述がある (§6.3) .以下に,その記述の最初の部分に相当する1節を引用する.
6.31. A good deal of confusion arises from some words being both prepositions and conjunctions. A characteristic example is but; cf NED with examples, especially under the heads C. 3 and 4. It should, however, be noted that the confusion in the use of but is not, as said in NED, a consequence of the want of distinct case-endings in the nouns and the use of the obl. case instead of the nom. in other connexions. In my opinion, on the contrary, the existence of such two-sided words as but, etc, is one of the primary causes of mistakes of me for I or vice versa, and careless uses of the cases generally. Even in such a language as German, where the cases are generally kept neatly apart, we find such combinations as "niemand kommt mir entgegen ausser ein unverschämter" (Lessing); "wo ist ein gott ohne der herr" (Luther); "kein gott ist ohne ich," etc. See Pau, Principien4 372; In Danish similar examples abound (ingen uden jeg, etc).
If we use in one place the term preposition and in another conjunction in speaking of such words, the real meaning is that in one case the word concerned is definitely felt as part of the (main) sentence (no one but me),
引用後半にあるように,この問題と混乱は,英語史を通じて名詞(句)の格の区別が形態的に明示されないようになったために生じたという見解がある.しかし,Jespersen はむしろ逆の考え方を提案している.but が前置詞でもあり接続詞でもあるという2面的な性質を示すがゆえに,一般的な格の混同が助長されたのだというのだ.はたして鶏が先か,卵が先か?
・ Jespersen, Otto. A Modern English Grammar on Historical Principles. Part 7. Syntax. 1954. London: Routledge, 2007.
2024-08-13 Tue
■ #5587. 古英語 niht "night" の屈折 [oe][inflection][gender][case][paradigm]
現代英語の night に対応する古英語単語は niht である.これは古英語の形態カテゴリーとしては女性強変化名詞なのだが,女性強変化名詞の多数派とは少々異なる屈折形を示す少数派のグループに属する名詞なので注意が必要である.
具体的にいえば,多数派では単数主格と単数対格とを比べるとで,後者に -e 語尾が付くという差異がみられるのだが,少数派では両者が無語尾で同形となるのである.また,少数派では,複数主格・対格が -a を取らず -e で一致する という特徴もある.
屈折表 (paradigm) を挙げるのが早いだろう.まず,女性強変化名詞の多数派に属する2つの名詞,短語根の ġiefu "gift" と長語根の lār "teaching" の屈折表を示そう.
| Sing. | Pl. | Sing. | Pl. | |
| N. | ġief-u | ġief-a, -e | lār | lār-a, -e |
| A. | ġief-e | ġief-a, -e | lār-e | lār-a, -e |
| G. | ġief-e | ġief-a, -ena | lār-e | lār-a, -ena |
| D. | ġief-e | ġief-um | lār-e | lār-um |
一方,niht のように少数派に属するものは,次の通りの屈折を示す.
| Sing. | Pl. | |
| N. | niht | niht-e |
| A. | niht | niht-e |
| G. | niht-e | niht-a, -ena |
| D. | niht-e | niht-um |
niht タイプの女性強変化名詞を他に挙げると,ǣht "property", brȳd "bride", cwē "queen", cyst "virtue", dǣd "deed", fierd "army", hǣs "command", lyft "air", miht "power", nīed "need", tīd "tide", wēn "hope", wynn "oyj", wyrd "fate", wyrt "plant" などがある.
以上 Sweet's Anglo-Saxon Primer の §§17--18 を参照した.
・ Davis, Norman. Sweet's Anglo-Saxon Primer. 9th ed. Oxford: Clarendon, 1953.
[ 固定リンク | 印刷用ページ ]
2024-07-29 Mon
■ #5572. 歴史的な動名詞の統語パターン --- Visser の目次より [syntax][gerund][word_order][case][genitive][article]
「#5565. 中英語期,目的語を従える動名詞の構造6種」 ([2024-07-22-1]) で取り上げたように,動名詞の統語論については,発達過程において様々な語順やパターンがあり得た.
今回は Visser を参照し,-ing 形に意味上の主語が明示される場合と,意味上の目的語が明示される場合について,歴史的な統語パターンを挙げたい.各パターンについて,Visser が節を立てているので,その目次 (Vol. 2, xiii--xiv) を掲げるのが早い.ただし,Visser が取り上げているのは -ing 形に関する事例であり,動名詞のみならず現在分詞の例も含まれていることに注意が必要である.
THE SUBJECT OF THE FORM IN -ING
Type 'They doubted the truth of the boy's being dead'
Type 'It's a curious thing your saying that'
Type 'From the arysing of the sonne'
Type 'At the sun rising'
Type 'I hope it's all right me coming in'
Type 'Everybody was talking about you going over there'
Type 'They knew about it being so serious'
Type 'Don't talk of there being no one to help'
THE OBJECT OF THE FORM IN -ING
A. Object before the form in -ing
Type 'Thou desirest the kynges mordryng'
Type 'Excuse his throwing into the water'
Type 'Restrayne yow of vengeance taking'
Type 'To þi broþur burieng fare''
Type 'Hope-giving phrases'; 'his heart-percing dart'
Type 'The maner of þis arke-making'
Type 'His love-making struck us as unconvincing'
Type 'To be present at the iudgement geuing'
Type 'In dyteys-making she bare the pryse'
B. Object after the form in -ing
Type 'A daye was limited for justifying of the bill'
Type 'Wenches sitt in the shade syngyng of ballads'
Type 'He went prechynge cristes lay'
Type 'I slow Sampsoun in shakynge the piler'
'The reading the book' versus 'the reading of the book'
動名詞の統語論と関連して,先日の Voicy heldio の配信回2つも参照.
・ 「#1150. 動名詞の統語論とその歴史 --- His/Him speaking Japanese surprised us all.」
・ 「#1151. 動名詞の統語論はさまざまだった」
・ Visser, F. Th. An Historical Syntax of the English Language. 3 vols. Leiden: Brill, 1963--1973.
2024-07-22 Mon
■ #5565. 中英語期,目的語を従える動名詞の構造6種 [syntax][gerund][me][preposition][word_order][case][genitive][article]
標記について,宇賀治 (274) により,Tajima (1985) を参照して整理した6種の構造が現代英語化した綴字とともに一覧されている.
I 属格目的語+動名詞,例: at the king's crowning (王に王冠を頂かせるとき)
II 目的語+動名詞,例: other penance doing (ほかの告解をすること)
III 動名詞+of+名詞,例: choosing of war (戦いを選択すること)
IV 決定詞+動名詞+of+名詞,例: the burying of his bold knights (彼の勇敢な騎士を埋葬すること)
V 動名詞+目的語,例: saving their lives (彼らの命を助けること)
VI 決定詞+動名詞+目的語,例: the withholding you from it (お前たちをそこから遠ざけること)
目的語が動名詞に対して前置されることもあれば後置されることもあった点,後者の場合には前置詞 of を伴う構造もあった点が興味深い.また,動名詞の主語が属格(後の所有格)をとる場合と通格(後の目的格)をとる場合の両方が混在していたのも注目すべきである.さらに,動名詞句全体が定冠詞 the を取り得たかどうかという問題も,統語論史上の重要なポイントである.

・ Tajima, Matsuji. The Syntactic Development of the Gerund in Middle English. Tokyo: Nan'un-Do, 1985.
・ 宇賀治 正朋 『英語史』 開拓社,2000年.
2024-07-02 Tue
■ #5545. 古英語の定冠詞・疑問詞の具格 [oe][article][determiner][interrogative_pronoun][case][instrumental][inflection][etymology][comparative_linguistics][germanic]
昨日の記事「#5544. 古英語の具格の機能,3種」 ([2024-07-01-1]) に引き続き,具格 (instrumental) について.古英語の定冠詞(あるいは決定詞) (definite article or determiner) の屈折表を「#154. 古英語の決定詞 se の屈折」 ([2009-09-28-1]) で示した.それによると,þȳ, þon といった独自の形態をとる具格形があったことがわかる.同様に疑問(代名)詞 (interrogative_pronoun) についても,その屈折表を「#51. 「5W1H」ならぬ「6H」」 ([2009-06-18-1]) に示した.そこには hwȳ という具格形が見られる.
Lass (144) によると,これらの具格形は比較言語学的にも,直系でより古い形に遡るのが難しいという.純粋な語源形が突きとめにくいようだ.この辺りの事情を,直接 Lass に語ってもらおう.
There are remains of what is usually called an 'instrumental' in the masculine and neuter sg; this term as Campbell remarks 'is traditional, but reflects neither their origin nor their prevailing use' (1959: §708n). The two forms are þon, þȳ, neither of which is historically transparent. In use they are most frequent in comparatives, e.g. þȳ mā 'the more' (cf. ModE the more, the merrier), and as alternatives to the dative in expressions like þȳ gēare '(in) this year'. There is probably some relation to the 'instrumental' interrogative hwȳ 'why?', which in sense is a real one (= 'through/by what?'), but the /y:/ is a problem; hwȳ has an alternative form hwī, which is 'legitimate' in that it can be traced back to the interrogative base */kw-/ + deictic */ei/.
比較言語学の手に掛かっても,すべての語源を追いかけて明らかにすることは至難の業のようだ.
・ Lass, Roger. Old English: A Historical Linguistic Companion. Cambridge: CUP, 1994.
・ Campbell, A. Old English Grammar. Oxford: OUP, 1959.
2024-07-01 Mon
■ #5544. 古英語の具格の機能,3種 [oe][noun][pronoun][adjective][article][demonstrative][determiner][case][inflection][instrumental][dative][comparative_linguistics]
古英語には名詞,代名詞,形容詞などの実詞 (substantive) の格 (case) として具格 (instrumental) がかろうじて残っていた.中英語までにほぼ完全に消失してしまうが,古英語ではまだ使用が散見される.
具格の基本的な機能は3つある.(1) 手段や方法を表わす用法,(2) その他,副詞としての用法,(3) 時間を表わす用法,である.Sweet's Anglo-Saxon Primer (47) より,簡易説明を引用しよう.
Instrumental
88. The instrumental denotes means or manner: Gāius se cāsere, ōþre naman Iūlius 'the emperor Gaius, (called) Julius by another name'. It is used to form adverbs, as micle 'much, by far', þȳ 'therefore'.
It often expresses time when: ǣlċe ȝēare 'every year'; þȳ ilcan dæȝe 'on the same day'.
具格はすでに古英語期までに衰退してきていたために,古英語でも出現頻度は高くない.形式的には与格 (dative) の屈折形に置き換えられることが多く,残っている例も副詞としてなかば語彙化したものが少なくないように思われる.比較言語学的な観点からの具格の振る舞いについては「#3994. 古英語の与格形の起源」 ([2020-04-03-1]) を参照されたい.ほかに具格の話題としては「#811. the + 比較級 + for/because」 ([2011-07-17-1]) と「#812. The sooner the better」 ([2011-07-18-1]) も参照.
・ Davis, Norman. Sweet's Anglo-Saxon Primer. 9th ed. Oxford: Clarendon, 1953.
2024-04-06 Sat
■ #5458. 理論により異なる主語の捉え方 [subject][terminology][semantics][syntax][logic][case][generative_grammar]
昨日の記事「#5457. 主語をめぐる論点」 ([2024-04-05-1]) に続き,別の言語学用語辞典からも主語 (subject) の項目を覗いてみよう.Crystal の用語辞典より引用する.
subject (n.) (S, sub, SUB, Subj, SUBJ) A term used in the analysis of GRAMMATICAL FUNCTIONS to refer to a major CONSTITUENT of SENTENCE or CLAUSE structure, traditionally associated with the 'doer' of an action, as in The cat bit the dog. The oldest approaches make a twofold distinction in sentence analysis between subject and PREDICATE, and this is still common, though not always in this terminology; other approaches distinguish subject from a series of other elements of STRUCTURE (OBJECT, COMPLEMENT, VERB, ADVERBIAL, in particular. Linguistic analyses have emphasized the complexity involved in this notion, distinguishing, for example, the grammatical subject from the UNDERLYING or logical subject of a sentence, as in The cat was chased by the dog, where The cat is the grammatical and the dog the logical subject. Not all subjects, moreover, can be analyzed as doers of an action, as in such sentences as Dirt attracts flies and The books sold well. The definition of subjects in terms of SURFACE grammatical features (using WORD-ORDER or INFLECTIONAL criteria) is usually relatively straightforward, but the specification of their function is more complex, and has attracted much discussion (e.g. in RELATIONAL GRAMMAR). In GENERATIVE grammar, subject is sometimes defined at the NP immediately DOMINATED by S. While NP is the typical formal realization of subject, other categories can have this function, e.g. clause (S-bar), as in That oil floats on water is a fact, and PP as in Between 6 and 9 will suit me. The term is also encountered in such contexts as RAISING and the SPECIFIED-SUBJECTION CONDITION.
昨日引用・参照した McArthur の記述と重なっている部分もあるが,今回の Crystal の記述からは,拠って立つ言語理論に応じて主語の捉え方が異なることがよく分かる.関係文法では主語の果たす機能に着目しており,生成文法ではそもそも主語という用語を常用しない.あらためて主語とは伝統文法に基づく緩い用語であり,そしてその緩さ加減が適切だからこそ広く用いられているのだということが分かる.
・ Crystal, David, ed. A Dictionary of Linguistics and Phonetics. 6th ed. Malden, MA: Blackwell, 2008. 295--96.
2023-09-13 Wed
■ #5252. 絶対格的見方と能格的見方 [ergative][case][voice][semantic_role][syntax][transitivity]
言語学には,絶対格性 (absolutive) と能格性 (ergativity) という,言語に表出する世界観の重要な違いがある.同じ過程 (process) であっても,各々の見方を通してみると,まったく異なる解釈がなされ,まったく異なる(統語)表現が現われてくる.
トムが目を閉じるシーンを見たとしよう.これを「トムの目が閉じた」と描写するか,「トムは目を閉じた」と描写するかは視点の違いといわれる.日本語でも英語でも,統語的にはそれぞれを自動詞文,他動詞文と呼ぶことが多い.いずれの文でも過程 (Process) は「閉じる」で一致しているが,前者の文では主語(意味役割としては Agent)は「トムの目」,後者の文では「トム」となる.また,後者の文では「(トムの)目」という目的語 (Goal) が現われる.これが絶対格性の言語観である.
ところが,能格性の言語観によると,いずれの文においても「閉じる」が過程 (Process) であることは異ならないが,「トムの目」が媒体 (Medium) として同じ意味役割を担っているものと解釈される.それは,いずれにせよ「閉じる」という過程が成立するためになければならない「媒体」だからだ.この言語観によれば,後者の文における「トム」は媒体を発動させる主体 (Agent) とみなされる.
つまり,2つの文のペアについて,絶対格的見方と能格的見方があることになる.Halliday (341) より,いくつかの英語の短文を挙げつつ,2つの言語観を比較してみよう.
(a) transitive interpretation
| the boat | sailed | vs. | Mary | sailed | the boat |
| the cloth | tore | vs. | the nail | tore | the cloth |
| Tom's eyes | closed | vs. | Tom | closed | his eyes |
| the rice | cooked | vs. | Pat | cooked | the rice |
| my resolve | weakened | vs. | the news | weakened | my resolve |
| Actor | Process | vs. | Actor | Process | Goal |
|---|
| the boat | sailed | vs. | Mary | sailed | the boat |
| the cloth | tore | vs. | the nail | tore | the cloth |
| Tom's eyes | closed | vs. | Tom | closed | his eyes |
| the rice | cooked | vs. | Pat | cooked | the rice |
| my resolve | weakened | vs. | the news | weakened | my resolve |
| Medium | Process | vs. | Agent | Process | Medium |
|---|
能格については「#4314. 能格言語は言語の2割を占める」 ([2021-02-17-1]),「#4315. 能格言語の発想から英語をみる」 ([2021-02-18-1]) も参照.
・ Halliday, M. A. K. Halliday's Introduction to Functional Grammar. 4th ed. Rev. Christian M. I. M. Matthiessen. Abingdon: Routledge, 2004.
[ 固定リンク | 印刷用ページ ]
2022-08-17 Wed
■ #4860. 生成文法での受動文の作られ方 [generative_grammar][passive][syntax][case][case_filter]
学校文法では,能動文(ここではSVOの文型を仮定)から受動文を派生させる際に,もとの能動文の主語と目的語をクロスさせ,be 動詞を補ったり,動詞を過去分詞にしたり,前置詞 by を補ったりと,いろいろなことが起こると解説される.
the teacher scolded John │ │ │ │ │ │ ┌─┼────┼──┘ │ └────┼────┐ │ │ │ │ ┌──┘ │ ↓ ↓ ↓ John was scolded by the teacher
生成文法では,このように能動文から受動文を派生させることはしない.深層構造 (D-structure) においてすでに独自の構造を想定し,そこから目的語に相当する要素を主語位置に移動させるという過程を考える.
[IP___[I'[I was][VP[V' scolded John] by the teacher]]]
↓
[IP Johni [I'[I was][VP[V' scolded ti] by the teacher]]]
このように考える理屈は次の通りである.深層構造では,能動文さながらに [V' scolded John] という構造が想定されている.通常であれば scold という他動詞が John に対格を付与するはずだが,scolded のように過去分詞になると格付与能力を失うと考えられ,John は格付与されないままに宙ぶらりんとなる.すると「John のような名詞句は必ず格付与されなければならない」という格フィルター (case filter) の原理に抵触してしまうため,これを回避するために John は格を付与してもらえる位置,つまり深層構造の先頭の ___ へと移動していく.この位置は,定動詞 was によって主格を付与してもらえる位置だからである.こうして,めでたく表層構造が導かれる.
この生成文法流の仕掛けには様々な前提が設けられており,なぜその前提を据えることが妥当なのかは,おおいに議論しなければならない.しかし,この例から,生成文法の特徴の1つとして格付与を重視する伝統があることが分かるだろう.以上,三原 (79) を参照した.
・ 三原 健一 「第3章 生成文法」『日英対照 英語学の基礎』(三原 健一・高見 健一(編著),窪薗 晴夫・竝木 崇康・小野 尚久・杉本 孝司・吉村 あき子(著)) くろしお出版,2013年.
2022-05-20 Fri
■ #4771. 古英語の3人称単数女性代名詞の対格 hie が与格 hire に飲み込まれた時期 [case][personal_pronoun][oe][inflection][paradigm][eme][laeme]
she の語源説について,連日 Laing and Lass の論文を取り上げてきた(cf. 「#4769. she の語源説 --- Laing and Lass による "Yod Epenthesis" 説の紹介」 ([2022-05-18-1]),「#4770. she の語源説 --- Laing and Lass による "Yod Epenthesis" 説の評価」 ([2022-05-19-1])) .
同論文の主な関心は3人称単数女性代名詞主格の形態についてだが,対格と与格の形態についても触れている.古英語の標準的なパラダイムによれば,対格は hīe,与格は hire の形態を取ったが,後の歴史をみれば明らかな通り,与格形が対格形を飲み込む形で「目的格 her」が生じることになった.この点でいえば,他の3人称代名詞でも同じことが起こっている.単数男性与格の him が対格 hine を飲み込み,複数与格の him が対格 hīe を飲み込んだ(後にそれ自身が them に置換されたが).
3人称代名詞に関して与格が対格を飲み込んだというこの現象(与格方向への対格の水平化)はあまり注目されず,およそいつ頃のことだったのだろうかと疑問が生じるが,単数女性に関しては Laing and Lass (209) による丁寧な説明があった.
By the time ME proper begins to emerge, and to survive in the written record in the mid to late twelfth century, the new 'she' type for the subject pronoun already begins to be found. For the object pronoun the levelling of the 'her/hir' type from the OE DAT/GEN variants is also already the majority for direct object function. For the fem sg personal pronoun used as direct object ($/P13OdF), LAEME CTT has 60 tokens of the 'heo/hi(e)' type across only 7 texts. If one includes hi(e) spellings for IT ($/P13OdI) showing survival of feminine grammatical gender in inanimates, the total rises to 77 tokens across 14 texts. Only 2 texts (with 3 tokens between them) have 'heo/hie' exclusively in direct object function for HER. The other 5 texts show 'her/hir' types beside 'heo/hie' types. Against this are 494 tokens of the 'her/hir' type for HER found across 51 texts. Or, if one includes 'her/hir' type spellings for IT showing the survival of grammatical gender, the total rises to 590 across 58 texts.
要するに,対格の与格方向への水平化は,意外と早く初期中英語期の段階ですでに相当に進んでいたということになる.おそらく単数男性や複数でも似たような状況だったと想像されるが,これについては別に裏を取る必要がある.
この問題と関連して関連して,「#155. 古英語の人称代名詞の屈折」 ([2009-09-29-1]),「#975. 3人称代名詞の斜格形ではあまり作用しなかった異化」 ([2011-12-28-1]),「#4080. なぜ she の所有格と目的格は her で同じ形になるのですか?」 ([2020-06-28-1]) を参照.
2021-05-01 Sat
■ #4387. なぜ名詞(句)が副詞的に用いられることがあるのですか? [sobokunagimon][preposition][adverbial_accusative][adverbial_genitive][adverb][case][dative][japanese][khelf_hel_intro_2021]
次の各文の赤字の部分をみてください.いずれもその形態だけみれば名詞(句)ですが,文中での働き(統語)をみれば副詞として機能しています.前置詞 (preposition) がついていれば分かりやすい気もしますが,ついていません.形式は名詞(句)なのに機能は副詞というのは何か食い違っているように思えますが,このような例は英語では日常茶飯で枚挙にいとまがありません.
・ I got up at five this morning.
・ Every day they run ten kilometers.
・ He repeated the phrase twice.
・ She lives just three doors from a supermarket.
・ We cook French style.
・ You are all twenty years old.
・ They travelled first-class.
上記のような副詞的に用いられる名詞句は,歴史的には副詞的対格 (adverbial_accusative),副詞的与格 (adverbial dative),副詞的属格 (adverbial_genitive) などと呼ばれます.本ブログでも歴史的な観点から様々に取り上げてきた話題です.
昨日大学院生により公表された「英語史導入企画2021」のためのコンテンツ「先生,ここに前置詞いらないんですか?」は,この問題に英語史の観点から迫った,読みやすい導入的コンテンツです.古英語の事例を提示しながら,最後は「名詞が副詞の働きをするというのは,格変化が豊かであった古英語時代の用法が現代にかすかに生き残ったものなのである」と締めくくっています.
古英語期に名詞(句)が格変化して副詞的に用いられていたものが,中英語期以降に格変化を失った後も化石的に生き残ってきたという説明は,およそその通りだと考えています.一方で,それだけではないとも思っています.とりわけ時間,空間,様態に関わる副詞が,名詞(句)から発達するということは,歴史的な格変化を念頭におかずとも,通言語的にありふれているように思われるからです.日本語の,「昨日」「今日」「明日」「先週」「来年」はもとより「短時間」「半世紀」「未来永劫」や「突然」「畢竟」「誠心誠意」も形態的には典型的な名詞句のようにみえますが,機能的には副詞で用いられることも多いでしょう.
上記コンテンツで例示されているように,古英語には名詞が対格・与格・属格に屈折して副詞として用いられている例は多々あります.しかし,例えば hwīlum ("sometimes, once"; > PDE whilom) などは,語源・形態的には語尾の -um は複数与格を表わすとはいえ,すでに古英語の時点で語彙化していると考えられます.名詞 hwīl (> PDE while) が格屈折したものであるという意識は,古英語話者にすら稀薄だったのではないかと想像されるのです.屈折の衰退を待たずして,古英語期にも名詞由来の hwīlum がすでに副詞として認識されていた(もし仮に認識されることがあったとして)のではないかと思われます.
中英語期以降の格変化の衰退が,現代につながる「副詞的名詞(句)」の拡大に貢献したことは認めつつも,歴史的経緯とは無関係に,時間,空間,様態などを表わす名詞(句)が副詞化する傾向は一般的にあるのではないでしょうか.
2021-03-25 Thu
■ #4350. 剥奪の of について格の観点から再考 [preposition][case][syntax][word_order][semantic_role]
いわゆる「剥奪の of」と呼ばれる用法や構文について,「#1775. rob A of B」 ([2014-03-07-1]) の記事で英語史の観点から少し考えてみた.なかなか難しい問題で,英語学的にもきれいには解決していないようである.
Blake (134) が,格 (case) や意味役割 (semantic_role) の観点からこの問題に迫っている議論をみつけたので,そちらを引用したい.
(39) a. The vandals stripped the branches off the tree agent patient source b. The vandals stripped the tree of its branches agent source patient
The roles appropriate for (39a) are noncontroversial. The vandals are clearly the agent, the branches patient and the tree source. Of the two sentences (39a) would appear to be unmarked, since it exhibits a normal association of role and relation: patient with direct object and source with a noncore or peripheral relation. The ascription of roles in (39b) is more problematic. Under a common interpretation of constructions like this the tree in (39b) would still be the source and the branches the patient. But note the different in meaning. (39a) presents the situation from the point of view of the effect of the activity on the branches, whereas (39b) emphasises the fate of the tree. In fact, the phrase of its branches can be omitted from (39b). This makes it problematic for those who claim that every clause has a patient. The problem could be avoided by claiming that the tree in (39b) has been reinterpreted as a patient, but that creates the further problem of finding a different role for the branches.
剥奪の構文の問題について格の理論的観点から議論したものだが,およそ私たちの直感的な問題意識に通じる議論となっており,結局のところ未解決なのである.最後に触れられているように,(39b) において the tree の意味役割を patient とするのであれば,of its branches の意味役割は何になるのか.そして,その意味役割を担わせる前置詞 of の意味・用法はいかなるものであり,それは of の原義や他の主要語義からどのように派生したものと考えるべきなのか.
1つ気になるのは,両文で用いられている前置詞が,起源を同じくする off と of であることだ(ただし,前者は from でも言い換えられる).両語の同一起源については「#55. through の語源」 ([2009-06-22-1]),「#4095. 2重語の分類」 ([2020-07-13-1]) を参照.
・ Blake, Barry J. Case. 2nd ed. Cambridge: CUP, 2001.
2021-02-21 Sun
■ #4318 主格ではなく対格がデフォルト? [case][indo-european]
主格 (nominative) は,その名称からもうかがえるように,統語意味論的に他の格と比べて標準的・基本的な格である.形態的にも原形というべき形を示しており,まさにデフォルトの格といえる.文から独立して単語そのものに言及するときにも用いられるし,辞書の「見出し語形」としても採用される形だ.コーパス言語学でいうレンマ (lemma) と理解してもよい.主格については,このような理解が一般的だろう.
確かに,多くの言語では主格形がデフォルトの形態を体現しており,他の斜格形はそこからの変形として生成される.そのような言語では,主格のデフォルト性を認めることはたやすいだろう.
ところが,印欧語の歴史を振り返ると,主格形は斜格形と同様に独自の特別な屈折形を示したことが分かる.つまり,印欧語については,主格がデフォルト形であるという形態論的な証拠はない.英語を含め,印欧祖語から派生した比較的新しい諸言語では,この事実が見えにくくなっているが,主格形がデフォルト形を形成しないという点で,実は印欧語は類型論的にかなり特殊な語族なのである (Blake 30) .
この事実と関係しているかどうかは分からないが,印欧語では,名詞が多かれ少なかれ統語的に独立して用いられる場合に,主格以外の形態で現われることがある.具体的にいえば,先日の記事「#4312. 呼格,主格,対格の関係について一考」 ([2021-02-16-1]) で触れたように,対格(や呼格)が用いられる場合があるのだ.Blake (31) は,この事実を類型論的に有標な用法とみている節がある.
. . . the nominative is generally thought of as the case used outside syntax, the case used in naming, the case used in talking about a lexeme, but Rubio argues that in Latin the accusative as well as the nominative is used in isolation and metalinguistically. He sees both of them as case of pure denotation (1966: 95--7). We are reminded of the use of the oblique forms of pronouns in English: Who wants it? Me. Me, I'll get it. De Carvalho also notes that the accusative in Latin is used out of context (1982: 257ff, 1985). He sees the nominative in more positive terms as the case in which one expresses the protagonist (1982: 248, 263).
関連して,英語史において対格が主格を追い落とした例として,2人称代名詞の you,そして現代英語の口語において1人称単数代名詞の I に代わって me が用いられる Me and my sister went shopping. のような文を参照.
・ Blake, Barry J. Case. 2nd ed. Cambridge: CUP, 2001.
・ Rubio, L. Introductión a la sintaxis estructural del Latin. Vol. 1: Casos y preposiciones. Barcelona: Ariel, 1966.
・ Carvalho, P. de. "Reflexions sur les cas: vers une théorie des cas latins." L'information Grammaticale 7 (1980): 3--11.
2021-02-20 Sat
■ #4317. なぜ「格」が "case" なのか [terminology][case][grammar][history_of_linguistics][etymology][dionysius_thrax][sobokunagimon][latin][greek][vocative]
本ブログでは種々の文法用語の由来について「#1257. なぜ「対格」が "accusative case" なのか」 ([2012-10-05-1]),「#1258. なぜ「他動詞」が "transitive verb" なのか」 ([2012-10-06-1]),「#1520. なぜ受動態の「態」が voice なのか」 ([2013-06-25-1]),「#3307. 文法用語としての participle 「分詞」」 ([2018-05-17-1]),「#3983. 言語学でいう法 (mood) とは何ですか? (1)」 ([2020-03-23-1]),「#3984. 言語学でいう法 (mood) とは何ですか? (2)」 ([2020-03-24-1]),「#3985. 言語学でいう法 (mood) とは何ですか? (3)」 ([2020-03-25-1]) などで取り上げてきた.今回は「格」がなぜ "case" と呼ばれるのかについて,連日参照・引用している Blake (19--20) より概要を引用する.
The term case is from Latin cāsus, which is in turn a translation of the Greek ptōsis 'fall'. The term originally referred to verbs as well as nouns and the idea seems to have been of falling away from an assumed standard form, a notion also reflected in the term 'declension' used with reference to inflectional classes. It is from dēclīnātiō, literally a 'bending down or aside'. With nouns the nominative was taken to be basic, with verbs the first person singular of the present indicative. For Aristotle the notion of ptōsis extended to adverbial derivations as well as inflections, e.g. dikaiōs 'justly' from the adjective dikaios 'just'. With the Stoics (third century BC) the term became confined to nominal inflection . . . .
The nominative was referred to as the orthē 'straight', 'upright' or eutheia onomastikē 'nominative case'. Here ptōsis takes on the meaning of case as we know it, not just of a falling away from a standard. In other words it came to cover all cases not just the non-nominative cases, which in Ancient Greek were called collectively ptōseis plagiai 'slanting' or 'oblique cases' and for the early Greek grammarians comprised genikē 'genitive', dotikē 'dative' and aitiatikē 'accusative'. The vocative which also occurred in Ancient Greek, was not recognised until Dionysius Thrax (c. 100 BC) admitted it, which is understandable in light of the fact that it does not mark the relation of a nominal dependent to a head . . . . The received case labels are the Latin translations of the Greek ones with the addition of ablative, a case found in Latin but not Greek. The naming of this case has been attributed to Julius Caesar . . . . The label accusative is a mistranslation of the Greek aitiatikē ptōsis which refers to the patient of an action caused to happen (aitia 'cause'). Varro (116 BC--27? BC) is responsible for the term and he appears to have been influenced by the other meaning of aitia, namely 'accusation' . . . .
この文章を読んで,いろいろと合点がいった.英語学を含む印欧言語学で基本的なタームとなっている case (格)にせよ declension (語形変化)にせよ inflection (屈折)にせよ,私はその名付けの本質がいまいち呑み込めていなかったのだ.だが,今回よく分かった.印欧語の形態変化の根底には,まずイデア的な理想形があり,それが現世的に実現するためには,理想形からそれて「落ちた」あるいは「曲がった」形態へと堕する必要がある,というネガティヴな発想があるのだ.まず最初に「正しい」形態が設定されており,現実の発話のなかで実現するのは「崩れた」形である,というのが基本的な捉え方なのだろうと思う.
日本語の動詞についていわれる「活用」という用語は,それに比べればポジティヴ(少なくともニュートラル)である.動詞についてイデア的な原形は想定されているが,実際に文の中に現われるのは「堕落」した形ではなく,あくまでプラグマティックに「活用」した形である,という発想がある.
この違いは,言語思想的にも非常におもしろい.洋の東西の規範文法や正書法の考え方の異同とも,もしかすると関係するかもしれない.今後考えていきたい問題である.
・ Blake, Barry J. Case. 2nd ed. Cambridge: CUP, 2001.
2021-02-19 Fri
■ #4316. 日本語型 SOV 言語は形態的格標示をもち,英語型 SVO 言語はもたない [typology][case][syntax][word_order][morphology][japanese]
標題は,類型論的な傾向として指摘されている.日本語などの SO 語順をもつ言語は,何らかの形態的な格標示をもつ可能性が高いという.実際,日本語には「が」「を」「の」などの格助詞があり,名詞句に後接することで格が標示される仕組みだ.一方,英語を典型とする SV 語順をもつ言語は,そのような形態的格標示を(顕著には)もたないという.英語にも人称代名詞にはそれなりの格変化はあるし,名詞句にも 's という所有格を標示する手段があるが,全般的にいえば形態的な格標示の仕組みは貧弱といってよい.英語も古くは語順が SV に必ずしも固定されておらず,SO などの語順もあり得たのだが,上記の類型論が予測する通り,当時は形態的な格標示の仕組みが現代よりも顕著に機能していた.
上記の類型論上の指摘は,Blake を読んでいて目にとまったものだが,もともとは Greenberg に基づくもののようだ.Blake (15) より関係する箇所を引用する.
It has frequently been observed that there is a correlation between the presence of case marking on noun phrases for the subject-object distinction and flexible word order and this would appear to hold true. From the work of Greenberg it would also appear that there is a tendency for languages that mark the subject-object distinction on noun phrases to have a basic order of subject-object-verb (SOV), and conversely a tendency for languages lacking such a distinction to have the order subject-verb-object (SVO) . . . . The following figures are based on a sample of 100 languages. They show the relationship between case and marking for the 85 languages in the sample that exhibit one of the more commonly attested basic word orders. The notation [+ case] in this context means having some kind of marking, including appositions, on noun phrases to mark the subject-object distinction . . . .
| VSO | [+ case] | 3 | SVO | [+ case] | 9 | SOV | [+ case] | 34 |
| [- case] | 6 | [- case] | 26 | [- case] | 7 |
The SVO 'caseless' languages are concentrated in western Europe (e.g. English), southern Africa (e.g. Swahili) and east and southeast Asia (e.g. Chinese and Vietnamese).
この類型論的傾向が示す言語学的な意義は何なのだろうか.
・ Blake, Barry J. Case. 2nd ed. Cambridge: CUP, 2001.
2021-02-18 Thu
■ #4315. 能格言語の発想から英語をみる [ergative][case][middle_voice][passive][voice][semantic_role][transitivity]
昨日の記事「#4314. 能格言語は言語の2割を占める」 ([2021-02-17-1]) にて,統語意味論的なカテゴリーとしての能格 (ergative) に触れた.英語は能格言語ではなく対格言語であり,直接には関係しない話題とも思われるかもしれないが,能格性 (ergativity) という観点から英語を見直してみると,新鮮な発見がある.動詞の自他の問題と密接に関わってくるし,受動態 (passive) や中動態 (middle_voice) の問題とも深く交わる.実際,動詞の自他の区別は英語の動詞や構文を考える際の伝統的で基本的な見方を提供してくれているが,これを能格性の視点から見直すと,景色がガランと変わってくるのだ.
Malmkjær (532) の "Ergativity" の項の一部を引用する.
Complementary to the transitive model of the grammar is the ergative model, an additional property of the system of transivitity, which foregrounds the role of Agency in providing a 'generalised representational structure common to every English clause' (Halliday and Matthiessen 2004: 281). This system is simultaneous with those of process type and circumstance . . . . Here the key variable is not a model of extension, as in transitivity, but of causation: 'The question at issue is: is the process brought about from within, or from outside?' (Halliday and Matthiessen 2004: 287). Every process must have one participant central to the actualisation of the process; 'without which there would be no process at all' (Halliday and Matthiessen 2004: 288). This is the Medium and along with the process forms the nucleus of the clause. The Medium is obligatory and is the only necessary participant, if the process is represented as being self-engendering. If the process is engendered from outside, then there is an additional participant, the Agent. Options in the ergative model of transitivity define the voice, or agency, of the clause. A clause with no feature of 'agency' is neither active nor passive but middle (for example, Europeans arrives). One with agency is non-middle, or effective, in agency (for example, Europeans invaded Australia). An effective clause is then either operative or receptive in voice. In an operative clause, the Subject is the Agent and the process is realised by an active verbal group; in a receptive clause the Subject is the Medium and the process is realised by a passive verbal group (Australia was invaded by Europeans) (Halliday and Matthiessen 2004: 297).
昨日も触れたように,世界の諸言語には対格言語 (accusative language) と能格言語 (ergative language) という2大タイプがある.各々 transitivity 重視の言語と ergativity 重視の言語と言い換えてもよい.文法観の大きく異なるタイプではあるが,一方に属する言語を他方の発想で眺めてみると,新たな洞察が得られる.結局のところ,人間が言語で表現したいことを表現する方法には少数のパターンしかなく,表面的には異なっているようにみえても,それはコード化の方法を少しく違えているにすぎない,と評することもできそうだ.
・ Malmkjær, Kirsten, ed. The Routledge Linguistics Encyclopedia. 3rd ed. London and New York: Routledge, 2010.
・ Halliday, M. A. K. and Matthiessen, C. M. I.M. An Introduction to Functional Grammar. 3rd ed. London: Edward Arnold, 2004.
2021-02-17 Wed
■ #4314. 能格言語は言語の2割を占める [ergative][case][world_languages][statistics][typology][caucasian][language_family][terminology]
世界の諸言語について,主要な格 (case) のあり方という観点から分類するとき,英語のような nominative-accusative タイプの言語と,バスク語やグルジア語のような absolutive-ergative タイプの言語に大きく分けられる.前者は対格言語 (accusative language),後者は能格言語 (ergative language) と呼ばれる.
英語のような対格言語の格体系は,私たちが当然視しているものであり,ほとんど説明を要しないだろう.He opened the door. と The door opened. の2文において,各々文頭に立っている名詞句 He と The door が主語の役割を果たす主格 (nominative case) に置かれているのに対し,第1文の the door は目的語の役割を果たす対格 (accusative case) に置かれているといわれる.
しかし,能格言語においては,第1文と第2文の両方の the door が絶対格 (absolutive case) に置かれ,第2文の He は能格 (ergative case) に置かれる.いずれの文でも,自然に開こうが誰かが開こうが,結果的に開いている「扉」は絶対格に置かれ,第2文のみに明示されている,その状態を能動的に引き起こした「彼」が能格に置かれるのだ.
類型論などでしばしば言及される能格言語というものは,世界の諸言語のなかでは稀なタイプの言語だと思い込んでいたが,それほど稀でもないようだ.対格言語に比べれば圧倒的な少数派であることは間違いないが,世界言語の2割ほどはこのタイプだと知って驚いた.Blake (121) によると,分布は世界中に広がっている.
Ergative systems are often considered rare and remote, but in fact they make up at least twenty per cent of the world's languages. Ergative systems are to be found in all families of the Caucasian phylum, among the Tibeto-Burman languages, in Austronesian, in most Australian languages, in some languages of the Papuan families, in Zoque and the Mayan languages of Central America and in a number of language families in South America: Jé, Arawak, Tupí-Guaraní, Panoan, Tacanan, Chibchan and Carib. Outside these phyla and families where ergative systems of marking are common, ergativity is also to be found in some other languages including Basque, Hurrian and a number of other extinct languages of the Near East, Burushaski (Kashmir, Tibet), Eskimo, Chukch, and Tsimshian and Chinook (these last two being Penutian languages of British Columbia).
ちなみに,英語は能格言語ではないが,上の例で挙げた open(ed) のように自動詞にも他動詞にも用いられる動詞を指して能格動詞 (ergative verb) と呼ぶことがある.
・ Blake, Barry J. Case. 2nd ed. Cambridge: CUP, 2001.
2021-02-16 Tue
■ #4313. 呼格,主格,対格の関係について一考 [greetings][interjection][formula][syntax][exclamation][pragmatics][syncretism][latin][case]
昨日の記事「#4312. 「呼格」を認めるか否か」 ([2021-02-15-1]) で話題にしたように,呼格 (vocative) は,伝統的な印欧語比較言語学では1つの独立した格として認められてきた.しかし,ラテン語などの古典語ですら,第2活用の -us で終わる単数にのみ独立した呼格形が認められるにすぎず,それ以外では形態的に主格に融合 (syncretism) している.「呼格」というよりも「主格の呼びかけ用法」と考えたほうがスッキリするというのも事実である.
このように呼格が形態的に主格に融合してきたことを認める一方で,語用的機能の観点から「呼びかけ」と近い関係にあるとおぼしき「感嘆」 (exclamation) においては,むしろ対格に由来する形態を用いることが多いという印欧諸語の特徴に関心を抱いている.Poor me! や Lucky you! のような表現である.
細江 (157--58) より,統語的に何らかの省略が関わる7つの感嘆文の例を挙げたい.各文の名詞句は形式的には通格というべきだが,機能的にしいていうならば,主格だろうか対格だろうか.続けて,細江の解説も引用する.
How unlike their Belgic sires of old!---Goldsmith.
Wonderful civility this!---Charlotte Brontë.
A lively lad that!---Lord Lytton.
A theatrical people, the French?---Galsworthy.
Strange institution, the English club.---Albington.
This wish I have, then ten times happy me!---Shakespeare.
この最後の me は元来文の主語であるべきものを表わすものであるが,一人称単数の代名詞は感動文では主格の代わりに対格を用いることがあるので,これには種々の理由があるらしい(§130参照)が,ラテン語の語法をまねたことも一原因であったと見られる.たとえば,
Me miserable!---Milton, Paradise Lost, IV. 73.
は全くラテン語の Me miserum! (Ovid, Heroides, V. 149) と一致する.
引用最後のラテン語 me miserum と関連して,Blake の格に関する理論解説書より "ungoverned case" と題する1節も引用しておこう (9) .
In case languages one sometimes encounters phrases in an oblique case used as interjections, i.e. apart from sentence constructions. Mel'cuk (1986: 46) gives a Russian example Aristokratov na fonar! 'Aristocrats on the street-lamps!' where Aristokratov is accusative. One would guess that some expressions of this type have developed from governed expressions, but that the governor has been lost. A standard Latin example is mē miserum (1SG.ACC miserable.ACC) 'Oh, unhappy me!' As the translation illustrates, English uses the oblique form of pronouns in exclamations, and outside constructions generally.
さらに議論を挨拶のような決り文句にも引っかけていきたい.「#4284. 決り文句はほとんど無冠詞」 ([2021-01-18-1]) でみたように,挨拶の多くは,歴史的には主語と動詞が省略され,対格の名詞句からなっているのだ.
語用的機能の観点で関連するとおぼしき呼びかけ,感嘆,挨拶という類似グループが一方であり,歴史形態的に区別される呼格,主格,対格という相対するグループが他方である.この辺りの関係が複雑にして,おもしろい.
・ 細江 逸記 『英文法汎論』3版 泰文堂,1926年.
・ Blake, Barry J. Case. 2nd ed. Cambridge: CUP, 2001.
Powered by WinChalow1.0rc4 based on chalow