この2日間の記事 ([2014-02-17-1], [2014-02-18-1]) で,18世紀後半から19世紀にかけてのロマン派と synaesthesia 表現の関係について見てきた.言語学的あるいは意味論的にいえば,synaesthesia 表現のもつ最大の魅力は,「下位感覚から上位感覚への意味転用」という方向性,あるいは,背伸びした表現でいえば,法則性にある.
この方向性についての仮説を,英語の共感覚表現によって精緻に実証し,論考したのが,Williams である.Williams は,100を超える感覚を表わす英語の形容詞について,関連する語義の初出年代を OED や MED で確かめながら,意味の転用の通時的傾向を明らかにした.さらに,英語に限っていえば,単に下位から上位への転用という一般論を述べるだけではなく,特定の感覚間での転用が目立つという点をも明らかにした.Williams (463) の結論は明快である.
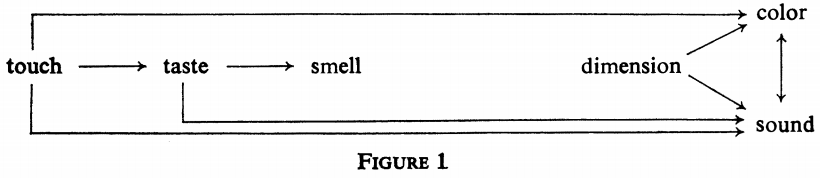
THE MAJOR GENERALIZATION is this: if a lexeme metaphorically transfers from its earliest sensory meaning to another sensory modality, it will transfer according to the schedule shown in Figure 1.
この方向性を,生理学的な観点から表現すれば,"Sensory words in English have systematically transferred from the physiologically least differentiating, most evolutionary primitive sensory modalities to the most differentiating, most advanced, but not vice versa." (Williams 464--65) となる.Williams (464) より,具体的な形容詞を挙げる.
TOUCH TO TASTE: aspre, bitter, bland, cloying, coarse, cold, cool, dry, hard, harsh, keen, mild, piquant, poignant, sharp, smooth.
TOUCH TO COLOR: dull, light, warm.
TOUCH TO SOUND: grave, heavy, rough, smart, soft.
TASTE TO SMELL: acrid, sour, sweet.
TASTE TO SOUND: brisk, dulcet.
DIMENSION TO COLOR: full.
DIMENSION TO SOUND: acute, big, deep, empty, even, fat, flat, high, hollow, level, little, low, shallow, thick.
COLOR TO SOUND: bright, brilliant, clear, dark, dim, faint, light, vivid.
SOUND TO COLOR: quiet, strident.
もちろん,Ullmann のロマン派詩人の調査にも見られたように,この方向性に例外がないわけではない.Williams (464) は,以下の例外リストを挙げている.
TOUCH TO DIMENSION: crisp.
TOUCH TO SMELL: hot, pungent.
TASTE TO TOUCH: eager, tart.
TASTE TO COLOR: austere, mellow.
DIMENSION TO TASTE: thin.
DIMENSION TO TOUCH: small.
SOUND TO TASTE: loud.
SOUND TO TOUCH: shrill.
Williams は,この仮説に沿う共感覚表現は,数え方にもよるが,全体の83--99%であると述べている.しかし,ここまで高い率であれば,少なくとも傾向とは呼べるし,さらには一種の法則に近いものとみなしても差し支えないだろう.
Williams (470--72) は,この仮説の大筋は他言語にも当てはまるはずだと見込んでおり,実際に日本語の共感覚表現について『広辞苑』と日本語母語話者インフォーマントを用いて,同じ方向性を91%という整合率を挙げながら確認している.
この意味転用の方向性の仮説が興味を引く1つの点は,嗅覚 (smell) がどん詰まりであるということだ.嗅覚からの転用はないということになるが,これは印欧語にも日本語にも言えることである.また,touch -> taste -> smell の方向性についていえば,アリストテレスが味覚 (taste) は特殊な触覚 (touch) であると考えたことと響き合い,一方,味覚 (taste) は嗅覚 (smell) と近いために前者が後者に用語を貸し出していると解釈することができるかもしれない (Williams 472) .言語的な共感覚表現と,人類進化論や生理学との平行性に注目しながら,Williams (473) はこう述べている.
Though I do not suggest that Fig. 1 represents more than chronological sequence, the 'dead-end' appearance of the olfactory sense is a striking visual metaphor for the evolutionary history of man's sensory development.
論文の最後で,Williams (473--74) は「意味法則」([2014-02-16-1]の記事「#1756. 意味変化の法則,らしきもの?」を参照)への自信を覗かせている.
. . . what is offered here constitutes not only a description of a rule-governed semantic change through the last 1200 years of English---a regularity that qualifies for lawhood, as the term LAW has ordinarily been used in historical linguistics---but also as a testable hypothesis in regard to past or future changes in any language.
・ Williams, Joseph M. "Synaethetic Adjectives: A Possible Law of Semantic Change." Language 52 (1976): 461--78.